The Adobe I/O Theme for building markdown/gdocs powered sites.
Themes allow site functionality to be packaged as a standalone product for others to easily reuse. Using a theme, all of your default configuration lives in an npm package.
View the site templates using the Adobe I/O Theme:
Documentation template
Platform template
Product template
- Getting started
- Content structure
- Configuration
- Building the site
- Deploying the site
- Writing Enhanced Markdown
- Metadata with Front matter
- OpenAPI
- JSDoc
- MDX
- Modular Content System
- JSX Blocks
- Hero Block
- Resources Block
- Discover Block
- Code Block
- Inline Alert Block
- Media Block
- Announcement Block
- Summary Block
- Title Block
- Text Block
- Tabs Block
- Product Card
- Product Card Grid
- Resource Card
- Carousel
- Embedding markdown documents and filtering content
- Customizations
- Upgrading
- Issue tracker
- Contributing
- Releases
This section will help you get started building a site with the Adobe I/O Theme.
Pre-requisites
- Install Node.js LTS
- Install a package manager like npm
To initialize a site repository, you can use one of the available site templates mentioned above. Simply click on the “Use this template” button to create a new GitHub repository of the template.
The templates are pre-configured with example pages.
First install the Adobe I/O CLI via the Terminal
npm install -g @adobe/aio-cliThen install the Doc Plugin by running.
aio discover -iSelect the @adobe/aio-cli-plugin-doc plugin by pressing the Spacebar and finally press Enter to install it.
For more information about the Doc plugin, see https://github.com/adobe/aio-cli-plugin-doc.
Now you can create your site by running
aio doc init path/to/site/folderwhich will use by default the Documentation site template.
You can specify another template with
aio doc init path/to/doc/folder --template URL_TO_TEMPLATE_GIT_REPOThe content of the site is written in Markdown which is both easy to read and easy to learn.
As in most cases, the markdown content is stored in GitHub, we support GitHub Flavored Markdown (GFM), which provides additional functionality for common formatting needs. Additionally, Adobe extended Markdown in a few ways to support certain features see Writing Enhanced Markdown.
Make sure the markdown content is located under src/pages.
It is recommended to use a folder structure to define your site pages e.g. :
root
├- src/pages [/]
│ ├- index.md
│ ├- hero.png
│ ├- api [/api/]
│ │ └- index.md
│ └- guides [/guides/]
│ ├─ index.md
│ └- get_started [/guides/get_started/]
│ ├- index.md
│ └- debugging [/guides/get_started/debugging/]
│ └- index.md
├- .env
├─ gatsby-config.js
└─ package.json
Using a folder structure with only index.md files gets you close to the final site build files. During the build process, md files will be transformed into index.html files.
The build files can be found in the public folder. Please read the Overview of the Build Process for more information.
Here's a simple example of a content structure with md files and the resulting html files:
root
├- src/pages [/]
│ ├- index.md
│ ├- i_follow_recommendation [/i_follow_recommendation/]
│ │ └- index.md
│ └- i_dont_follow_recommendation.md [/i_dont_follow_recommendation/]
├- .env
├─ gatsby-config.js
└─ package.json
will output:
root
└- public
├- index.html
├- i_follow_recommendation
│ └- index.html
├- i_dont_follow_recommendation
│ └- index.html
└- Minified JS, CSS files
You can exclude pages from the build by either moving them out of src/pages or by prefixing the filename with _.
Using markdown links to link to pages e.g. :
Relative link
[Link to mypage](../mypage.md)
Absolute link
[Link to mypage](/src/pages/mypage.md)
Add the suffix # to a link to jump to a section of the page for example if your page has a heading named Join the future, you can link to it:
[Link to mypage](../mypage.md#join-the-future)
You can also use absolute links or relative links to link between markdown pages e.g. with the example folder structure from Content Structure you can add a link from /guides/index.md to /api/index.md with:
Relative link
[Link to API](../api/)
Absolute link
[Link to API](/api/)
Please note that currently only absolute links will work with transcluded content.
External links will automatically open in a new tab or window.
[Link to example.com](https://example.com)
You can prevent this behavior by adding the search parameter ?aio_internal to the link.
Images can be placed next to markdown pages inside src/pages and referenced using relative links. In this case, they'll be optimized during the build process and resulting file names are hashed to resolve potential caching issues.
Other asset types (e.g. PDFs etc.) can be placed inside a static folder at the root. Those assets are not being processed but simply copied into the public folder.
Here's a simple example of a content structure with a markdown page file and 2 different asset types:
root
├- src/pages [/]
│ ├- index.md
│ └- image.png
├- static [/]
│ └- document.pdf
├─ gatsby-config.js
└─ package.json
where image.png is referenced in index.md as an image:

