DagTeam Data Engineering
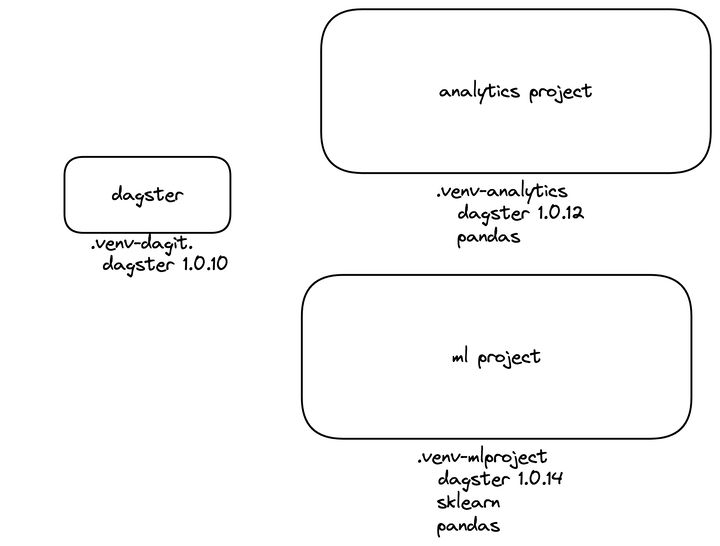
This repository houses the data engineering code for DagTeam. The repository contains multiple dagster projects:
dagteam
- analytics_project
- ml_project
The project structure allows each team to maintain their own code with its own Python dependencies. One team's code changes, or dependency upgrades, do not impact the other teams.
For example, to work within the analytics project:
cd analytics_project
source .venv-analytics/bin/activate
dagit
In addition to running dagit within their project, teams can confirm their code is loadable through tests:
cd analytics_project
pytest analytics_project_tests
======================== test session starts ==========================
platform darwin -- Python 3.10.7, pytest-7.2.0, pluggy-1.0.0
rootdir: /Users/lopp/Projects/dagteam/analytics_project
plugins: anyio-3.6.2
collected 1 item
analytics_project_tests/test_project_loads.py . [100%]
======================== 1 passed in 0.55s =============================
These tests can be added to CI/CD prior to pushing any changes to production.
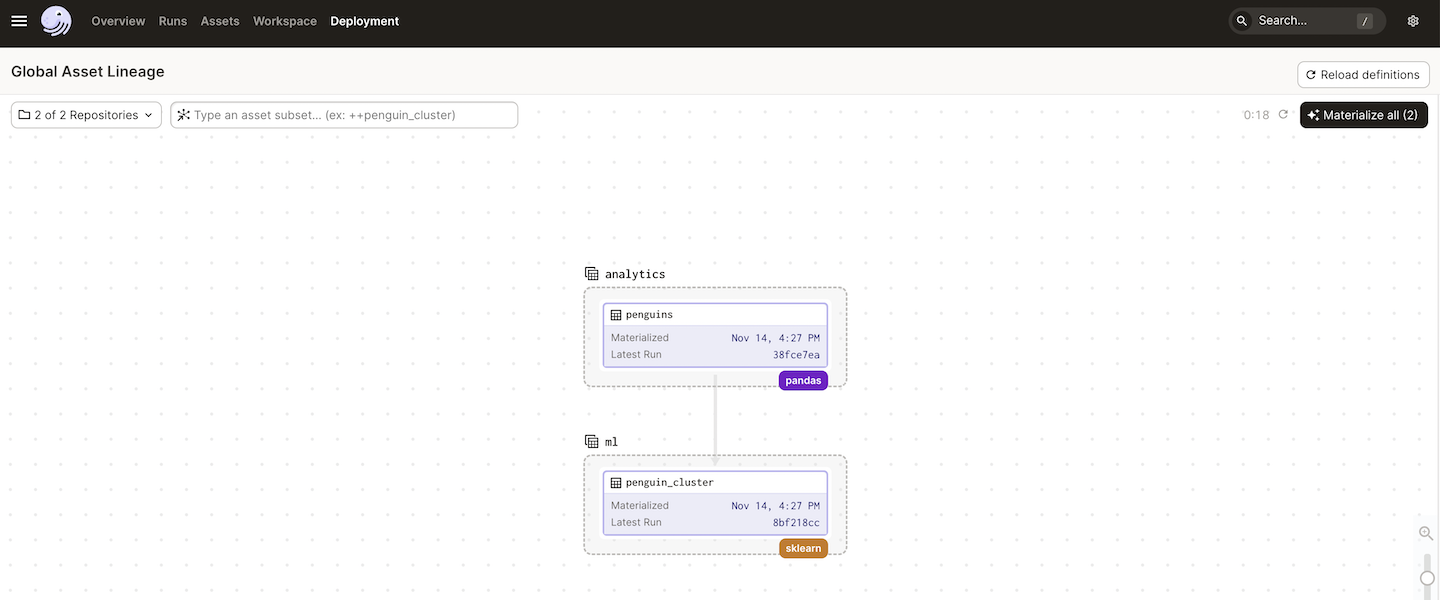
While the team's projects are separate, they can have shared assets. As an example:
ml_project/ml_project/assets/__init__.py
# ML team depends on an asset from the analytics project
penguins = SourceAsset(key = AssetKey("penguins"))
@asset(
group_name = "ml",
compute_kind = "sklearn"
)
def penguin_cluster(penguins):
...
return penguin_cluster
For cross-project assets, like penguin_cluster, scheduling is done through sensors. For example:
- The
analytics_project/repository.pydefines a regular schedule to updatepenguinsevery minute. - The
ml_project/repository.pydefines a sensor that runspenguin_clusteranytimepenguinsis updated.
To run the entire global data platform:
# load the global virtual environment, which only contains dagit and dagster
source .venv-dagit
dagit
To run the entire global data platform with schedules and sensors enabled:
# in a first terminal
source .venv-dagit
export DAGSTER_HOME=/some/path
dagit
# in a second terminal
source .venv-dagit
export DAGSTER_HOME=/some/path
dagster-daemon run
This global run uses workspace.yaml to load a virtualenv for analytics and a virtualenv for ml-project.
The Python dependencies for the orchestrator (dagster and dagit, contained in .venv-dagit) are separate and isolated from all of the project code.
On Dagster Cloud the setup is similar, and dagster_cloud.yaml ensures each project is represented as a unique code location with its own dependencies.
Often it is useful to have shared utilities. The utils directory represents an internal python package with a shared utility function. The ml_project imports this utility package. In order for this to work, the utils package must be compatible with all project environments, and should be installed in those project environments. Locally this can be done with:
source ml_project/.venv-mlproject/bin/activate
cd utils
pip install .You can see that the utils package is installed in the ml_project environment by inspecting ml_project/local_requirements.txt.
For Dagster Cloud, the utils package must be installed as part of the build process. This can be done in a few ways:
-
Hosting the utils package in a private PyPI repository, and then adding a
requirements.txtin the project directory (egml_project/requirements.txt) that specifies to install the utility package from the private PyPI. -
Customizing the GitHub action workflows (
.github/workflows) to copy the the utils package into the project build directory (egcp -r utils ml_project/utils) and then adding arequirements.txtin the project directory (egml_project/requirements.txt) that specifies to install the utility package from the copied subdirectory.