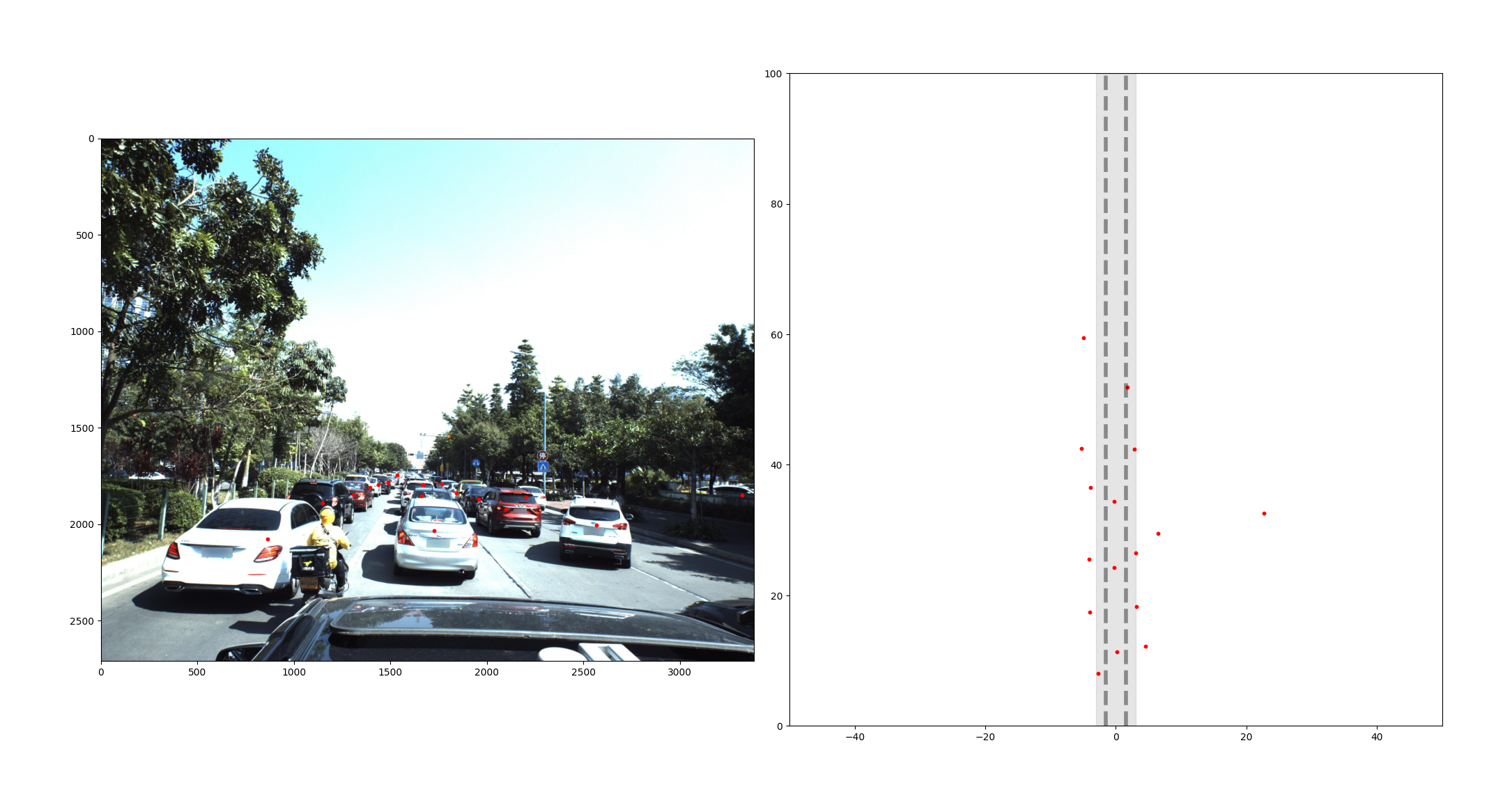
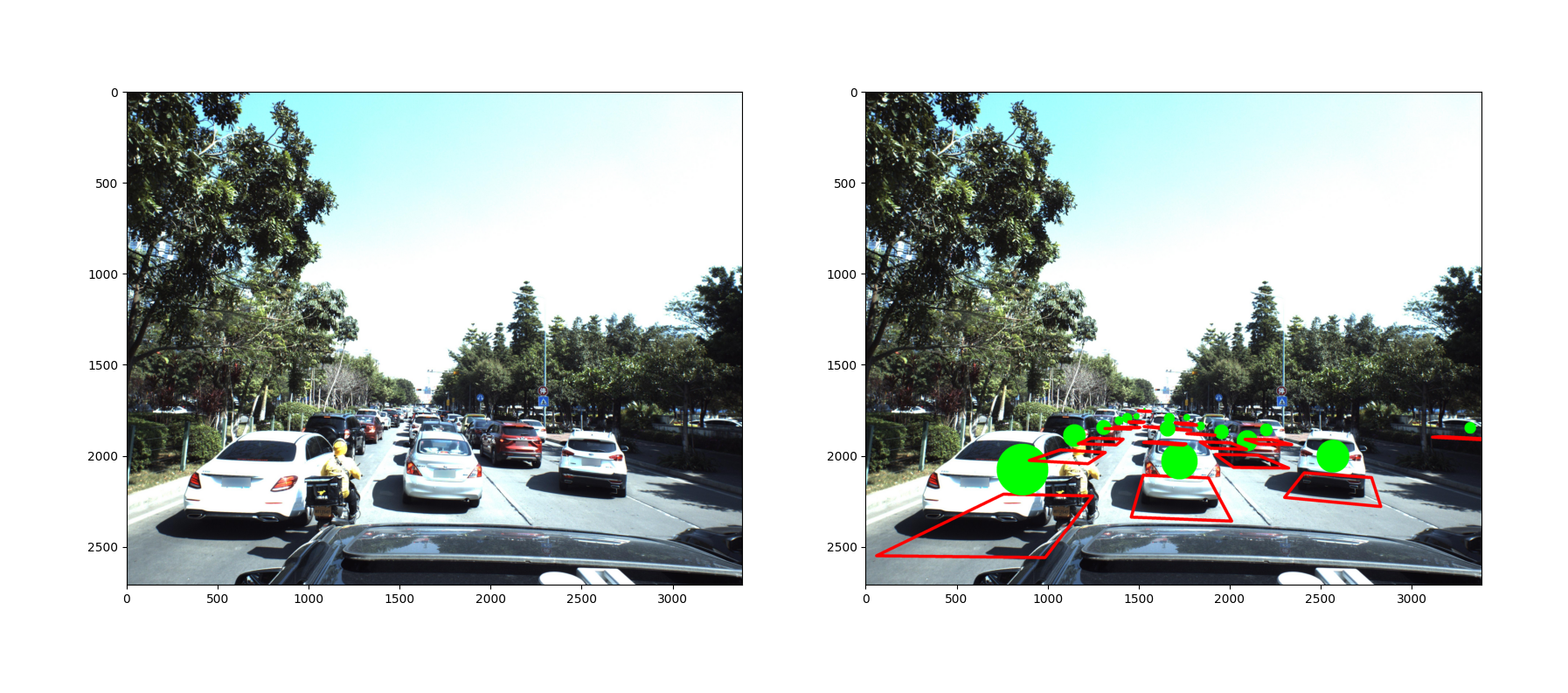
카메라 보정과 관련하여 참고한 내용은 노션에 정리하였습니다.
먼저, 카메라의 파라미터는 다음과 같습니다.
fx = 2304.5479
fy = 2305.8757
cx = 1686.2379
cy = 1354.9849
intrinsic_matrix = np.array([[2304.5479, 0, 1686.2379],
[0, 2305.8757, 1354.9849],
[0, 0, 1 ]],
dtype=np.float32)Annotation에 주어진 Camera 좌표계 상의 x, y, z를 intrinsic matrix와 곱하여 Image 좌표계로 변환합니다. 이떄, z는 초점거리 f는 z와 같기 때문에 x와 y를 z로 나눠주었습니다.
def coords2imgcoords(coords, intrinsic_matrix):
xs = [c['x'] for c in coords]
ys = [c['y'] for c in coords]
zs = [c['z'] for c in coords]
P = np.array(list(zip(xs, ys, zs))).T # (n,3)->(3,n)
img_p = np.dot(intrinsic_matrix, P).T # (3,3)@(3,n) -> (3,n)
# Intrinsic matrix @ 3d point
img_p[:, 0] /= img_p[:, 2]
img_p[:, 1] /= img_p[:, 2]
img_xs = img_p[:, 0]
img_ys = img_p[:, 1]
img_zs = img_p[:, 2] # z = Distance from the camera
return img_xs, img_ysAnnotation 정보에 있는 차량들의 회전 각도를 Image 좌표계로 투영하기 위한 회전 행렬을 만든다.
yaw@pitch@roll = rotation matrix
def euler_to_Rot(yaw, pitch, roll):
X_p = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(pitch), -sin(pitch)],
[0, sin(pitch), cos(pitch)]])
Y_y = np.array([[cos(yaw), 0, sin(yaw)],
[ 0, 1, 0],
[-sin(yaw), 0, cos(yaw)]])
Z_r = np.array([[cos(roll), -sin(roll), 0],
