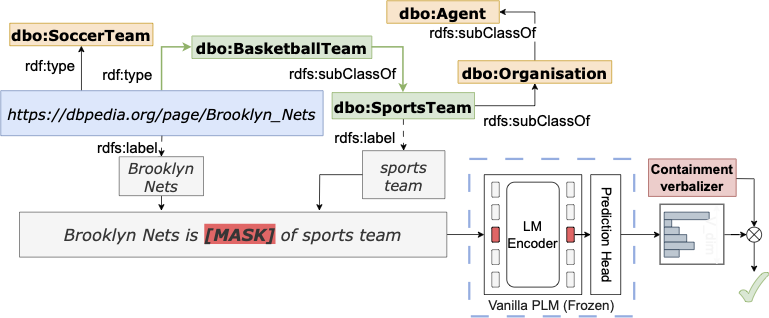
Reference code for paper "PRONTO: Prompt-based Detection of Semantic Containment Patterns in MLMs" (Submitted at ISWC 2024-Research Track). This work investigates whether MLMs can model the semantic containment relationship (is-a/subclass-of) presenting a novel approach to automatically leverage the predictions heads of MLMs to discover semantic containment relations in unstructured text.
Masked Language Models (MLMs) like BERT and RoBERTa excel at predicting missing words based on context, but their ability to understand deeper semantic relationships is still being assessed. While MLMs have demonstrated impressive capabilities, it is still unclear if they merely exploit statistical word co-occurrence or if they can capture a deeper, structured understanding of meaning, similar to how knowledge is organized in ontologies. This is a topic of increasing interest, with researchers seeking to understand how MLMs might internally represent concepts like ontological classes and semantic containment relations (e.g., sub-class and instance-of). Unveiling this knowledge could have significant implications for Semantic Web applications, but it necessitates a profound understanding of how these models express such relationships. This work investigates whether MLMs can understand these relationships, presenting a novel approach to automatically leverage the predictions returned by MLMs to discover semantic containment relations in unstructured text. We achieve this by constructing a verbalizer, a system that translates the model's internal predictions into classification labels. Through a comprehensive probing procedure, we assess the method's effectiveness, reliability, and interpretability. Our findings demonstrate a key strength of MLMs: their ability to capture semantic containment relationships. These insights bring significant implications for MLM application in ontology construction and aligning text data with ontologies.
PRONTO Schematization: given a pair representing a containment in a reference taxonomy, representing a semantic containment relationship ("is-a"), PRONTO predicts the plausibility of the pair with a learned verbalizer.
- Python >= 3.10.12
- PyTorch >= 2.2.1
- CUDA 12.1
- Clone repo
git clone https://github.com/masked_until_acceptance.git cd PRONTO - Install dependent packages
# Create virtual environment python -m venv venv . ./venv/bin/activate # Install requirements pip install -r requirements.txt
-
To replicate our results on the paper, run
python run_model_train.pyfor each of the experiments related to semantic containment prediction (Tables 4,7, and 8).Warning: Define the customizable variables (see below) according to the details of the experiment to run.
python run_model_train.py -
To replicate our results on zero-shot entity typing task, run the following command: Warning: it requires a verbalizer checkpoint resulting from
run_model_train.py.python run_fewnerd.py
Note: we noticed that results may slightly vary according to the underlying hardware architecture. Our experiments were run on a NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 (24GB), Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-5820K CPU @ 3.30GHz.
-
Line arguments for
run_model_train.py:Warning: Custom templates (different from the ones in the paper) need to be specified directly in the script, as well as soft tokens.
--verbalizer_type str default="mav" choices=["mav", "vf", "lin", "ws"] The type of verbalizer to use.
--model_name str default="test_model" The name of the output model.
--pretrained_model_name str default="FacebookAI/roberta-base" The name of the pretrained model to use.
--no_save_models flag store_false Whether to save the models.
--no_save_results flag store_false Whether to save the results.
--load_models flag store_true Whether to load existing models.
--no_train_models flag store_false Whether to train the models.
--with_context flag store_true Whether to use textual descriptions.
--reversed_test flag store_true Whether to perform the positive-reverse negatives test.
--unseen_instances float default=0 Percentage of instances in the test set to drop associated triples from the train set.
--epochs int default=50 Number of training epochs.
--batch_size int default=64 Batch size for training.
--alpha float default=0.8 Alpha parameter value for the focal loss.
--weight_decay float default=1e-6 Weight decay value.
--learning_rate float default=1e-5 Learning rate.
--l1_reg float default=0 L1 regularization value.
--noise_scaling float default=0 Noise scaling value (DEPRECATED).
-
Line arguments for
run_fewnerd.py:Warning: to test different prompt templates, it is required to customize the TEMPLATE variable in the script (and SPECIAL_TOKENS if needed). By default, the script uses the "[1] is [MASK] of [2]" prompt template (h_1 in the paper), which has template_id 0 by default in the run_model_train.py script.
--verbalizer_type str default="mav" choices=["mav", "vf", "lin", "ws"] The type of verbalizer to use.
--model_name str default="test_model" The name of the saved verbalizer model (trained with run_model_train.py).
--results_name str default="results" The name of the experiment.
--pretrained_model_name str default="FacebookAI/roberta-large" The name of the pretrained model to use.
--template_id int default=0 The zero-indexed ID of the prompt template to use.
--experiment_type str default="coarse" choices=["coarse", "per", "loc", "org"] The type of experiment to run.
Warning: the following commands are based on the RoBERTa-Large model. In order to test the other models, specify the respective huggingface name with the --pretrained_model_name argument ("FacebookAI/roberta-base" or "bert-base-cased" are also supported).
-
Running Pronto-MAV training with RoBERTa-Large:
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-mav-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="mav"-
Running Few-NERD evaluation (coarse) with the resulting model (Warning: the NER split can be specified with the
--experiment_typeargument):python run_fewnerd.py --experiment_type="coarse" --model_name="pronto-mav-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="mav" -
Running Pronto-MAV evaluation with node descriptions with RoBERTa-Large (after training):
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-mav-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="mav" --with_context --no_save_results --load_models --no_train_models -
Running Pronto-MAV training with RoBERTa-Large (80% entities of test set removed from train set):
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-mav-roberta-unseen" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="mav" --unseen_instances=0.80
-
-
Running Pronto-VF training with RoBERTa-Large:
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-vf-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="vf" -
Running Pronto-WS training with RoBERTa-Large:
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-ws-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="ws" --learning_rate=1e-1 --l1_reg=1e-4 --weight_decay=0-
Running Pronto-WS evaluation with RoBERTa-Large on reverse negatives (after training):
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-ws-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="ws" --reversed_test --load_models --no_train_models
-
-
Running Pronto-LIN training with RoBERTa-Large:
python run_model_train.py --model_name="pronto-lin-roberta" --pretrained_model_name="FacebookAI/roberta-large" --verbalizer_type="lin" --learning_rate=1e-1 --l1_reg=1e-4 --weight_decay=0
This source code is released under the Apache 2.0 license.
The details will be released upon acceptance
If you have any question, please email masked email until acceptance.