and document.pdf is referenced in index.md as a link:
[document](/document.pdf)
You'll find more information about the static folder at Using the Static Folder.
Please find guidance on ideal illustration sizes in this document.
Instead of writing markdown pages, you can use Google Docs as external content source. Google Docs documents will be transformed into markdown pages under the hood and placed by default into src/pages.
To connect to Google Docs, you'll need to setup 4 .env variables in your project :
GOOGLE_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=2...m.apps.googleusercontent.com
GOOGLE_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=Q...axL
GOOGLE_DOCS_TOKEN={"access_token":"ya...J0","refresh_token":"1..mE","scope":"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.metadata.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/documents.readonly","token_type":"Bearer","expiry_date":1598284554759}
GOOGLE_DOCS_FOLDER_ID=1GHc4k.....8E5OyzuAT0Fy9
To generate the first 3 variables, open the terminal at the root of your project and run the command:
gatsby-source-gdocs2mdThen simply follow the instructions.
The last variable GOOGLE_DOCS_FOLDER_ID can be generated by retrieving the Google Docs root folder ID of your documents e.g. https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/FOLDER_ID
Google Docs won't allow you to insert relative links by default but you can workaround it by prefixing your relative urls with #! e.g. #!../mypage.
Fill the document description field in Google Drive with a YAML object:
title: Page title
description: Page descriptionExclude folders/documents by adding exclude: true in the description field of folders/documents to create draft pages which shouldn't be published.
To make sure you don't run into troubles during the site build process, please follow the below configuration steps.
Follow these steps to configure your .env file.
- Copy
.env.exampleto.env - Add the appropriate values in the
.envfile
The .env should not be committed.
GitHub's API is being called during the site build phase to retrieve the authors of every markdown page under src/pages.
If the GitHub Token information is missing, the build will just print a warning, and no contributor information will be retrieved (just the contributor information in a page's front matter, if any, will be used).
To retrieve your GitHub personal access token, you can follow these steps.
Only READ permissions on repositories are required for the token.
For example, if your doc site repo was at https://github.com/adobe/aio-theme using the main branch, this would be what your .env would look like:
REPO_GITHUB_TOKEN=YOUR_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN_HERE
REPO_OWNER=adobe
REPO_NAME=aio-theme
REPO_BRANCH=main
REPO_ROOT=exampleBy default, you can omit the ROOT env var, and it should use the root folder as the source of the documentation pages. If your site is in a sub-folder, add the relative path as the ROOT.
- You need to set up Adobe Launch, with an Adobe Analytics Reporting Suite
- In Adobe Analytics, add a custom eVar (Text String type) to capture the feedback. This eVar will contain either "yes" or "no".
- In Adobe Launch, create two Data Elements:
- Feedback-Yes: edit the code and paste in
return document.querySelectorAll('button.feedback-yes')[0].innerText - Feedback-No: edit the code and paste in
return document.querySelectorAll('button.feedback-no')[0].innerText
- Feedback-Yes: edit the code and paste in
- In Adobe Launch, for the two Data Elements, make sure these checkboxes are checked:
- Enable Default Value
- Force lowercase value
- Clean text
- In Adobe Launch, create three Rules:
- Feedback-Yes: On click, it will set variables in Adobe Analytics (set the custom eVar to value of the Feedback-Yes Data Element), and then Send the Beacon
- Feedback-No: On click, it will set variables in Adobe Analytics (set the custom eVar to the value of the Feedback-No Data Element), and then Send the Beacon
- Analytics: On library loaded (page top), Send the Beacon
- In Adobe Launch:
- Go through the
Publishing Flow, don't forget toAdd All Resources - In
Environments, select the appropriate environment, and under theInstallcolumn, select the icon - Copy the url displayed in the
scripttag
- Go through the
This last value will be the value you put in GATSBY_ADOBE_LAUNCH_SRC.
GATSBY_ADOBE_LAUNCH_SRC=https://your.adobe.launch.url.hereTo enable IMS on the browser side, you'll need to set following env variables:
GATSBY_IMS_CONFIG- Map ofclient_idandscopesetc.GATSBY_IMS_SRC- URL source of IMS library
Sites hosted on the developer.adobe.com domain can now add Algolia search to help users find content fast.
There are two parts to adding the Algolia search feature to your site:
- Add server-side environment variables to create and publish your site's content to Algolia's servers. This is an admin-only feature. Consult your site administrator for more details.
- Add client-side environment variables to search your content on Algolia's servers and return content matches (with links) to users.
Admin Only. To publish your site's content to Algolia so it's searchable, add the following variables to your site's .env file:
ALGOLIA_INDEXATION_MODE—[skip | console | index]skipmode - skip running of search indexation (default)consolemode - index data will be published to console, but not pushed to real search indexindexmode - index data will be pushed to real search index
ALGOLIA_WRITE_API_KEY- Alpha-numeric string required to write index files to Algolia's servers. You should never commit this key to GitHub.GATSBY_ALGOLIA_APP_ID- Alpha-numeric string required to access Adobe's documentation indexes.ALGOLIA_INDEX_NAME- The name of the Algolia index where the site's content will be published. If you don't add this variable (or if you leave it blank), your site's index is auto-generated using the name of your repo. If you need to publish the site's content to another site's index (creating a shared index), add the name of the other site's index here.
To enable search on the browser side, you'll need to set the following variables in your site's .env file:
GATSBY_ALGOLIA_APP_ID- Alpha-numeric string required to access Adobe's documentation indexes.GATSBY_ALGOLIA_API_KEY- Alpha-numeric string required to search indexes on Algolia servers.GATSBY_ALGOLIA_INDEX_ALL- List of all indexes to search e.g.["index1", "index2"]GATSBY_ALGOLIA_SEARCH_INDEX- Map of individual indexes with labels to perform search operations[{"index1": "Index 1"}, {"all": "All Results"}]. Useallto indicate that all indexes should be searched.
The Global navigation links are configurable in gatsby-config.js under pages.
If you follow the recommended content structure, you can define the path value using the folder names.
For example, the following folder structure maps to the URL defined in brackets:
src/pages [/]
├- index.md
├- api [/api/]
│ └- index.md
└- guides [/guides/]
└─ index.md
then define your Global Navigation using pages in gatsby-config.js:
pages: [
{
title: 'Adobe Analytics',
path: '/'
},
{
title: 'Guides',
path: '/guides/'
},
{
title: 'API Reference',
path: '/api/'
}
]
You can also define it by pointing to the markdown files:
pages: [
{
title: 'Adobe Analytics',
path: 'index.md'
},
{
title: 'Guides',
path: 'guides.md'
},
{
title: 'API Reference',
path: 'api.md'
}
]
Search ?foo=bar and hash #foo values are also supported.
The order in which the pages are defined is respected in the Global Navigation.
If the current location corresponds to a path defined under pages, the correspond tab in the Global Navigation is set as active.
Otherwise, the first defined tab is set as active by default.
At least one defined page is required. It's recommended to define the first page path as the root path /.
You can group links inside a dropdown menu in the Global Navigation with the menu field.
Optionally, you can set a description to better differentiate grouped links e.g. based on the previous example:
pages: [
{
title: 'Adobe Analytics',
path: 'index.md'
},
{
title: 'Guides',
path: 'guides.md'
},
{
title: 'API Reference',
menu: [{
title: 'v2.0'
description: 'Version 2.0 of API' // optional,
path: '2.0/api.index'
}, {
title: 'v1.4'
description: 'Version 2.0 of API' // optional,
path: '1.4/api.index'
}]
}
]
The home link should be used to inform the user about a parent or sibling site external to the current one. Breadcrumbs will be displayed automatically to help the user understand its current location.
You can define a home link in gatsby-config.js for instance:
home: {
title: 'Photoshop',
path: 'https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html'
}
A default home link is displayed if none provided. If you don't want to display any home link, set hidden to true:
home: {
hidden: true
}
The Side navigation links are configurable in gatsby-config.js under subPages.
You have to create a directory hierarchy which will be represented literally in the URL so that any sub page path starts with a path from pages.
For example, the following folder structure maps to the URL defined in brackets:
src/pages [/]
├- index.md
├- api [/api/]
│ └- index.md
└- guides [/guides/]
├─ index.md
└- get_started [/guides/get_started/]
├- index.md
└- debugging [/guides/get_started/debugging/]
└- index.md
then define your Side Navigation for /guides/ using subPages in gatsby-config.js:
pages: [
{
title: 'Adobe Analytics',
path: '/'
},
{
title: 'Guides',
path: '/guides/'
},
{
title: 'API Reference',
path: '/api/'
}
],
subPages: [
{
title: 'Get Started',
path: '/guides/get_started',
pages: [
{
title: 'Debugging',
path: '/guides/get_started/debugging/'
}
]
}
]
Similarly to the Global Navigation:
- The order in which the sub pages are defined is respected in the Side Navigation.
- Setting search and hash values in the path is supported
- Linking markdown files is supported
