SublimeLinter-gcc
This linter plugin for SublimeLinter provides an interface to gcc or other gcc-like (cross-)compiler. It will be used with files that have the C/C++ syntax. If you are using clang, you may want to check SublimeLinter-clang.
Installation
SublimeLinter must be installed in order to use this plugin. If SublimeLinter is not installed, please follow the instructions here.
Linter installation
Before using this plugin, you must ensure that gcc or other gcc-like (cross-)compiler is installed on your system.
You may install gcc with the following method:
- Mac OS X: OSX GCC Installer
- Linux:
gcccould be installed by using most package managers. - Windows: MinGW-w64
Once gcc is installed, you must ensure it is in your system PATH so that SublimeLinter can find it.
This may not be as straightforward as you think, so please read How linter executables are located in the documentation.
Plugin installation
Please use Package Control to install the linter plugin. This will ensure that the plugin will be updated when new versions are available. If you want to install from source so you can modify the source code, you probably know what you are doing so we won't cover that here.
To install via Package Control, do the following:
-
Within Sublime Text, bring up the Command Palette and type
install. Among the commands you should seePackage Control: Install Package. If that command is not highlighted, use the keyboard or mouse to select it. There will be a pause of a few seconds while Package Control fetches the list of available plugins. -
When the plugin list appears, type
gcc. Among the entries you should seeSublimeLinter-gcc. If that entry is not highlighted, use the keyboard or mouse to select it.
Settings
For general information on how SublimeLinter works with settings, please see Settings. For information on generic linter settings, please see Linter Settings.
In addition to the standard SublimeLinter settings, SublimeLinter-gcc provides its own settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| executable | If you are not using gcc, you have to set this to your compiler binary. (like arm-none-eabi-gcc) |
| include_dirs | A list of directories to be added to the header search paths (-I is not needed). |
| extra_flags | A list of extra flags to pass to the compiler. These should be used carefully, as they may cause linting to fail. |
-
All settings above could be
CorC++specific as well. To do that, simply addc_orc++_prefix to a setting's key. -
For project-specific settings,
${project_folder}can be used to specify relative path.
Here is an example settings:
{
"linters":
{
"gcc": {
"disable": false,
// C-specific settings
"c_executable": "gcc",
"c_extra_flags": [
"-fsyntax-only",
"-std=c90",
],
// C++-specific settings
"c++_executable": "g++",
"c++_extra_flags": [
"-fsyntax-only",
"-std=c++11",
],
// include_dirs for both C and C++
"include_dirs": [
"${project_folder}/include",
"/usr/local/include",
],
},
},
}Notes
-
Here is the official list of warning options in gcc 8.2.0. I prefer turn on all warnings via
-Wall(this is default for this plugin) and then suppress unwanted warnings via-Wno-prefix. -
Flag
-fsyntax-onlygives a much faster syntax-only checking but some warnings which are emitted in the code optimization phase would not be caught.
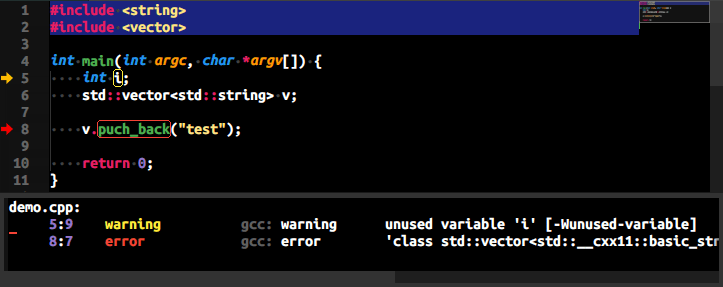
Demo
Troubleshooting
C/C++ linting is not always straightforward. A few things to try when there's (almost) no linting information available:
- Try to compile from the command line, and verify it works.
- The linter might be missing some header files. They can be added with
include_dirs. - Sometimes gcc fails to locate the C/C++ standard library headers.
Assuming the compilation works when executed via command line, try to compile with g++ -v.
This will display all of the hidden flags that gcc uses.
As a last resort, they can all be added in extra_flags.
Contributing
If you would like to contribute enhancements or fixes, please do the following:
- Fork the plugin repository.
- Hack on a separate topic branch created from the latest
master. - Commit and push the topic branch.
- Make sure your modification could pass unittests.
- Make a pull request.
- Be patient.
Please note that modifications should follow these coding guidelines:
- Indent is 4 spaces.
- Code should pass flake8 and pep257 linters.
- Vertical whitespace helps readability, don’t be afraid to use it.
- Please use descriptive variable names, no abbreviations unless they are very well known.
Thank you for helping out!
Supporters 
Thank you guys for sending me some cups of coffee.