前端进阶算法4:链表原来如此简单(+leetcode刷题)
sisterAn opened this issue · 9 comments
引言
链表相对于数组来说,要复杂的多,首先,链表不需要连续的内存空间,它是由一组零散的内存块透过指针连接而成,所以,每一个块中必须包含当前节点内容以及后继指针。最常见的链表类型有单链表、双链表以及循环链表。
学习链表最重要的是 多画图多练习 ,没有捷径可循,在遇到链表问题时,瓶子君总结了一下,可以按照以下五步骤:
- 确定解题的数据结构:单链表、双链表或循环链表等
- 确定解题思路:如何解决问题
- 画图实现:画图可以帮助我们发现思维中的漏洞(一些思路不周的情况)
- 确定边界条件:思考解题中是否有边界问题以及如何解决
- 代码实现:解题完成✅
本文会给常用链表(单链表、双链表以及循环链表)的基本操作已经代码实现,并给出实现思路,这些都是链表解题的基石,请务必掌握!⛽️⛽️⛽️
最后附赠一道 leetcode 题目,并按照链表解题五步骤给出答案!
下面开始本节的学习吧!!!👇👇👇
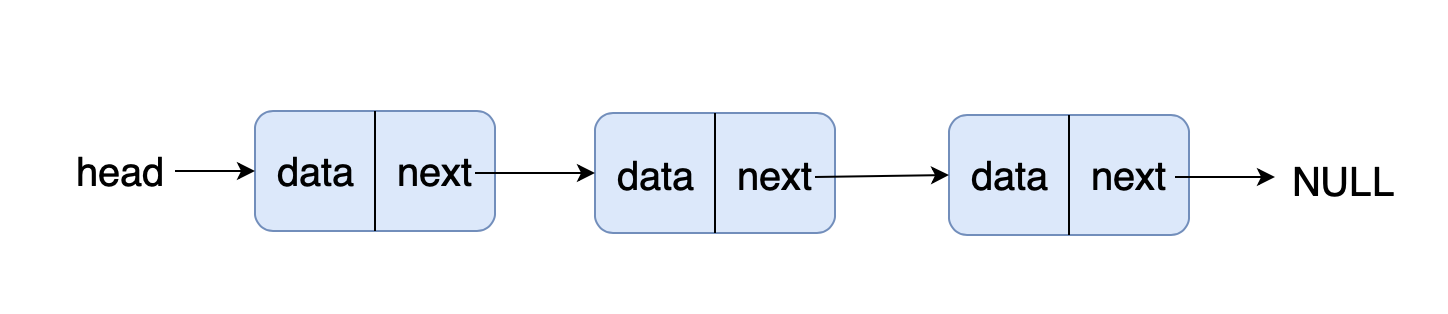
一、单链表
单链表结构:
function List () {
// 节点
let Node = function (element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
}
// 初始头节点为 null
let head = null
// 链表长度
let length = 0
// 操作
this.getList = function() {return head}
this.search = function(list, element) {}
this.append = function(element) {}
this.insert = function(position, element) {}
this.remove = function(element){}
this.isEmpty = function(){}
this.size = function(){}
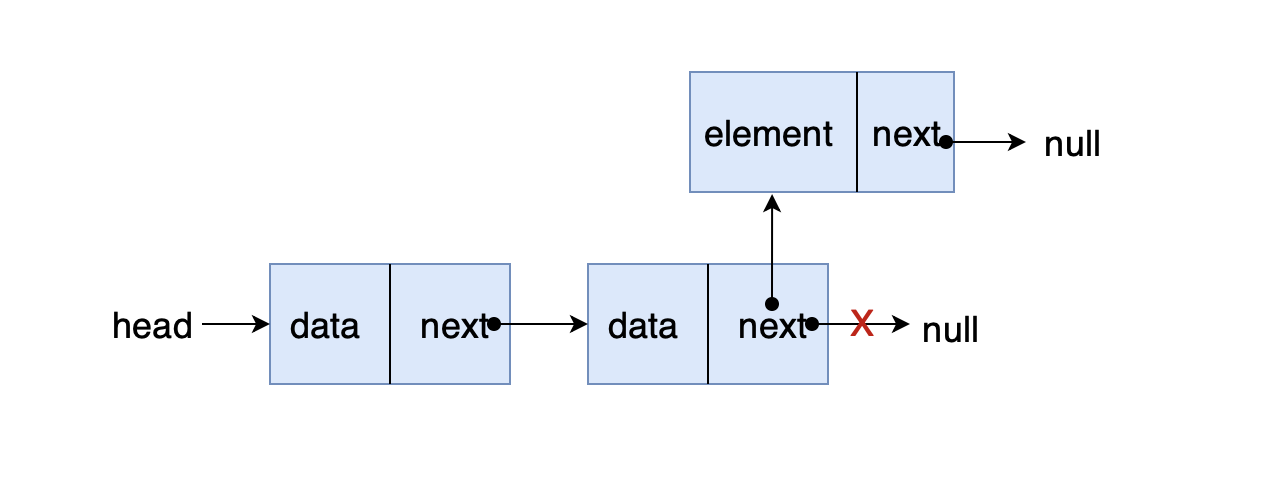
}1. 追加节点:
**确定解题的数据结构:**单链表
确定解题思路: 初始化一个节点(待追加节点),遍历到链尾,在尾节点后插入该节点
画图实现:
确定边界条件: 当链表为 null ,直接将 head 指向待插入节点,不需要遍历