Important: All sub pages paths have to be children of a top-level navigation path.
There are 3 variations of the Side Navigation:
- Single-level side navigation
- Categorical single-level side navigation
- Multi-level side navigation
Please refer to the section use the right variation to understand which side navigation variation to use.
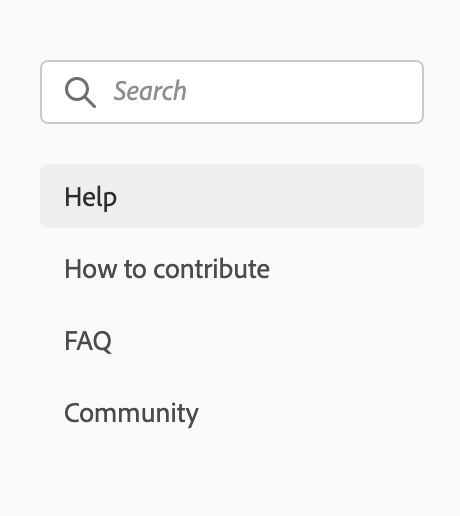
To create a single-level side navigation, you shouldn't specify pages for subPages for example:
is matching to the following config:
pages: [
{
title: 'Support',
path: '/support/'
}
],
subPages: [
{
title: 'Help',
path: '/support/'
},
{
title: 'How to contribute',
path: '/support/contribute/'
},
{
title: 'FAQ',
path: '/support/FAQ/'
},
{
title: 'Community',
path: '/support/community/'
}
]
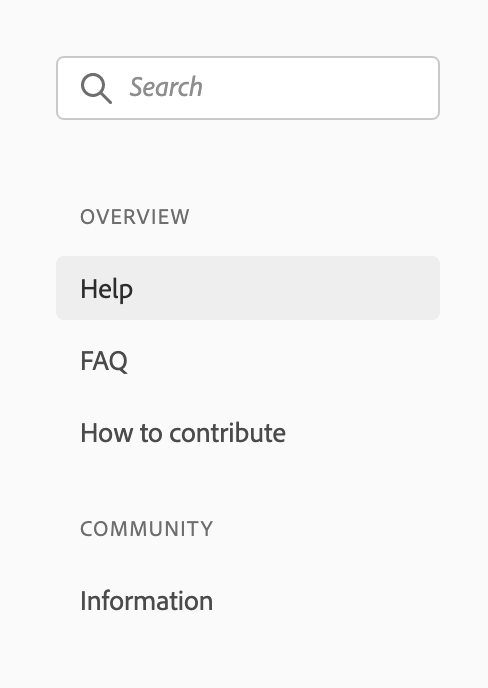
To create a single-level side navigation with headers, you should set header: true on top-level subPages and follow the auto-collapsing rules for example:
is matching the following config:
pages: [
{
title: 'Support',
path: '/support/'
}
],
subPages: [
{
title: 'Overview',
path: '/support/',
header: true,
pages: [
{
title: 'Help',
path: '/support/'
},
{
title: 'FAQ',
path: '/support/FAQ/'
},
{
title: 'How to contribute',
path: '/support/contribute/'
}
]
},
{
title: 'Community',
path: '/support/community/',
header: true,
pages: [
{
title: 'Information',
path: '/support/community/'
}
]
}
]
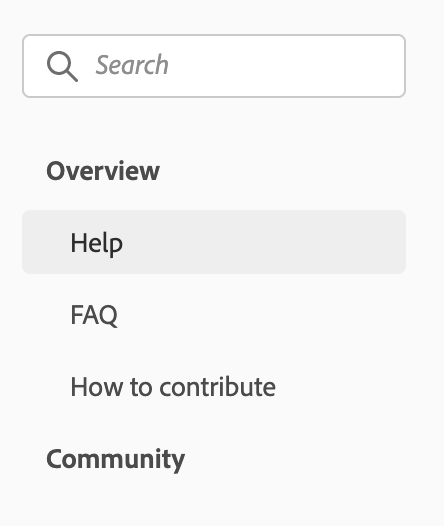
To create a multi-level side navigation, you have to define pages for subPages for example:
is matching the following config:
pages: [
{
title: 'Support',
path: '/support/'
}
],
subPages: [
{
title: 'Overview',
path: '/support/',
pages: [
{
title: 'Help',
path: '/support/'
},
{
title: 'FAQ',
path: '/support/FAQ/'
},
{
title: 'How to contribute',
path: '/support/contribute/'
}
]
},
{
title: 'Community',
path: '/support/community/',
pages: [
{
title: 'Information',
path: '/support/community/'
}
]
}
]
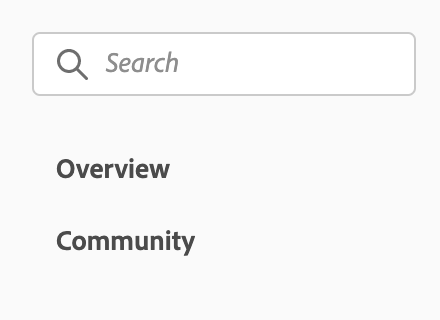
In the previous multi-level side navigation example, if the current location is /support/, Overview auto-collapses and selects Help by default because Overview and Help paths both matches the current location /support/.
It also means that if you don't want the auto-collapsing behavior, you have to define different paths for subPages than you defined for pages e.g. for the previous example, to avoid auto-collapsing of Overview,
you would have to define a different path for Overview and Help:
pages: [
{
title: 'Support',
path: '/support/'
}
],
subPages: [
{
title: 'Overview',
path: '/support/overview/',
pages: [
{
title: 'Help',
path: '/support/overview/help/'
},
{
title: 'FAQ',
path: '/support/overview/FAQ/'
},
{
title: 'How to contribute',
path: '/support/overview/contribute/'
}
]
},
{
title: 'Community',
path: '/support/community/',
pages: [
{
title: 'Information',
path: '/support/community/'
}
]
}
]
which will render:
Navigation should be helpful. Choose titles for navigation items that clearly represent the surfaces where they'll go. Avoid using titles that are arbitrary or un-useful, since this can pose usability issues for your product.
Along with being descriptive, navigation items should be succinct. Reduce any unnecessary words in order to ensure simplicity. Navigation items should never be so long that they require truncation, except in instances where navigation is user-generated.
Navigation items should be written in sentence case.
Make sure that you are using the right variation for your products’ context and users’ needs. Don’t mix behavior, styles, or variations together in a single navigation menu:
- When navigation is simple, use the single-level side navigation.
- When navigation is simple but categorical, use the single-level side navigation with headers.
- When navigation is expansive, hierarchical, and/or you need progressive disclosure in your menu behavior, use the multi-level side navigation.
The multi-level side navigation should only go 3 levels deep. More than 3 levels will make the indentation indiscernible, which can become a major usability issue in your product.
If top-level navigation items have a location associated with them, send the user to that location and open the sub-level navigation items. If a top-level navigation item does not have any associated location, only open the sub-level navigation items.
Side navigation can use either of these behaviors, but should never mix behaviors in the same experience.
You can specify multiple versions for your site in gatsby-config.js under versions.
The first entry is the selected version by default.
versions: [
{
title: 'v2.0',
selected: true
},
{
title: 'v1.4',
path: 'https://github.com/AdobeDocs/analytics-1.4-apis'
}
],
Important: managing multiple versions inside a single repository is not supported.
You can generate a production version of the site using following commands:
With the CLI:
aio doc generateOr run following commands:
- To build and preview a production version of the site:
npm run start. - To build and preview a production version of the site with path prefix:
npm run start:prefix. - To build and preview a development version of the site with hot reloading:
npm run dev.
Many applications are hosted at something other than the root (/) of their domain.
For example, a blog could live at example.com/blog/, or a site could be hosted on GitHub Pages at example.github.io/my-site/.
To add a Path Prefix, go to your gatsby-config.js file and specify the prefix with:
pathPrefix: process.env.PATH_PREFIX || '/MY_PREFIX/'
To enable GitHub Pages, go to your repository settings under the GitHub Pages section, select the gh-pages branch as source and press Save. Your site will be available for preview at https://ORG_NAME.github.io/REPO_NAME.
On every commit to the main branch, the site will be built to GitHub Pages automatically, for you to preview as a development version. This is the default branch for new repos in GitHub.
GitHub Contributors component: this will use the GitHub token automatically provided by the GitHub Action to retrieve data
Feedback component: no environmental variable should be set since GitHub Pages should only be for development purposes
You can manually trigger the deploy workflow by pressing the Run workflow button:
- Go to your repository actions overview page i.e. https://github.com/ORG/REPOSITORY/actions
- Click on the "Deploy" workflow
- Press Run workflow. You can choose which branch the workflow is run on and specify the deployment type (
devfor development or/andprodfor production).
Pre-requisites:
- Setting your
PATH_PREFIXas explained here. This is the sub-folder to deploy this micro-site to.
- For example, if you want to deploy to
https://example.com/foo/bar, you must setPATH_PREFIXto/foo/bar/ - For sites deployed to the
root, use/as thePATH_PREFIX
- The person initiating the deploy workflow must have
writeaccess to the repository.
Front matter allows an author to specify metadata for a page. For example, you can define the page meta title and description by adding front matter to the beginning of your markdown file:
--- title: Guides - Adobe Analytics description: This is the guides overview page of Adobe Analytics ---
In addition to the GitHub contributors of a markdown file, you can specify external contributors with front matter. They'll show up first before the GitHub contributors.
--- contributors: - https://github.com/simonwex ---
We use Redoc to render OpenAPI specs. Simply use front matter to define the spec URL.
--- openAPISpec: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AdobeDocs/analytics-2.0-apis/master/docs/swagger.json ---
We currently recommend to use the JSDoc to markdown converter.
Use front matter to specify a JSDoc markdown document.
--- jsDoc: true ---
Then annotate your JS parameters with <JsDocParameters/> to render them nicely see the example markdown file.
MDX is supported out of the box. MDX enables writing JSX React components in markdown giving authors new powers.
Despite the markdown files having all an md extension, they are actually treated as MDX files. You can use md and mdx extensions interchangeably.
As we try to limit the use of MDX in favor of pure markdown, we have come up with a way to couple the use of basic markdown syntax with JSX.
Always make sure to close JSX blocks and use line breaks between JSX blocks and markdown content to avoid MDX parser issues.
The modular content system is a set of content blocks with variants and compositions that can be used to create pages.
-
Content Blocks are goal-focused. A group of content that has a specific goal or intention, to structure and support the overall narrative. Examples are groupings of text, groupings of buttons, and hero content.
-
Variants are messaging-focused. The messaging points/content (this includes both written and visual content/images) that makes the goal of the content block happen. Examples are text content blocks with icons vs no icons.
-
Compositions are layout-focused. The overall narrative for the page.
A variant can go into a content block. Multiple content blocks make up a composition.
The Content Blocks are defined as JSX Blocks. They use a slots property to identify which markdown elements to ingest using only string properties.
This helps maintain better readability when rendered on https://github.com.
Common slots are: heading, image and text. See below examples for full details.
A Hero Block should be used on every home page. Only 1 Hero Block per page is allowed. They are used to set up the tone of the page and optionally add call to actions and intentions for users.
There are 3 different variants:
- The default variant for Documentation pages.
- The half width variant for Product/Platform authored pages.
- The full width variant for Index home pages.
Default variant:
<Hero slots="image, heading, text" background="rgb(64, 34, 138)"/>

