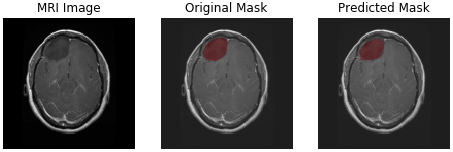
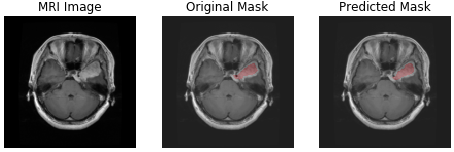
Here, I have implemented a U-Net from the paper "U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation" to segment tumor in MRI images of brain.
There are 3 types of brain tumor:
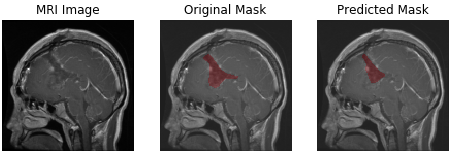
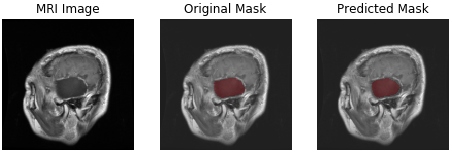
- meningioma
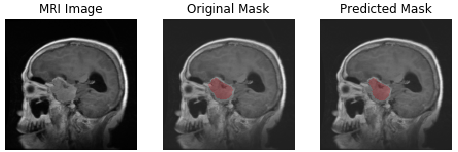
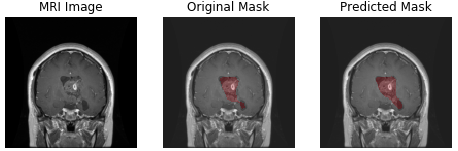
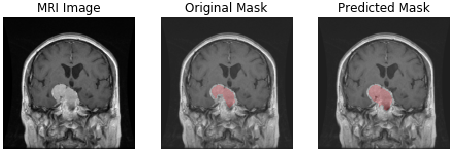
- glioma
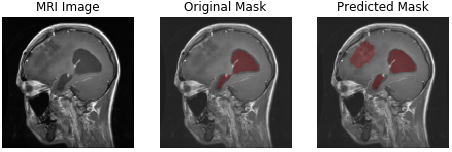
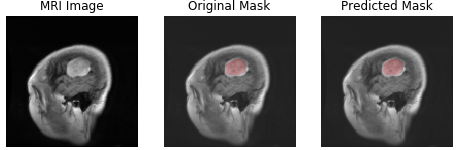
- pituitary tumor
| meningioma | glioma | pituitary tumor |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Here I will explain how to get the data and convert it into the usable form. You can run the train and run model using notebook.
You will need Python 3.X.X with some packages which you can install direclty using requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
I have used brain-tumor segment dataset which is available on the internet. You can run download_data.sh shell script to download all data. It contains 3064 MRI images and 3064 masks.
bash tumor-segmentation-unet/download_data.sh
After that run the following command to convert data in useable form.
python tumor-segmentation-unet/mat_to_numpy.py brain_tumor_dataset/
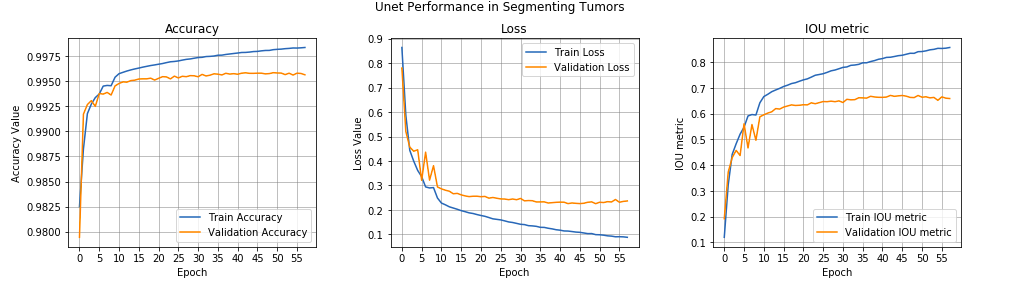
I have used combination of multiple losses which includes binary crossentropy, dice loss with equal weightage. Also I have used Conv2D transpose layers for upsampling.
I have used the metric called IOU (Intersection over Union) metric to track progress of training and trained Unet with Adam optimizer for 40-60 epochs with decaying learning rate between 1e-3 to 1e-4. I have also performed only one Image augmentation i.e. horizontal flip. Train and test split was stratified using type of tumor.
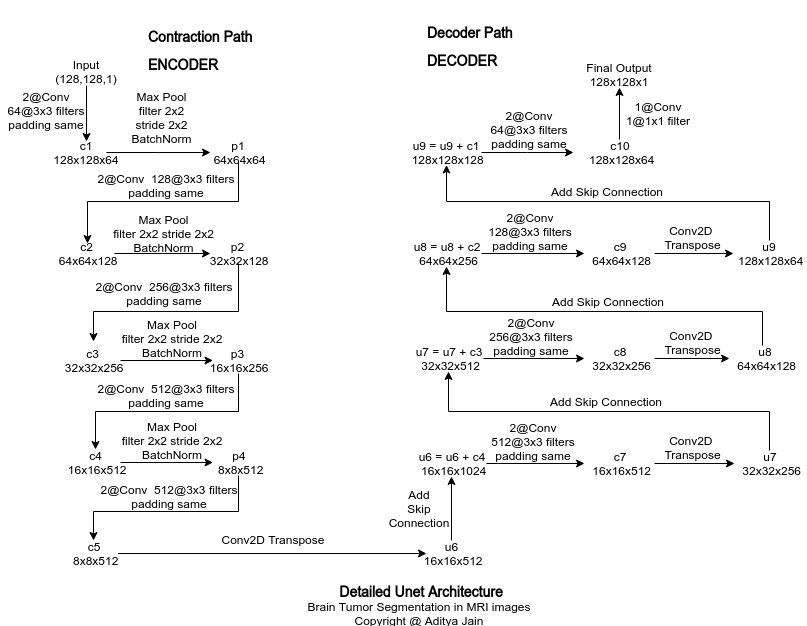
Detailed architecure is given below.
- Can use transfer learning to utilize state-of-the-art model like VGG, Inception, Resnet.
- We can use more types of image augmentation like vertical flip, brightness, zoom etc.
- Include lovasz loss with higher weightage.
- Learn and use Hypercolumns
- Aditya Jain : Portfolio