代码实现:
function append (element) {
let node = new Node(element),
p = head
if (!head){
head = node
} else {
while (p.next) {
p = p.next
}
p.next = node
}
length += 1
}
// 测试
let list = new List()
for(let i = 0; i < 5; i+=1) {
list.append(i)
}解题完成✅
2. 查找:
**确定解题的数据结构:**单链表
确定解题思路: 遍历单链表,判断节点值是否等于待查找值,相等则返回 true ,否则继续遍历下一个节点,直到遍历完整个链表还未找到,则返回 false
画图实现: 很简单,读者可以尝试画一下
确定边界条件: 当链表为 null ,可直接返回 false
代码实现:
// 判断链表中是否存在某节点
function search(element) {
let p = head
if (!p) return false
while(p) {
if (p.element === element) return true
p = p.next
}
return false
}
// 测试
list.search(4) // true
list.search(11) // false解题完成✅
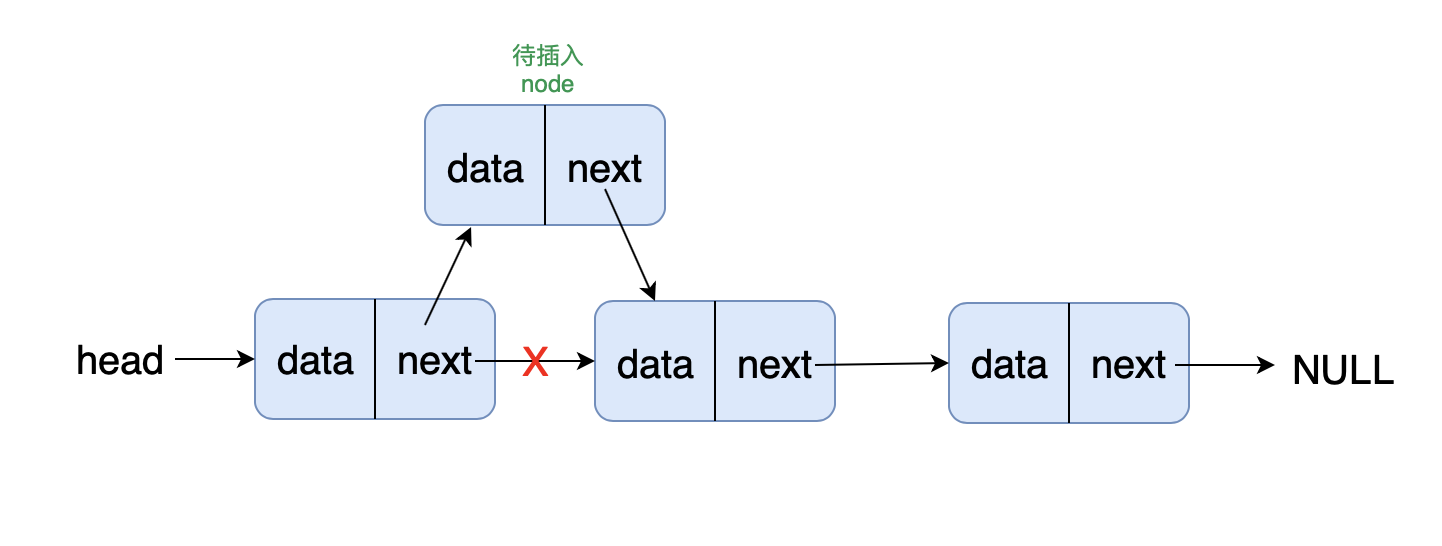
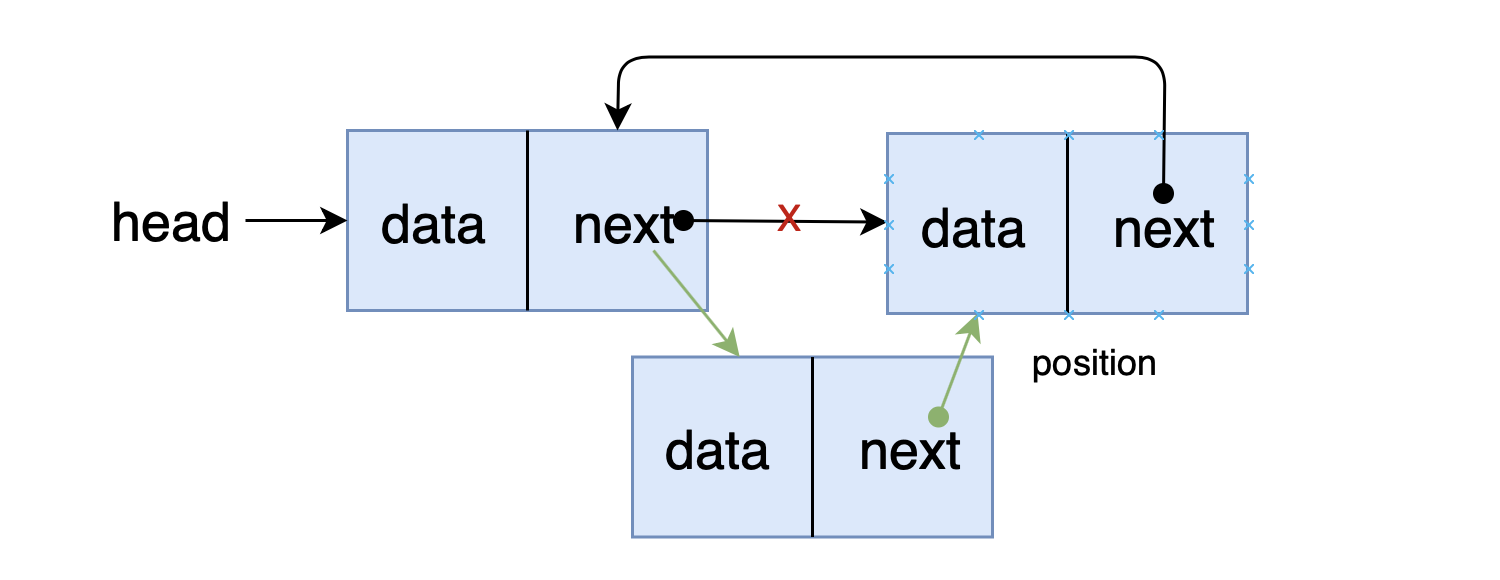
3. 在 position 位置插入:
**确定解题的数据结构:**单链表
确定解题思路: 初始化一个节点(待插入节点 node ),遍历到 position 前一个位置节点,在该节点后插入 node
画图实现:
确定边界条件:
- 当
position为0时,直接将插入节点node.next指向head,head指向node即可,不需要遍历 - 当待插入位置
position < 0或超出链表长度position > length,都是有问题的,不可插入,此时直接返回null,插入失败
代码实现:
// 插入 position 的后继节点
function insert (position, element) {
// 创建插入节点
let node = new createNode(element)
