Continuum Analytics, H2O.ai, and MapD Technologies have announced the formation of the GPU Open Analytics Initiative (GOAI) to create common data frameworks enabling developers and statistical researchers to accelerate data science on GPUs. GOAI will foster the development of a data science ecosystem on GPUs by allowing resident applications to interchange data seamlessly and efficiently.
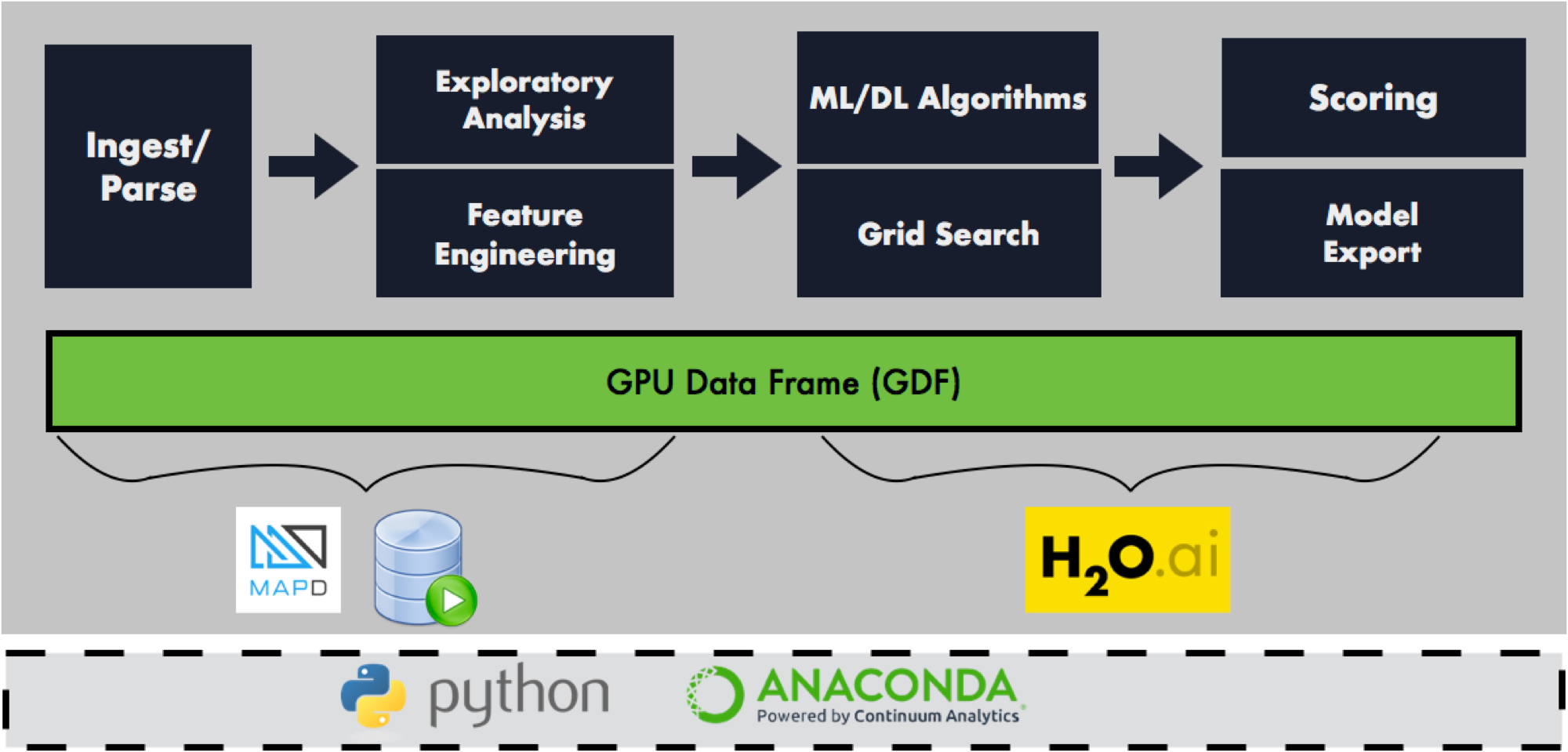
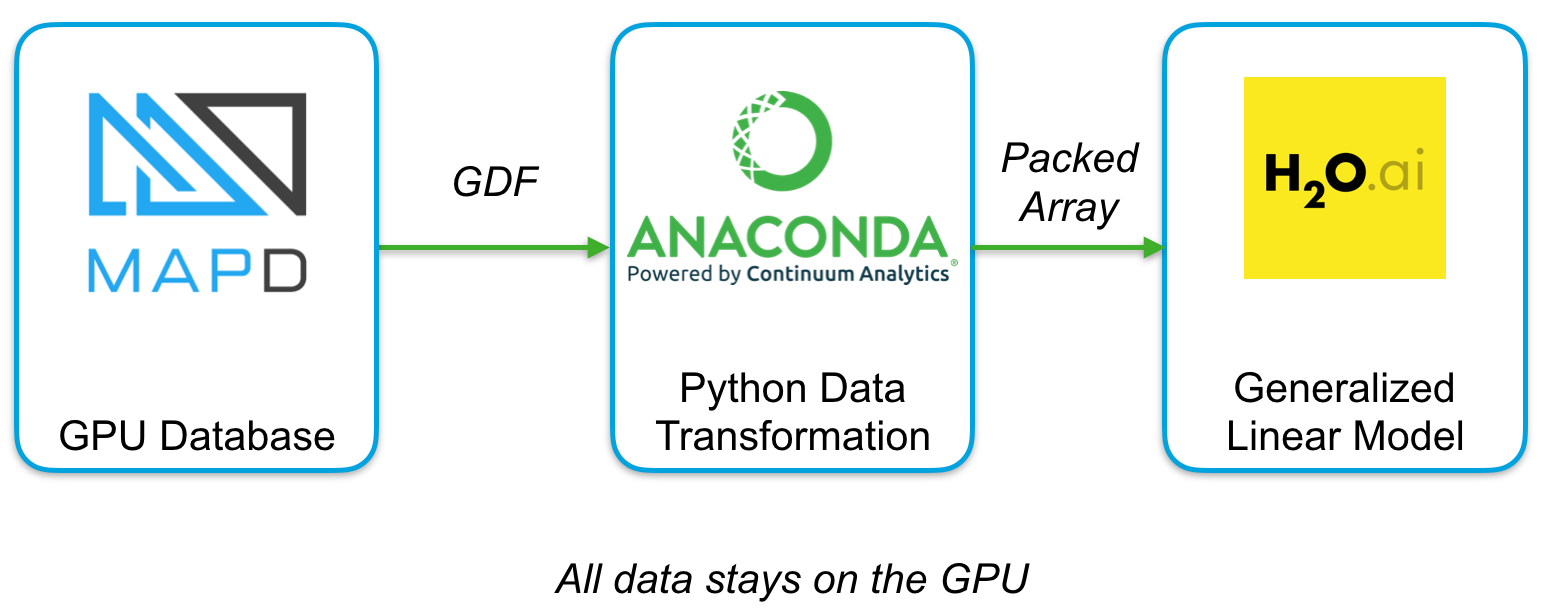
Our first project: an open source GPU Data Frame with a corresponding Python API. The GPU Data Frame is a common API that enables efficient interchange of data between processes running on the GPU. End-to-end computation on the GPU avoids transfers back to the CPU or copying of in-memory data reducing compute time and cost for high-performance analytics common in artificial intelligence workloads. Users of the MapD Core database can output the results of a SQL query into the GPU Data Frame, which then can be manipulated by the Continuum Analytics’ Anaconda NumPy-like Python API or used as input into the H2O suite of machine learning algorithms without additional data manipulation.
Users of the MapD Core database can output the results of a SQL query into the GPU Data Frame, which then can be manipulated by the Continuum Analytics’ Anaconda NumPy-like Python API or used as input into the H2O suite of machine learning algorithms without additional data manipulation. In early internal tests, this approach exhibited order-of-magnitude improvements in processing times compared to passing the data between applications on a CPU.
- Siu Kwan Lam
- Arno Candel
- Minggang Yu
- Stanley Seibert
- Jon Mckinney
- Bill Maimone
- Vinod Iyengar
- Todd Mostak
The following instructions are tested on Linux and OSX systems.
This project uses cmake for building the C/C++ library. To configure cmake, run:
mkdir build # create build directory for out-of-source build
cd build # enter the build directory
cmake .. # configure cmakeTo build the C/C++ code, run make. This should produce a shared library
named libgdf.so or libgdf.dylib.
To make development and testing more seamless, the python files and tests
can be symlinked into the build directory by running make copy_python.
With that, any changes to the python files are reflected in the build
directory. To rebuild the libgdf, run make again.
It is recommended to setup a conda environment for the dependencies.
# create the conda environment (assuming in build directory)
$ conda env create --name libgdf_dev --file ../conda_environments/dev_py35.yml
# activate the environment
$ source activate libgdf_devFor additional information, the python cffi wrapper code requires cffi and
pytest. The testing code requires numba and cudatoolkit as an
additional dependency.
Currently, all tests are written in python with py.test. A make target is
available to trigger the test execution. In the build directory (and with the
conda environment activated), run below to exceute test:
make pytest # this auto trigger target "copy_python"