The CVE Binary Tool is a free, open source tool to help you find known vulnerabilities in software, using data from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) list of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) as well as known vulnerability data from Redhat, Open Source Vulnerability Database (OSV), Gitlab Advisory Database (GAD), and Curl.
CVE Binary Tool uses the NVD API but is not endorsed or certified by the NVD.
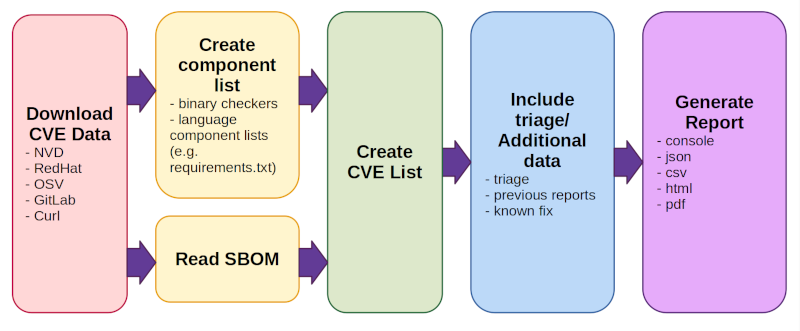
The tool has two main modes of operation:
-
A binary scanner which helps you determine which packages may have been included as part of a piece of software. There are 365 checkers. Our initial focus was on common, vulnerable open source components such as openssl, libpng, libxml2 and expat.
-
Tools for scanning known component lists in various formats, including .csv, several linux distribution package lists, language specific package scanners and several Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) formats.
It is intended to be used as part of your continuous integration system to enable regular vulnerability scanning and give you early warning of known issues in your supply chain. It can also be used to auto-detect components and create SBOMs.
What CVE Binary Tool does when it runs:
- Download CVE Data (from NVD, Redhat, OSV, Gitlab, and Curl).
- This happens once per day by default, not every time a scan is run.
- On first run, downloading all data can take some time.
- Create/read a component list. There are two modes of operation:
- Creates a component list (including versions) using a combination of binary checkers and language component lists (such as python's requirements.txt).
- Read SBOM (use an existing component list in a standardized Software Bill of Materials format.)
- Create CVE List
- This looks up all components found or read from an existing bill of materials and reports back any known issues associated with them
- Include triage/additional data
- There are several options for adding triage/notes, information from previous reports to track vulnerability change over time, or known fix data
- Generate report in one or more formats (console, json, csv, html, pdf)
For more details, see our documentation or this quickstart guide
- CVE Binary Tool quick start / README
CVE Binary Tool can be installed using pip:
pip install cve-bin-toolIf you want to try the latest code from
the cve-bin-tool github or do development, you can also pip install --user -e . to install a local copy from a directory. The Contributor Documentation covers how to set up for local development in more detail.
Pip will install the python requirements for you, but for some types of extraction we use system libraries. If you have difficulties extracting files, you may want to look at our additional Requirements lists for Linux and Windows.
On first usage (and by default, once per day) The tool will download vulnerability data from a set of known vulnerability data sources. Due to reliability issues with NVD, as of release 3.3 we will be using our own NVD mirror at https://cveb.in/ by default rather than contacting NVD directly. If you wish to get data directly from the NVD servers you must provide your own NVD_API_KEY to use their API.
If you are using a release prior to 3.3 that does not use our mirror, please use an NVD_API_KEY as described above.
To run the binary scanner on a directory or file:
cve-bin-tool <directory/file>Note: That this option will also use any language specific checkers to find known vulnerabilities in components.
By default, the tool assumes you are attempting to scan a whole directory, but if you provide it with a single .csv or .json file that lists dependencies it will treat it as a bill of materials. You can also specify bill of materials files directly using the --input-file option or scan SBOMs with the instructions below.
To scan a software bill of materials file (SBOM):
cve-bin-tool --sbom <sbom_filetype> --sbom-file <sbom_filename>Valid SBOM types are SPDX, CycloneDX, and SWID. Scanning of product names within an SBOM file is case insensitive.