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
let prev = head,
curr = head,
index = 0
if(position === 0) {
node.next = head
head = node
} else {
while(index < position) {
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
index ++
}
prev.next = node
node.next = curr
}
length += 1
} else {
return null
}
}
// 测试
list.insert(10)解题完成✅
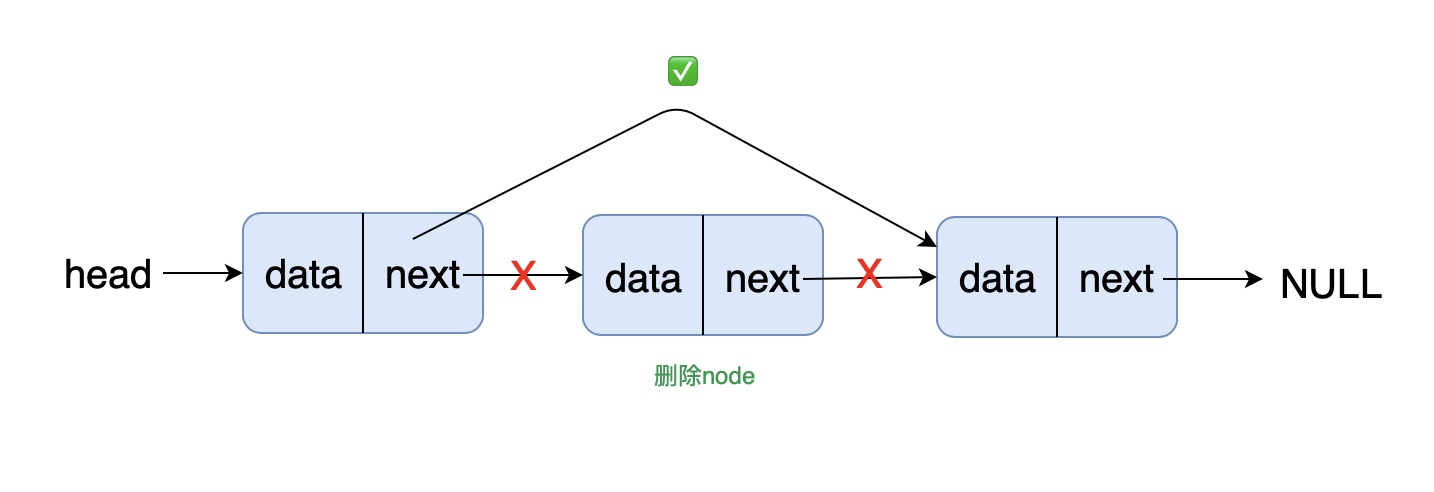
4. 删除:
**确定解题的数据结构:**单链表
确定解题思路: 遍历单链表,找到待删除节点,删除
画图实现:
确定边界条件: 当链表为 null ,直接返回
代码实现:
// 删除值为 element 节点
function remove (element) {
let p = head, prev = head
if(!head) return
while(p) {
if(p.element === element) {
p = p.next
prev.next = p
} else {
prev = p
p = p.next
}
}
}解题完成✅
5. 复杂度分析:
查找:从头节点开始查找,时间复杂度为 O(n)
插入或删除:在某一节点后插入或删除一个节点(后继节点)的时间复杂度为 O(1)
链表五步骤是不是很好用😊,下面看一下双链表👇
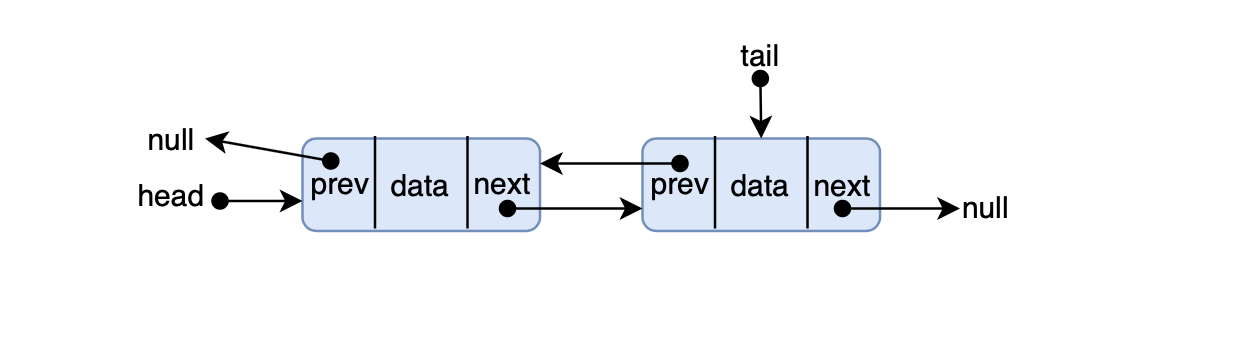
二、双链表
顾名思义,单链表只有一个方向,从头节点到尾节点,那么双链表就有两个方向,从尾节点到头节点:
function DoublyLinkedList() {
let Node = function(element) {
this.element = element
// 前驱指针
this.prev = null
// 后继指针
this.next = null
}
// 初始头节点为 null
let head = null
// 新增尾节点
let tail = null
// 链表长度
let length = 0
