- The dynamic programming approach is used in the basic version of sequence alignment problem solution.
- The combination of
divide and conquer, anddynamic programmingis used in the efficient version of the sequence alignment algorithm. - Here, the problem is divided into sub problems and solve them recursively.
- In each subproblem, The string
Xis split into half and the positiony_split_posis calculated by memory efficient version of sequence alignment to splitYstring. - Finally, the base case is to find out the alignment when length of
XandYis less than or equal to 2.
Time Complexity: O(m*n)
Space Complexity: O(m*n)
Time Complexity: O(m*n)
Space Complexity: O(m+n)
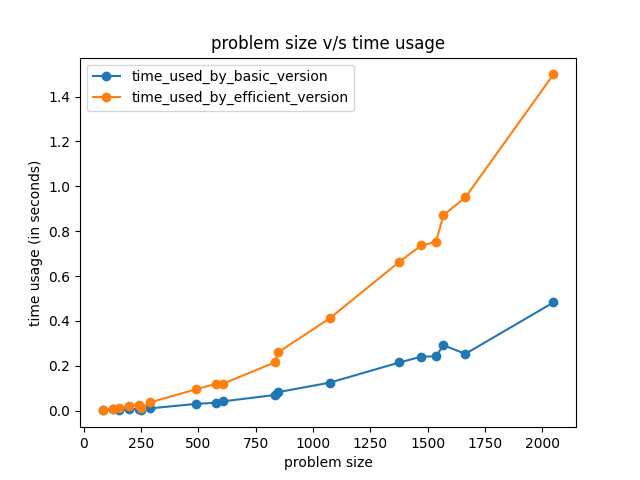
- Time taken by efficient version is higher than the basic version of sequence alignment algorithm.
- The overhead of recursion for divide and conquer, as well as the overhead for finding
y_split_posforYstring causes the time. for efficient algorithm to be little greater than basic version which contains onlym*niterations. - Therefore, the overhead associated with the efficient algorithm causes the time to be a bit greater than the basic version.
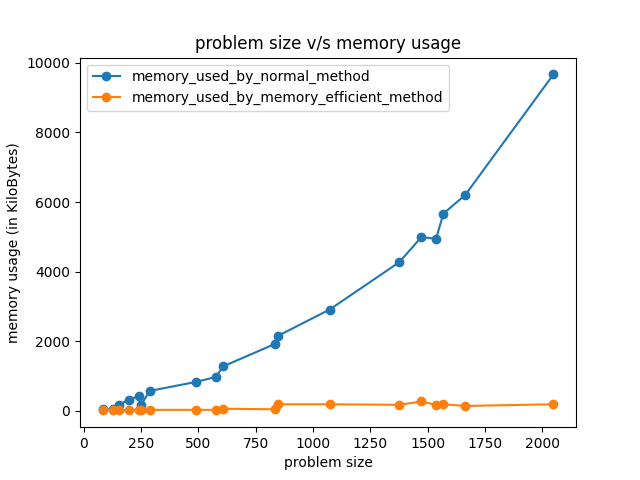
- The efficient algorithm uses
2*k(kbeing the size ofYstring) array to calculate the minimum sequence alignment for every recursion individe_and_conquermethod. Hence, the max memory allocated will be less than2*n(n is the max size of stringY). - Whereas, in case of basic version, the memory allocated is
m*n, which causes the memory size to increase linearly proportional to the input size.
Made with contrib.rocks.
- Sameer Khan Mohammad (Memory Efficient Version)
- Manidhar Mulagapaka (String Generator)
- Namrata Vasant Naik (Basic Version)
- Namrata Vasant Naik
- Sameer Khan Mohammad
- Sameer Khan Mohammad
- Manidhar Mulagapaka
- Namrata Vasant Naik
- Manidhar Mulagapaka