The SBOM scanning how-to guide provides additional SBOM scanning examples.
As well as scanning SBOMs, CVE Binary Tool can be used to generate an SBOM from a scan as follows:
cve-bin-tool --sbom-type <sbom_type> --sbom-format <sbom-format> --sbom-output <sbom_filename> <other scan options as required>Valid SBOM types are SPDX and CycloneDX.
The generated SBOM will include product name, version and supplier (where available). License information is not provided.
The SBOM generation how-to guide provides additional SBOM generation examples.
As well as scanning VEX, CVE Binary Tool can be used to generate an VEX from a scan as follows:
cve-bin-tool --vex-type <vex_type> --vex-output <vex_filename> <other scan options as required>Valid VEX types are CSAF, CycloneDX and OpenVEX.
The VEX generation how-to guide provides additional VEX generation examples.
The --vex-file option can be used to add extra triage data like remarks, comments etc. while scanning a directory so that output will reflect this triage data and you can save time of re-triaging (Usage: cve-bin-tool --vex-file test.json /path/to/scan).
The supported format is the CycloneDX,CSAF and OpenVEX VEX format which can be generated using the --vex-output option.
Typical usage:
- Generate triage file using
cve-bin-tool /path/to/scan --vex-output triage.json - Edit triage.json with your favourite text editor to provide triage information on the vulnerabilities listed.
- Use this triage file for future scans as follows:
cve-bin-tool /path/to/scan --vex-file triage.json
For better usage guide refer this link .
It should be possible to share triage data across different runs of cve-bin-tool or with other tools that support the CycloneDX VEX, OpenVEX and CSAF format. This would be particularly useful for teams that scan related products or containers, teams that need to use multiple tools for compliance reasons, companies that have a central security policy group that provides guidance on vulnerability triage, and more.
Specifying the --offline option when running a scan ensures that cve-bin-tool doesn't attempt to download the latest database files or to check for a newer version of the tool.
Note that you will need to obtain a copy of the vulnerability data before the tool can run in offline mode. The offline how-to guide contains more information on how to set up your database.
If you want to integrate cve-bin-tool as a part of your github action pipeline, you can use cve-bin-tool's official GitHub Action. Find more details here. The GitHub Action provide reports on the security tab, which is available to open source projects as well as GitHub customers who have paid for that access.
We also provide an example GitHub action if you wish to use the tool directly. This may be a good choice for teams who want to store reports in an evidence locker or those who don't have access to the GitHub Security tab.
The CVE Binary Tool provides console-based output by default. If you wish to provide another format, you can specify this and a filename on the command line using --format. The valid formats are CSV, JSON, JSON2, console, HTML and PDF. The output filename can be specified using the --output-file flag.
You can also specify multiple output formats by using comma (',') as separator:
cve-bin-tool file -f csv,json,json2,html -o reportNote: You must not use spaces between the commas (',') and the output formats.
The reported vulnerabilities can additionally be reported in the
Vulnerability Exploitability eXchange (VEX) format by specifying --vex-output with type defined using --vex-type command line option.
The generated VEX file can then be used as a --vex-file to support
a triage process.
If you wish to use PDF support, you will need to install the reportlab
library separately.
If you intend to use PDF support when you install cve-bin-tool you can specify it and report lab will be installed as part of the cve-bin-tool install:
pip install cve-bin-tool[PDF]If you've already installed cve-bin-tool you can add reportlab after the fact using pip:
pip install --upgrade reportlabNote that reportlab was taken out of the default cve-bin-tool install because it has a known CVE associated with it (CVE-2020-28463). The cve-bin-tool code uses the recommended mitigations to limit which resources added to PDFs, as well as additional input validation. This is a bit of a strange CVE because it describes core functionality of PDFs: external items, such as images, can be embedded in them, and thus anyone viewing a PDF could load an external image (similar to how viewing a web page can trigger external loads). There's no inherent "fix" for that, only mitigations where users of the library must ensure only expected items are added to PDFs at the time of generation.