// 操作
this.search = function(element) {}
this.insert = function(position, element) {}
this.removeAt = function(position){}
this.isEmpty = function(){ return length === 0 }
this.size = function(){ return length }
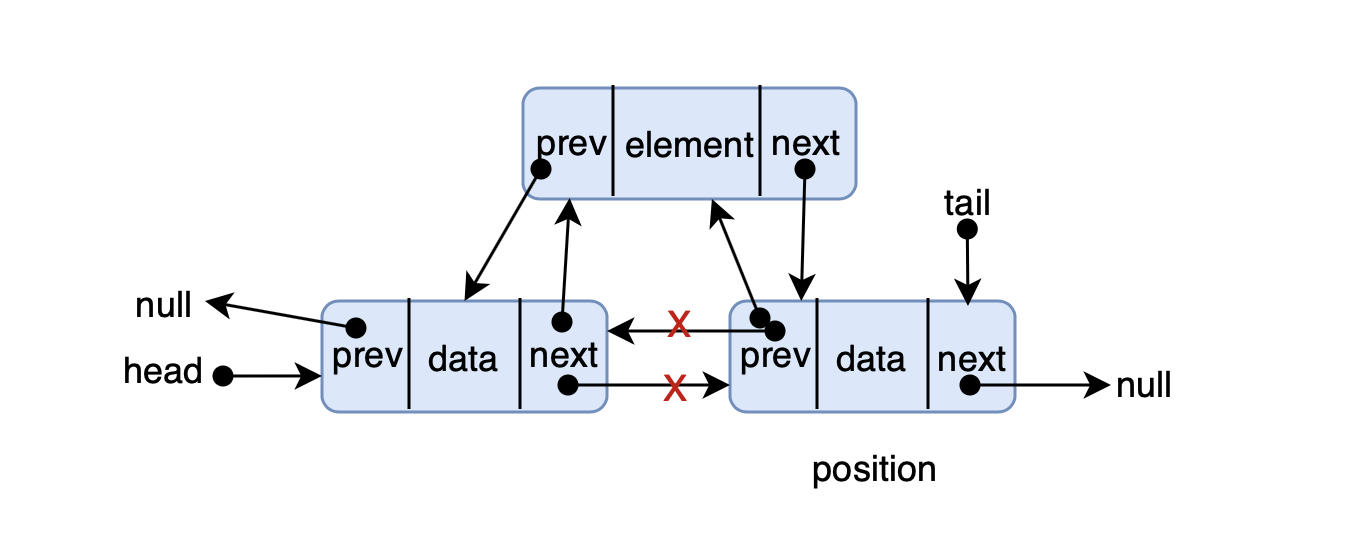
}1. 在 position 位置插入节点:
确定解题的数据结构: 双链表
确定解题思路: 初始化一个节点(待插入节点 node ),遍历链表到 position 前一个位置节点,在该节点位置后插入 node
画图实现:
确定边界条件:
当待插入位置 position < 0 或超出链表长度 position > length ,都是有问题的,不可插入,此时直接返回 null ,插入失败
代码实现:
// 插入 position 的后继节点
function insert (position, element) {
// 创建插入节点
let node = new Node(element)
if (position >= 0 && position < length) {
let prev = head,
curr = head,
index = 0
if(position === 0) {
// 在第一个位置添加
if(!head) { // 注意这里与单链表不同
head = node
tail = node
} else {
// 双向
node.next = head
head.prev = node
// head 指向新的头节点
head = node
}
} else if(position === length) {
// 插入到尾节点
curr = tial
curr.next = node
node.prev = curr
// tail 指向新的尾节点
tail = node
} else {
while(index < position) {
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
index ++
}
// 插入到 prev 后,curr 前
prev.next = node
node.next = curr
