The goal of vistool is to visualize optimization traces and aid in
teaching optimization-related concepts.
You can install the development version of vistool from GitHub with:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("slds-lmu/vistool")Please note that visualization features rely on plotly which in
turns relies on certain functionality provided by Python packages, which
are accessed via reticulate.
Most importantly this affects the $save() functionality for plots,
which uses plotly::save_image() internally, and requires the kaleido
Python package.
The following instructions are provided by ?plotly::save_image and
assume you do not have miniconda installed already:
install.packages('reticulate')
reticulate::install_miniconda()
reticulate::conda_install('r-reticulate', 'python-kaleido')
reticulate::conda_install('r-reticulate', 'plotly', channel = 'plotly')
reticulate::use_miniconda('r-reticulate')library(vistool)
library(mlr3verse)
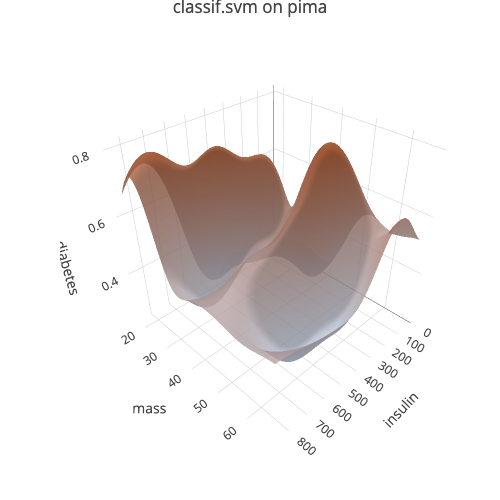
#> Loading required package: mlr3This examples shows how to visualize the prediction surface of an SVM on
the pima task included in mlr3:
# Create an example task, add missing data imputation and select 2 features
task = tsk("pima")
task = po("imputemean")$train(list(task))[[1]]
task$select(c("insulin", "mass"))
# Select example learner
learner = lrn("classif.svm", predict_type = "prob")
# Create the Visualizer object from task and learner
vis = as_visualizer(task, learner)
# Define a 3D scene
vis$set_scene(x = 1.4, y = 1.4, z = 1.4)View interactively:
vis$plot()Save static version as png:
vis$save("man/figures/demo_1.png", width = 500, height = 500)For visualization of…