Since users may not want to have software installed with an open, unfixable CVE associated with it, we've opted to make PDF support only available to users who have installed the library themselves. Once the library is installed, the PDF report option will function.
You can use --config option to provide configuration file for the tool. You can still override options specified in config file with command line arguments. See our sample config files in the
test/config
CVE Binary tool attempts to do auto-detection of components using binary checkers, supported language component lists, and file extraction methods. The supported tools for auto-detection are listed below.
The following checkers are available for finding components in binary files:
| Available checkers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| accountsservice | acpid | apache_http_server | apcupsd | apparmor | asn1c | assimp |
| asterisk | atftp | avahi | axel | bash | bind | binutils |
| bird | bison | bluez | boinc | botan | bro | bubblewrap |
| busybox | bwm_ng | bzip2 | c_ares | capnproto | ceph | chess |
| chrony | civetweb | clamav | collectd | commons_compress | connman | coreutils |
| cpio | cronie | cryptsetup | cups | curl | cvs | darkhttpd |
| dav1d | davfs2 | dbus | debianutils | dhclient | dhcpcd | dhcpd |
| dmidecode | dnsmasq | docker | domoticz | dosfstools | dotnet | dovecot |
| doxygen | dpkg | dropbear | e2fsprogs | ed | elfutils | emacs |
| enscript | exfatprogs | exim | exiv2 | f2fs_tools | faad2 | fastd |
| ffmpeg | file | firefox | flac | fluidsynth | freeradius | freerdp |
| fribidi | frr | gawk | gcc | gdal | gdb | gdk_pixbuf |
| ghostscript | gimp | git | glib | glibc | gmp | gnomeshell |
| gnupg | gnutls | go | gpgme | gpsd | graphicsmagick | grep |
| grub2 | gstreamer | gupnp | gvfs | gzip | haproxy | harfbuzz |
| haserl | hdf5 | heimdal | hostapd | hunspell | hwloc | i2pd |
| icecast | icu | iperf3 | ipmitool | ipsec_tools | iptables | irssi |
| iucode_tool | iwd | jack2 | jacksondatabind | janus | jasper | jhead |
| jq | json_c | kbd | keepalived | kerberos | kexectools | kodi |
| kubernetes | ldns | lftp | libarchive | libass | libbpg | libcoap |
| libconfuse | libcurl | libdb | libde265 | libebml | libevent | libexpat |
| libgcrypt | libgd | libgit2 | libheif | libical | libidn2 | libinput |
| libjpeg | libjpeg_turbo | libksba | liblas | libmatroska | libmemcached | libmicrohttpd |
| libmodbus | libnss | libopenmpt | libpcap | libraw | librsvg | librsync |
| libsamplerate | libseccomp | libsndfile | libsolv | libsoup | libsrtp | libssh |
| libssh2 | libtasn1 | libtiff | libtomcrypt | libupnp | libuv | libvips |
| libvirt | libvncserver | libvorbis | libvpx | libxslt | libyaml | lighttpd |
| linux_kernel | lldpd | logrotate | lrzip | lua | luajit | lxc |
| lynx | lz4 | mailx | mariadb | mbedtls | mdadm | memcached |
| micropython | minetest | mini_httpd | minicom | minidlna | miniupnpc | miniupnpd |
| moby | modsecurity | monit | mosquitto | motion | mp4v2 | mpg123 |
| mpv | msmtp | mtr | mupdf | mutt | mysql | nano |
| nasm | nbd | ncurses | neon | nessus | netatalk | netdata |
| netkit_ftp | netpbm | nettle | nghttp2 | nginx | ngircd | nmap |
| node | ntfs_3g | ntp | ntpsec | open_iscsi | open_vm_tools | openafs |
| opencv | openjpeg | openldap | opensc | openssh | openssl | openswan |
| openvpn | p7zip | pango | patch | pcre | pcre2 | pcsc_lite |
| perl | php | picocom | pigz | pixman | png | polarssl_fedora |
| poppler | postgresql | ppp | privoxy | procps_ng | proftpd | protobuf_c |
| pspp | pure_ftpd | putty | python | qemu | qpdf | qt |
| quagga | radare2 | radvd | raptor | rauc | rdesktop | readline |
| rpm | rsync | rsyslog | rtl_433 | rtmpdump | runc | rust |
| samba | sane_backends | sdl | seahorse | shadowsocks_libev | snapd | sngrep |