curr.prev = node
node.prev = prev
}
length += 1
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
// 测试
list.insert(10)解题完成✅
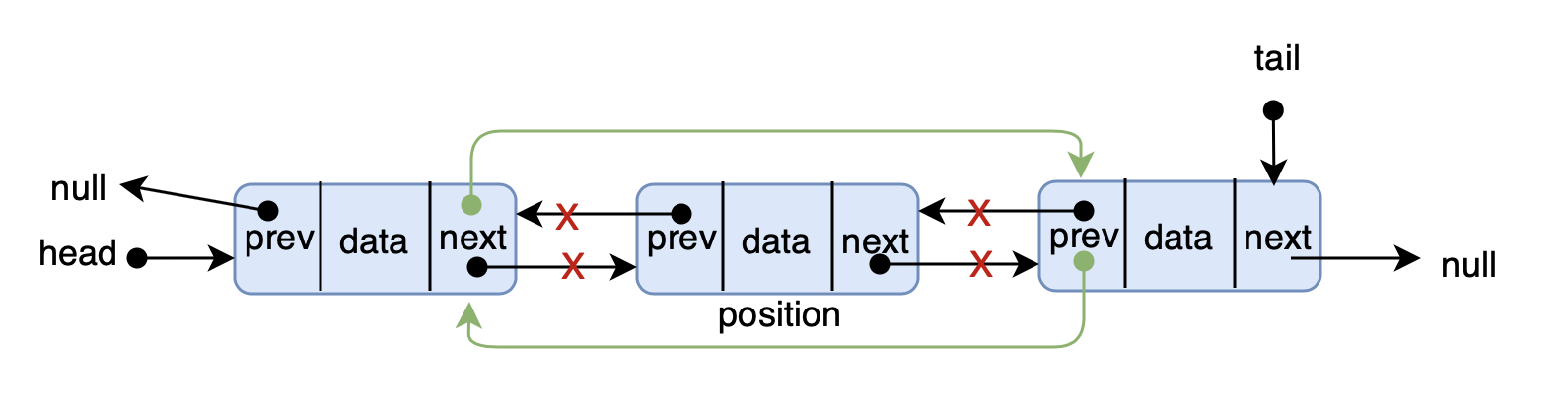
2. 删除:
确定解题的数据结构: 双链表
确定解题思路: 遍历双链表,找到待删除节点,删除
画图实现:
确定边界条件: 当链表为 null ,直接返回
代码实现:
// 删除 position 位置的节点
function removeAt (position) {
if (position >= 0 && position < length && length > 0) {
let prev = head,
curr = head,
index = 0
if(position === 0) {
// 移除头节点
if(length === 1) { // 仅有一个节点
head = null
tail = null
} else {
head = head.next
head.prev = null
}
} else if(position === length-1) {
// 移除尾节点
curr = tial
tail = curr.prev
tail.next = null
} else {
while(index < position) {
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
index ++
}
// 移除curr
prev.next = curr.next
curr.next.prev = prev
}
length -= 1
return curr.element
} else {
return null
}
}解题完成✅
3. 查找:
双链表的查找和单链表类似,都是遍历链表,找到返回 true,找不到返回 false 。
4. 复杂度分析:
查找:查找前驱节点或后继节点时间复杂度为 O(1),其它节点仍为 O(n)
插入或删除:插入或删除前驱节点或后继节点的时间复杂度都为 O(1)
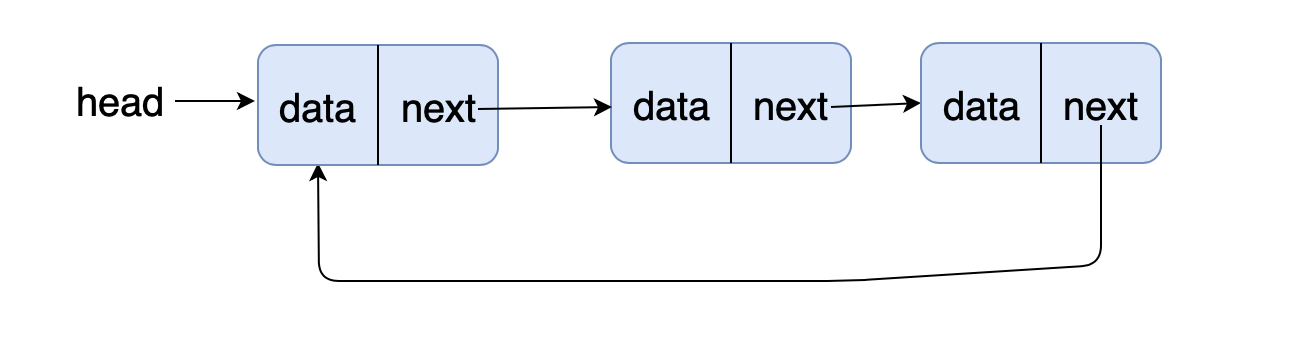
三、循环单链表
循环单链表是一种特殊的单链表,它和单链表的唯一区别是:单链表的尾节点指向的是 NULL,而循环单链表的尾节点指向的是头节点,这就形成了一个首尾相连的环:
既然有循环单链表,当然也有循环双链表,循环双链表和双链表不同的是:
- 循环双链表的
tail.next(tail的后继指针) 为null,循环双链表的tail.next为head - 循环双链表的
head.prev(head的前驱指针) 为null,循环双链表的head.prev为tail
这里以循环单列表为例
function CircularLinkedList() {
let Node = function(element) {
this.element = element
// 后继指针
this.next = null
}
// 初始头节点为 null
let head = null
// 链表长度
let length = 0
// 操作
this.search = function(element) {}
this.insert = function(positon, element) {}
this.removeAt = function(position){}
this.isEmpty = function(){ return length === 0 }
this.size = function(){ return length }
}1. 在 positon 后插入:
确定解题的数据结构: 循环单链表
确定解题思路: 初始化一个节点(待插入节点 node ),遍历到 position 前一个位置节点,在该节点后插入 node
画图实现:
确定边界条件:
- 当
position为0时,需要遍历到尾节点,然后在尾节点后插入节点 , 并将head指向 - 当待插入位置
position < 0或超出链表长度position > length,都是有问题的,不可插入,此时直接返回null,插入失败
代码实现:
// 插入 position 的后继节点
function insert (position, element) {
// 创建插入节点
let node = new createNode(element)
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
let prev = head,
curr = head,
index = 0
if(position === 0) {
// 与单链表插入不同的
while(index < length) {