# Adobe Analytics
Adobe Product API offers limitless ways to integrate your most important customer data into key business processes. Adobe Product API offer limitless ways.
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(required)image(optional)
Use background to set a custom background color matching your color scheme. Defaults to rgb( 29, 125, 238);
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to dark.
Half width variant
<Hero slots="image, icon, heading, text1, text2, buttons" variant="halfwidth" />


# Creativity for all
Start building.
Creative Cloud services include tools and capabilities to streamline your workflows so that you, your team, and your stakeholders stay perfectly in sync across projects of any size
* [Get started](https://adobe.io)
* [Sign up for the newsletter](https://adobe.io)
Use variant="halfwidth"" to set the half width variant.
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(required)image(required)background(optional)icon(optional)buttons(optional)
Full width variant
<Hero slots="image, heading, text, buttons" variant="fullwidth" background="rgb(51, 51, 51)" />

# The most memorable digital experiences are unleashed by developer creativity
Adobe products and technologies power them
* [Explore our APIs](https://adobe.io)
* [Subscribe](https://adobe.io)
Use variant="fullwidth"" to set the full width variant.
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(required)image(required)background(optional)buttons(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to dark.
Each Documentation overview page has a Resources Block with to display a list of links. They can point to internal or external documents or pages.
Only 1 Resource Block per page is allowed.
<Resources slots="heading, links"/>
#### Resources
* [Quickstart Guide](https://www.adobe.io/apis/experiencecloud/analytics/docs.html)
* [Adobe Analytics GitHub Repo](https://github.com/AdobeDocs/analytics-2.0-apis)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)links(required)
A Discover Block is a section of content that can be used to highlight certain areas of a Documentation overview page. There can be multiple Discover Blocks in a row. Discover Blocks can be illustrated but only one illustration per row is allowed.
Single Discover Block
<DiscoverBlock width="100%" slots="heading, link, text"/>
### Get Started
[Quickstart Guide](guides/)
Get started with the Adobe Analytics APIs.
Multiple Discover Blocks in a row
<DiscoverBlock slots="heading, link, text"/>
### Guides
[Calculated Metrics API](guides/calculated_metrics_api/)
Returns information on the user's company that is necessary for making other Adobe Analytics API calls.
<DiscoverBlock slots="link, text"/>
[Segments API](guides/segments_api/)
Provides configuration guidance and best practices for the /segments endpoint.
<DiscoverBlock slots="link, text"/>
[Reporting Guide API](guides/reporting_api/)
Provides configuration guidance and best practices for the /reports endpoint.
<DiscoverBlock slots="link, text"/>
Discover Block with illustrations
<DiscoverBlock slots="image, heading, link, text"/>

