Created by Yizhak Ben-Shabat (Itzik) and Stephen Gould from ANU and ACRV .
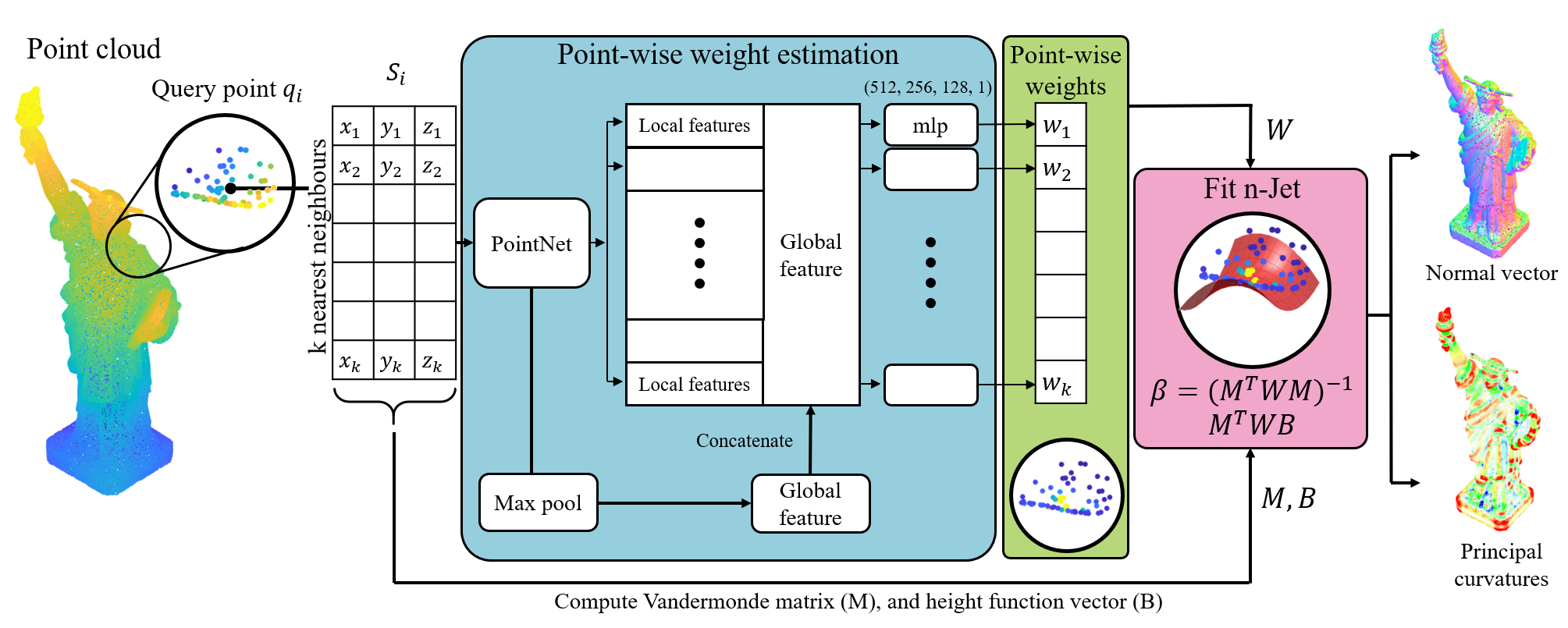 This is the code for unstructured 3D point cloud surface fitting using DeepFit.
It allows to train, test and evaluate our weight prediction models for weighted least squares in the context of normal estimation and principal curvature estimation.
We provide the code for train a model or use a pretrained model on your own data.
This is the code for unstructured 3D point cloud surface fitting using DeepFit.
It allows to train, test and evaluate our weight prediction models for weighted least squares in the context of normal estimation and principal curvature estimation.
We provide the code for train a model or use a pretrained model on your own data.
Please follow the installation instructions below.
A short YouTube video providing a brief overview of the methods is coming soon.
Abstract:
We propose a surface fitting method for unstructured 3D point clouds. This method, called DeepFit, incorporates a neural network to learn point-wise weights for weighted least squares polynomial surface fitting. The learned weights act as a soft selection for the neighborhood of surface points thus avoiding the scale selection required of previous methods. To train the network we propose a novel surface consistency loss that improves point weight estimation. The method enables extracting normal vectors and other geometrical properties, such as principal curvatures, the latter were not presented as ground truth during training. We achieve state-of-the-art results on a benchmark normal and curvature estimation dataset, demonstrate robustness to noise, outliers and density variations, and show its application on noise removal.
Our short video (2 minutes) and extended video (7.5 minutes) presentation are available on YouTUbe.
If you find our work useful in your research, please cite our paper:
@article{ben2020deepfit,
title={DeepFit: 3D Surface Fitting via Neural Network Weighted Least Squares},
author={Ben-Shabat, Yizhak and Gould, Stephen},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10826},
year={2020}
}
Install PyTorch.
The code was tested with Python 3.7.3, torch 1.4.0, torchvision 0.5.0, CUDA 10.1.243, and cuDNN 7605 on Ubuntu 18.04.
For a full list of requirements see requirements.txt.
To test DeepFit on your own data. Run the compute_normals.py in the ./tutorial directory.
It allows you to specify the input file path (.xyz file), output path for the estimated normals, jet order (1-4), and a mode (use pretrained DeepFit or our pytorch implementation of the classic jet fitting).
To help you get started, we provide a step by step tutorial ./tutorial/DeepFit_tutorial.ipynb with extended explanations, interactive visualizations and example files.
Run get_data.py to download PCPNet data.
Alternatively, Download the PCPNet data from this link and place it in ./data/pcpnet/ directory.
To test the model and output all normal estimations for the dataset run test_n_est.py. This will export the normal estimations for each file in the provided file list as a .normals file.
To evaluate the results and output a report run evaluate.py
To get all of the method's outputs exported (beta, weights, normals, curvatures) run test_c_est.py.
To evaluate curvature estimation performance run evaluate_curvatures.py (after exporting the results).
To train a model run train_n_est.py.
To train, test and evaluate run run_DeepFit_single_experiment.py.
Alternatively you can run individual train, test and evaluation.
Click on the link for details on how to visialize normal vectors on 3D point clouds.
For a quick visualization of a single 3D point cloud with the normal vector overlay run the visualize_normals.m script provided MATLAB code in ./MATLAB.
For visualizing all of the PCPNet dataset results and exporting images use export_visualizations.m.
See LICENSE file.