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
index ++
}
prev.next = node
node.next = curr
head = node
} else {
while(index < position) {
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
index ++
}
prev.next = node
node.next = curr
}
length += 1
} else {
return null
}
}
// 测试
list.insert(10)解题完成✅
2. 查找:
和单链表类似,唯一不同的是:循环单链表的循环结束条件为 index++ < length
// 判断链表中是否存在某节点
function search(element) {
if (!head) return false
let p = head, index = 0
// 和单链表的不同所在
while(index++ < length) {
if (p.element === element) return true
p = p.next
}
return false
}
// 测试
list.search(4) // true
list.search(11) // false解题完成✅
3. 删除:
和单链表类似,唯一不同的是:循环单链表的循环结束条件为 index++ < length
// 删除值为 element 节点
function remove (element) {
let p = head, prev = head, index = 0
// 空链表
if(!head || ) return
// 仅有一个节点且element一致
if(length === 1 && head.element === element){
head = null
length--
return
}
while(index++ < length) {
if(p.element === element) {
p = p.next
prev.next = p
length --
} else {
prev = p
p = p.next
}
}
}解题完成✅
4. 复杂度分析
查找:循环链表从任一节点开始查找目标节点,时间复杂度为 O(n)
插入或删除:它和单链表一样,后继节点插入及删除的时间复杂度为 O(1)