### Developer forum
[Get started](https://adobe.io)
Open discussion and support with community experts and Adobe staff.
<DiscoverBlock slots="link, text"/>
[Experience league](https://adobe.io)
Tutorials and videos for the community.
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(1 required per row)text(required)link(required)image(optional)
Use width to define the size of the block.
A Code Block is an enhanced code section which supports additional features like request/response format, multiple languages etc.
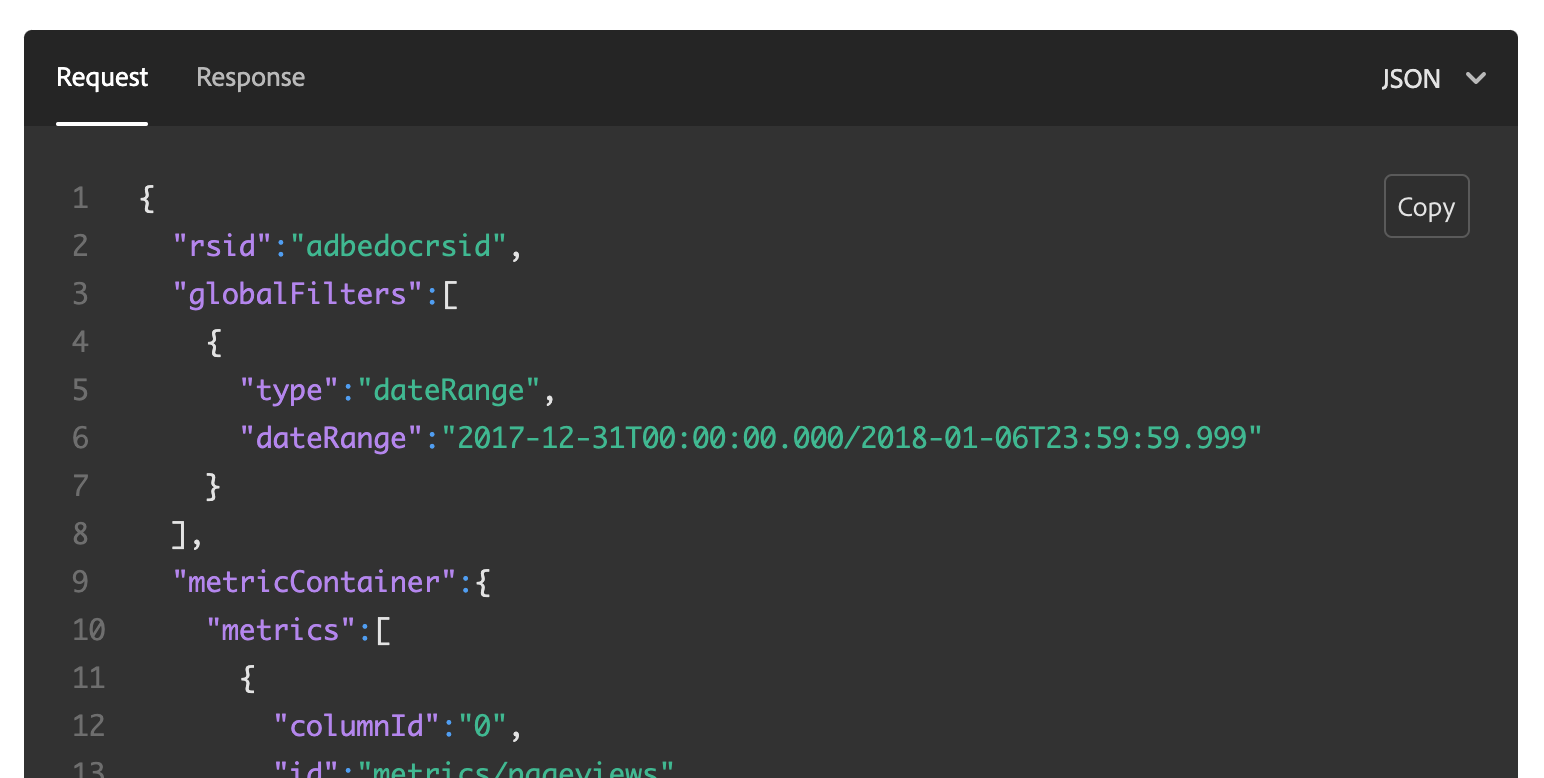
<CodeBlock slots="heading, code" repeat="3" languages="JSON, CURL, JSON" />
#### Request
```json
{
"rsid":"adbedocrsid",
"globalFilters":[
{
"type":"dateRange",
"dateRange":"2017-12-31T00:00:00.000/2018-01-06T23:59:59.999"
}
]
}
```
#### Request
```bash
curl -X POST \
https://analytics.adobe.io/api/{COMPANYID}/reports \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {ACCESSTOKEN}' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'x-api-key: {APIKEY}' \
-H 'x-proxy-global-company-id: {COMPANYID}' \
-d '{REQUESTJSON}'
```
#### Response
```json
{
"totalPages":1,
"numberOfElements":7,
"number":0,
"totalElements":7
}
```
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)code(required)
Use repeat to define how many code sections are part of the Code Block.
Use languages to define a language name for each code section. Code sections with the same heading are automatically grouped together.
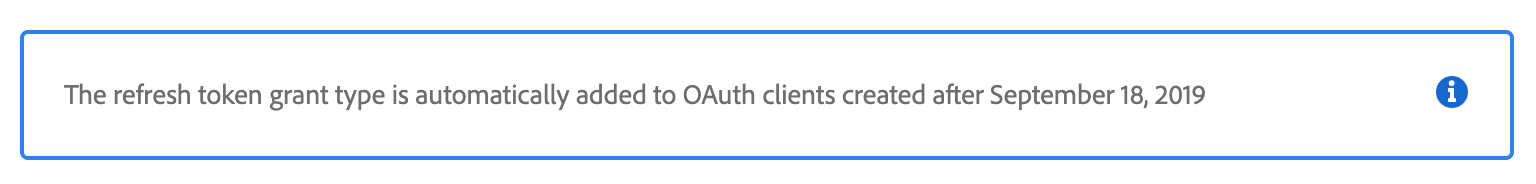
The Inline Alert Block is used to highlight information.
<InlineAlert variant="help" slots="text"/>
The refresh token grant type is automatically added to OAuth clients created after September 18, 2019
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
text(required)
Use variant to define the indicator type: info (default), help, error, success, warning.
The Media Block is used to display interactive medias like videos.
<Media slots="video"/>
<https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkgpeWbHrjA>
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
video(required)
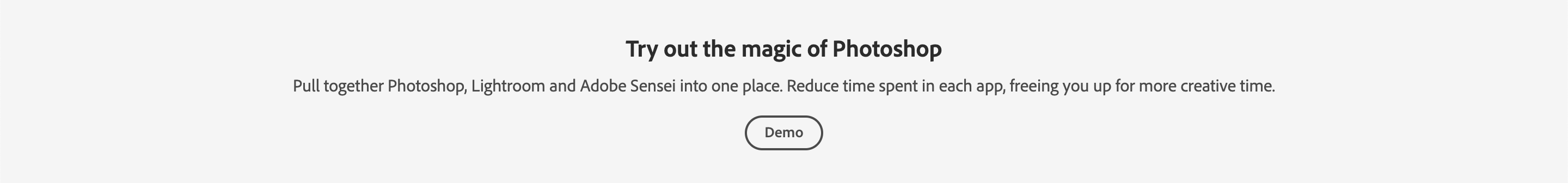
The Announcement Block goes directly underneath the Hero Block for Product/Platform pages. It's used to call out new features, blog posts, news etc. anything that needs that needs to be surfaced above the fold.
<AnnouncementBlock slots="heading, text, button" />
### Try out the magic of Photoshop
Pull together Photoshop, Lightroom and Adobe Sensei into one place. Reduce time spent in each app, freeing you up for more creative time.
[Demo](https://www.adobe.io/apis/creativecloud/photo-imaging-api/api-demo.html)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)button(required)text(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to light.
Use className to customize the component at your own risk.
The Summary Block acts as an anchor at the end of the page. It's a change for Products to give users another call to action, and encourage them to interact after they have gotten to the bottom of the page.
<SummaryBlock slots="image, heading, text, buttons" background="rgb(246, 16, 27)" />