| snort | socat | sofia_sip | speex | spice | sqlite | squashfs |
| squid | sslh | stellarium | strongswan | stunnel | subversion | sudo |
| suricata | sylpheed | syslogng | sysstat | systemd | tar | tcpdump |
| tcpreplay | terminology | tesseract | thrift | thttpd | thunderbird | timescaledb |
| tinyproxy | tor | tpm2_tss | traceroute | transmission | trousers | ttyd |
| twonky_server | u_boot | udisks | unbound | unixodbc | upx | util_linux |
| varnish | vim | vlc | vorbis_tools | vsftpd | webkitgtk | wget |
| wireshark | wolfssl | wpa_supplicant | xerces | xml2 | xscreensaver | xwayland |
| yasm | zabbix | zchunk | zeek | zlib | znc | zsh |
| zstandard |
All the checkers can be found in the checkers directory, as can the instructions on how to add a new checker. Support for new checkers can be requested via GitHub issues.
A number of checkers are available for finding vulnerable components in specific language packages.
| Language | Files supported |
|---|---|
| Dart | pubspec.lock |
| Go | Go.mod |
| Java | pom.xml; JAR, WAR and EAR archives |
| JavaScript | package-lock.json, yarn.lock |
| Rust | Cargo.lock |
| Ruby | Gemfile.lock |
| R | renv.lock |
| Swift | Package.resolved |
| Python | requirements.txt, PKG-INFO, METADATA; .whl and .egg files |
| Perl | cpanfile |
More information on language-specific checkers can be found in the CVE Binary Tool manual.
The following archive formats are currently supported by the auto-extractor:
| Archive Format | File Extension |
|---|---|
| zip | .zip, .exe, .jar, .msi, .egg, .whl, .war, .ear |
| tar | .tar, .tgz, .tar.gz, .tar.xz, .tar.bz2 |
| deb | .deb, .ipk |
| rpm | .rpm |
| cab | .cab |
| apk | .apk |
| zst | .zst |
| pkg | .pkg |
To use the auto-extractor, you may need the following utilities depending on the type of supported archive formats you need to extract.
The utilities below are required to run the full test suite on Linux:
filestringstarunziprpm2cpiocpioarcabextract
Most of these are installed by default on many Linux systems, but cabextract and
rpm2cpio in particular might need to be installed.
On windows systems, you may need:
ar7zExpandpdftotext
Windows has Expand installed by default, but ar and 7z might need to be installed.
If you want to run our test-suite or scan a zstd compressed file, We recommend installing this 7-zip-zstd
fork of 7zip. We are currently using 7z for extracting jar, apk, msi, exe and rpm files.
To install ar you can install MinGW (which has binutils as a part of it) from here and run the downloaded .exe file.
If you get an error about building libraries when you try to install from pip, you may need to install the Windows build tools. The Windows build tools are available for free from https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/visual-cpp-build-tools/
If you get an error while installing brotlipy on Windows, installing the compiler above should fix it.
pdftotext is required for running tests. (users of cve-bin-tool may not need it, developers likely will.) The best approach to install it on Windows involves using conda (click here for further instructions).
You can check our CI configuration to see what versions of python we're explicitly testing.
This scanner does not attempt to exploit issues or examine the code in greater detail; it only looks for library signatures and version numbers. As such, it cannot tell if someone has backported fixes to a vulnerable version, and it will not work if library or version information was intentionally obfuscated.
This tool is meant to be used as a quick-to-run, easily-automatable check in a non-malicious environment so that developers can be made aware of old libraries with security issues that have been compiled into their binaries.