四、leetcode21:合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4欢迎将答案提交到 #11 , 让更多人看到,瓶子君也会在明日放上自己的解答。
五、认识更多的前端道友,一起进阶前端开发
前端算法集训营第一期免费开营啦🎉🎉🎉,免费哟!
在这里,你可以和志同道合的前端朋友们(200+)一起进阶前端算法,从0到1构建完整的数据结构与算法体系。
在这里,瓶子君不仅介绍算法,还将算法与前端各个领域进行结合,包括浏览器、HTTP、V8、React、Vue源码等。
在这里,你可以每天学习一道大厂算法题(阿里、腾讯、百度、字节等等)或 leetcode,瓶子君都会在第二天解答哟!
更多福利等你解锁🔓🔓🔓!
在公众号「前端瓶子君」内回复「算法」即可加入。你的关注就是对瓶子君最大的支持😄😄😄
循环单链表的插入是有问题的,当链表为空时,插入会报错。最好在前面加一个length===0的判断
var deleteNode = function (head, val) {
if (head.val === val) {
return head.next
}
head.next = deleteNode(head.next, val);
return head
}
单链表中的删除节点remove是有问题的,没有考虑删除head节点
单链表中的insert 调用是不是少传了一个element?
插入链表 可以使用哑节点,代码更清晰
this.insert = function(position, element) {
// 边界条件
if(position < 0 || position > length) {
return null
}
// 如果head不存在,直接赋值
if(!head) {
head = node
length ++
return
}
// 边界条件 END
let node = new Node(element)
// 新增一个哑节点
let dummy = new Node()
dummy.next = head
let curr = dummy
// 开始遍历寻找position位置之前的那个元素
for(let pos = 0; pos < position; pos ++) {
curr = curr.next
}
node.next = curr.next
curr.next = node
length ++
}拜谢作者,快要考数据结构导论了,发现了宝藏
代码很有问题