## Subscribe to the Creative Cloud developers newsletter
A monthly newsletter featuring news for anyone who creates, develops, or build plugins, extensions, or integrations for the
Creative Cloud family of products.
* [Subscribe to the newsletter](https://adobe.io)
* [Learn more](https://adobe.io)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)buttons(1 button required at least)text(optional)image(optional)
Use background to set a custom background color matching your color scheme.
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to dark.
Use className to customize the component at your own risk.
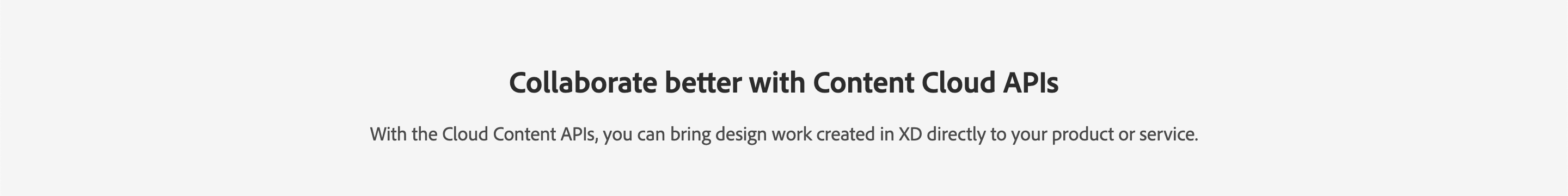
A Title Block is used at the beginning of sections, or to frame compositions on Product/Platform pages.
<TitleBlock slots="heading, text" theme="light" />
### Collaborate better with Content Cloud APIs
With the Cloud Content APIs, you can bring design work created in XD directly to your product or service.
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to lightest.
Use className to customize the component at your own risk.
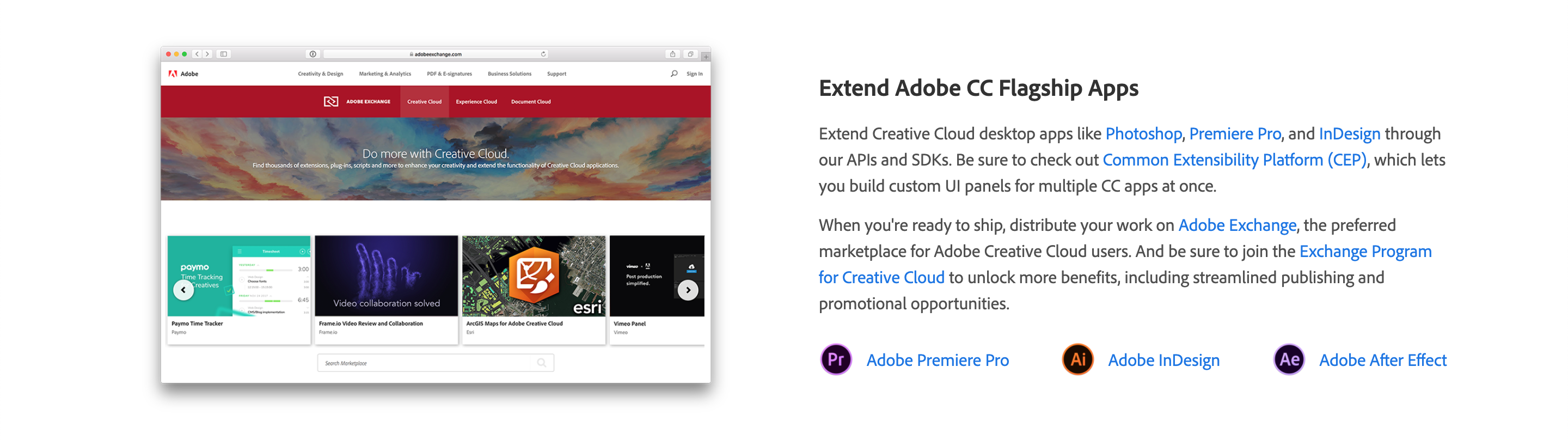
Text Blocks are used for layout compositions. They are areas for long blocks of text and explaining features etc. for Product/Platform pages. They are coupled with images or videos.
With an image, texts and links
<TextBlock slots="image, heading, text1, text2, links" />