[sin(roll), cos(roll), 0],
[ 0, 0, 1]])
return np.dot(Y_y, np.dot(X_p, Z_r))Projection matrix를 이용하여 Wolrd 좌표계의 차량을 Image 좌표계로 투영하는 과정이다.
x_l = 1.02
y_l = 0.80
z_l = 2.31
은 박스를 그리기 위한 3차원 객체의 지점을 의미한다.
def visualize(img, coords, intrinsic_matrix):
# Wolrd coordinate 상의 객체의 지점(mm)
x_l = 1.02
y_l = 0.80
z_l = 2.31
img = img.copy()
for point in coords:
# Get values
x, y, z = point['x'], point['y'], point['z']
yaw, pitch, roll = -point['pitch'], -point['yaw'], -point['roll']
# Math
Rt = np.eye(4)
t = np.array([x, y, z])
Rt[:3, 3] = t
Rt[:3, :3] = euler_to_Rot(yaw, pitch, roll).T
Rt = Rt[:3, :]
# Extrinsic matrix, (4, 4)
P = np.array([[x_l, -y_l, -z_l, 1],
[x_l, -y_l, z_l, 1],
[-x_l, -y_l, z_l, 1],
[-x_l, -y_l, -z_l, 1], # four points for drawing box of a car
[0, 0, 0, 1]]).T # No effective angle elements for drawing a center point of object
# wolrd position, (4, 1)
# Intrinsic matrix @ Extrinsic matrix @ world potision
img_cor_points = np.dot(intrinsic_matrix, np.dot(Rt, P))
img_cor_points = img_cor_points.T
img_cor_points[:, 0] /= img_cor_points[:, 2]
img_cor_points[:, 1] /= img_cor_points[:, 2]
img_cor_points = img_cor_points.astype(int)
# Drawing
img = draw_line(img, img_cor_points)
img = draw_points(img, img_cor_points[-1:])
return img