### Extend Adobe CC Flagship Apps
Extend Creative Cloud desktop apps like [Photoshop](https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html), [Premiere Pro](https://www.adobe.com/products/premiere.html), and [InDesign](https://www.adobe.com/products/indesign.html) through our APIs and SDKs.
Be sure to check out [Common Extensibility Platform (CEP)](https://www.adobe.io/apis/creativecloud/cep.html), which lets you build custom UI panels for multiple CC apps at once.
When you're ready to ship, distribute your work on [Adobe Exchange](https://exchange.adobe.com/), the preferred marketplace for Adobe Creative Cloud users.
And be sure to join the [Exchange Program for Creative Cloud](https://partners.adobe.com/exchangeprogram/creativecloud) to unlock more benefits, including streamlined publishing and promotional opportunities.
*  [Adobe Premiere Pro](https://www.adobe.com/products/premiere.html)
*  [Adobe InDesign](https://www.adobe.com/products/indesign.html)
*  [Adobe After Effect](https://www.adobe.com/products/aftereffects.html)
Multiple Text Blocks in a row
<TextBlock slots="image, heading, text, links" width="33%" />

### Microsoft teams
Easily share Creative Cloud assets and files, and get comment notifications on your prototypes.
* [Learn more](https://www.microsoft.com/microsoft-365/microsoft-teams/group-chat-software)
<TextBlock slots="image, heading, text, links" width="33%" />

### JIRA Cloud
Make designer to developer handoffs easy. Find the latest designs and specs and get thumbnail previews and asset info.
* [Learn more](https://www.atlassian.com/enterprise/cloud)
<TextBlock slots="image, heading, text, links" width="33%" />

### Slack
Instantly share Creative Cloud files, designs, specs, and notifications all in real time.
* [Learn more](https://slack.com/enterprise)
With a video, icons, buttons dark themed
<TextBlock slots="video, icons, heading, text, buttons" theme="dark" />
[Creative Cloud for a new era](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JemJbNJ4ZtU&ab_channel=AdobeCreativeCloud)
* 
* 
### Partner Success Story
Connect your users to Creative Cloud right from within your mobile or web apps with our service APIs. Give users access to
world-class creative assets with the Adobe Stock API, or sign up for early information on our upcoming CC Storage API.
* [Learn more](https://adobe.io)
* [Sign up for partner program](https://adobe.io)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(required). Support multiple texts e.gtext1, text2etc.links(optional). Supports 1 optional image per link.buttons(optional)icons(optional)image(optional).imageshould only be defined as first or last slot to define the layout.imageexcludesvideo.video(optional).videoshould only be defined as first or last slot to define the layout.videoexcludesimage.
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to lightest.
Use width to define the size of the block. Supported values are 100%, 50%, 33% and 25%;
Use isCentered to center the text.
Use className to customize the component at your own risk.
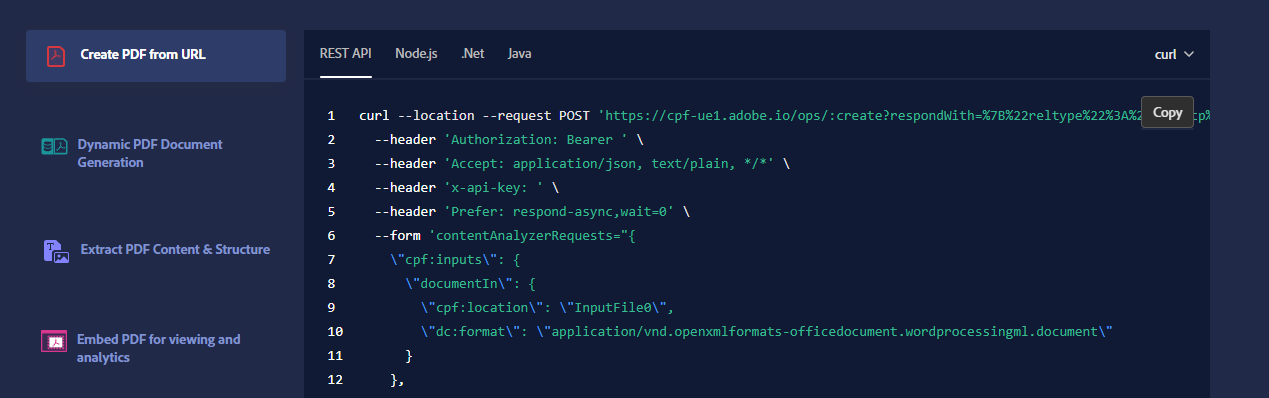
Tabs block is a custom block component that allows for tabbed content that can be displayed either vertically or horizontally.
<TabsBlock orientation="vertical" slots="heading, image, content" theme="light" />
### Create PDF from URL

<Overview/>
<TabsBlock orientation="vertical" slots="heading, content" theme="light" />
### Dynamic PDF Document Generation
<Overview/>
<TabsBlock orientation="horizontal" slots="heading, image, content" theme="light" />
### Create PDF from URL

<Overview/>
<TabsBlock orientation="horizontal" slots="heading, content" theme="light" />
### Dynamic PDF Document Generation
<Overview/>
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(1 required per row)image(optional)content(1 required per row)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to light.
Use orientation to tabs can be either horizontal or vertical. Defaults to horizontal.
Use repeat to define how many tab items sections are part of the tabs Block.
Product Cards group information that allow to browse a collection of related content.
<ProductCard slots="icon, heading, text, buttons" theme="light" width="33%" />

#### CC Storage API
CC Storage API lets you access and modify assets stored in the Creative Cloud, the world's most popular creative platform.
* [Learn more](https://adobe.io)
* [View docs](https://adobe.io)
<ProductCard slots="icon, heading, text, buttons" theme="light" width="33%" />

#### Adobe Stock
Gives your users access to the perfect Adobe Stock asset to enhance their creative projects.
* [Learn more](https://adobe.io)
* [View docs](https://adobe.io)
<ProductCard slots="icon, heading, text, buttons" theme="light" width="33%" />

#### Common Extensibility Platform
Build extensions with HTML, CSS, Javascript and Node. Deploy across multiple Adobe apps.
* [Learn more](https://adobe.io)
* [View docs](https://adobe.io)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
heading(required)text(required)buttons(1 button required at least)icon(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to lightest.
Use width to define the size of the block. Supported values are 100%, 50%, 33% and 25%;
Use Product Card Grid to display Product Cards with filter and sort options based on meta data.
Set interaction to true to display the filter and sort options.
See the data example to provide for clouds and products.
<ProductCardGrid clouds={clouds} products={products} interaction={true} />
Use orderBy to define the default ordering. Choose between last_updated and name.
Use filterByCloud to define the default cloud filter. You can define multiple clouds by default filterByCloud={[cloud1, cloud2]}.
Use filterByIds to define a custom filter e.g. filterByIds=[1, 3, 4] to display products with ids 1, 3 and 4 in that order.
Resource Cards are used on Product/Platform pages for external cross-promotion of materials. Examples includes articles, videos etc.
There are 2 variants: horizontal and vertical Resource Cards. Use multiple Resource Cards with different variants to create a Resource composition.
<ResourceCard slots="link, image, heading, text" width="33%"/>
[Adobe I/O](https://adobe.io)

### Creating a Great Adobe XD Plugin Listing
Rob Kleiman, July 8th 2020
<ResourceCard slots="link, image, heading, text" width="33%" />
[Adobe I/O](https://adobe.io)

### Pattern Builder: A Behind the Scenes Look at Adobe Capture
Nihil Gupta, July 24th 2020
<ResourceCard slots="link, image, heading, text" width="33%" />
[Adobe I/O](https://adobe.io)

### Photoshop Extensibility Enters a New Era Soon: How to get Involved Early
Ash Ryan Arnwine, March 12th 2020
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
link(required)heading(required)image(required)text(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to lightest.
Use width to define the size of the block. Supported values are 100%, 50% and 33%.
Carousel is used to show the information along with images and buttons.
<Carousel slots="image,heading, text, buttons" repeat="2" theme="light" />

#### CC Storage API
CC Storage API lets you access and modify assets stored in the Creative Cloud, the world's most popular creative platform.
* [Learn more](../guides)
* [View docs](../guides)

#### CC Storage API
CC Storage API lets you access and modify assets stored in the Creative Cloud, the world's most popular creative platform.
* [Learn more](../guides)
* [View docs](../guides)
Use slots to identify the markdown content:
image(required)heading(optional)text(required)buttons(optional)
Use theme to match the text color to your color scheme. Defaults to dark.
Use repeat to define how many code sections are part of the carousel.
You can use MDX transclusion to embed markdown documents into other markdown documents see the MDX documentation.
For example, if you want to include the content of overview.md into index.md:
index.md content:
import Overview from './overview.md'
# Welcome
Lorem ipsum
<Overview/>
## Questions
Lorem ipsum
overview.md content:
## Overview
Lorem ipsum
index.md will be rendered as:
# Welcome
Lorem ipsum
## Overview
Lorem ipsum
## Questions
Lorem ipsum
Sites are using npm to define dependencies so we can also include external markdown documents.
You have to define a name in the package.json like here to be able to include it
as a dependency in another site.
You don't have to release the site on npm since npm supports installing dependencies using github repository urls. For example, to install https://github.com/AdobeDocs/dev-site-documentation-template/
as a dependency in another site, you can run the command npm install --save adobedocs/dev-site-documentation-template;
Your site package will show up under node_modules/[PACKAGE_NAME] e.g. node_modules/dev-site-documentation-template.
See full example below using a Variant block.
Together with Variant Blocks, the author can query what should be rendered from external sources.
This allows to write content once, and reuse it everywhere.
For example, let's say there are 2 repositories named http://github.com/adobedocs/repo1 and http://github.com/adobedocs/repo2.
Both are sites using the theme and have markdown content defined under src/pages.
- repo1 has reusable markdown content written with Variant Blocks under
/src/pages/debugging/index.md:
## How to Debug Your Plugin
Bugs happen! In this tutorial, you will learn how to debug your plugin.
<Variant product="XD" repeat="2" />
First launch the XD console, by clicking Developer > Console
[XD link](https://adobe.io)
<Variant product="Photoshop" repeat="2" />
First launch the Photoshop console, by clicking Developer > Console
[Photoshop link](https://adobe.io)
<Variant test="image" repeat="2" />
#### Image

Use repeat to define how many elements are part of the Variant Block. Use any key=value property to mark your Variant Block.
-
repo2 added repo1 as dependency with
npm install --save adobedocs/repo1to be able to reference its markdown content. -
repo2 embeds repo1 content by using the
importstatement and inserts the content in its own markdown together with aqueryfilter to only display what is needed.
import Debugging from 'repo1/src/pages/debugging/index.md'
# Debugging
<Debugging query="product=Photoshop" />
More content
will be rendered as:
# Debugging
## How to Debug Your Plugin
Bugs happen! In this tutorial, you will learn how to debug your plugin.
First launch the Photoshop console, by clicking Developer > Console
[Photoshop link](https://adobe.io)
More content
You can query multiple elements, for example you can add the section with the image by adding it to the query.
<Debugging query="product=Photoshop&image=test" />
When using themes, you can take advantage of something called shadowing. This allows you to override the default component included in the theme with a custom one you’ve created.
The Adobe I/O Theme package has a component to render code using the Prism syntax highlighter. With shadowing, you can override the component to provide your own.
If you look at the file tree of your site, you’ll see it looks something like this:
root
├─ src/pages
│ ├- index.md
│ └- etc.
├- .env
├─ gatsby-config.js
└─ package.json
To enable shadowing, you need to add a folder called @adobe/gatsby-theme-aio.
Any file placed in that directory with a path that matches the path of a file from the theme will completely shadow the file.
So the new folder structure with shadowing enabled will look like following:
root
├─ src
│ ├- pages
│ │ ├- index.md
│ │ └- etc.
│ └- @adobe
│ └- gatsby-theme-aio
│ └- components
│ └- Code
│ └- index.js
├- .env
├─ gatsby-config.js
└─ package.json
You can define your own Code components under src/@adobe/gatsby-theme-aio/components/Code/index.js.
Notice omitting the src directory in the shadow folder.
You can build pages without the default layout by setting layout to none within the page front matter.
The Global Header, Footer, Side Navigation etc. are always shown but anything in between can be customized.
See the example markdown file.
This can be useful if you want to embed pages from another system. The embedded page will be framed between the Global Header and Footer.
Simply set frameSrc to the url of the external page within the front matter.
See the example parent page and child page which leverages the Penpal library to create a communication channel to exchange information.
Currently, you can only define a light or dark theme for Code blocks. By default, Code blocks are displayed in dark theme.
To change Code blocks from dark to light theme, you have to shadow the theme/index.js file:
export default {
code: 'light'
};
To upgrade to the latest version of the theme, simply run npm update if you have defined the dependency with a version range selector.
If not, update the version of the dependency by setting the version manually in the package.json and run npm install.
This will also update the lock file package-lock.json.
We recommend to setup GitHub dependabot in your site repository.
Simply copy the dependabot file in your .github folder.
The bot will automatically submit pull requests to keep your version of the theme up to date. Please make sure to use a version range selector for your dependencies in your package.json.
Use the GitHub issue tracker to report issues, ask questions or log feature requests. Any feedback is welcome !
Please check existing issues before filing anything new.
Contributions are welcomed! Read the Contributing Guide for more information.
See Conventional Commits for commit guidelines.
You can check the latest released version of the theme at https://github.com/adobe/aio-theme/releases.
This repository is setup as a monorepo using lerna for automated publishing to NPM.
Use GH_TOKEN=[YOUR_GH_TOKEN] lerna version --create-release github --conventional-commits --no-private -m "chore(release): publish" for publishing the theme on npm.