The tool does not guarantee that any vulnerabilities reported are actually present or exploitable, neither is it able to find all present vulnerabilities with a guarantee.
Users can add triage information to reports to mark issues as false positives, indicate that the risk has been mitigated by configuration/usage changes, and so on.
Triage details can be re-used on other projects so, for example, triage on a Linux base image could be applied to multiple containers using that image.
For more information and usage of triage information with the tool kindly have a look here.
If you are using the binary scanner capabilities, be aware that we only have a limited number of binary checkers (see table above) so we can only detect those libraries. Contributions of new checkers are always welcome! You can also use an alternate way to detect components (for example, a bill of materials tool such as tern) and then use the resulting list as input to cve-bin-tool to get a more comprehensive vulnerability list.
The tool uses a vulnerability database in order to detect the present vulnerabilities, in case the database is not frequently updated (specially if the tool is used in offline mode), the tool would be unable to detect any newly discovered vulnerabilities. Hence it is highly advised to keep the database updated.
The tool does not guarantee that all vulnerabilities are reported as the tool only has access to a limited number of publicly available vulnerability databases. Contributions to introduce new sources of data to the tool are always welcome.
Whilst some validation checks are performed on the data within the vulnerability database, the tool is unable to assert the quality of the data or correct any discrepancies if the data is incomplete or inconsistent. This may result, for example, in some vulnerability reports where the severity is reported as UNKNOWN.
Bugs and feature requests can be made via GitHub issues. Be aware that these issues are not private, so take care when providing output to make sure you are not disclosing security issues in other products.
Pull requests are also welcome via git.
- New contributors should read the contributor guide to get started.
- Folk who already have experience contributing to open source projects may not need the full guide but should still use the pull request checklist to make things easy for everyone.
CVE Binary Tool contributors are asked to adhere to the Python Community Code of Conduct. Please contact Terri if you have concerns or questions relating to this code of conduct.
Security issues with the tool itself can be reported to Intel's security incident response team via https://intel.com/security.
If in the course of using this tool you discover a security issue with someone else's code, please disclose responsibly to the appropriate party.
Usage:
cve-bin-tool <directory/file to scan>
options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -e EXCLUDE, --exclude EXCLUDE Comma separated Exclude directory path -V, --version show program's version number and exit --disable-version-check skips checking for a new version --disable-validation-check skips checking xml files against schema --offline operate in offline mode --detailed add CVE description in csv or json report (no effect on console, html or pdf) CVE Data Download: Arguments related to data sources and Cache Configuration -n {api,api2,json,json-mirror,json-nvd}, --nvd {api,api2,json,json-mirror,json-nvd} choose method for getting CVE lists from NVD -u {now,daily,never,latest}, --update {now,daily,never,latest} update schedule for data sources and exploits database (default: daily) --nvd-api-key NVD_API_KEY Specify NVD API key (used to improve NVD rate limit). Set to `no` to ignore any keys in the environment. -d DISABLE_DATA_SOURCE, --disable-data-source DISABLE_DATA_SOURCE comma-separated list of data sources (CURL, EPSS, GAD, NVD, OSV, PURL2CPE, REDHAT, RSD) to disable (default: NONE) --use-mirror USE_MIRROR use an mirror to update the database Input: directory directory to scan -i INPUT_FILE, --input-file INPUT_FILE provide input filename -C CONFIG, --config CONFIG provide config file -L PACKAGE_LIST, --package-list PACKAGE_LIST provide package list --sbom {spdx,cyclonedx,swid} specify type of software bill of materials (sbom) (default: spdx) --sbom-file SBOM_FILE provide sbom filename --vex-file VEX_FILE provide vulnerability exploitability exchange (vex) filename for triage processing Output: -q, --quiet suppress output -l {debug,info,warning,error,critical}, --log {debug,info,warning,error,critical} log level (default: info) -o OUTPUT_FILE, --output-file OUTPUT_FILE provide output filename (default: output to stdout) --html-theme HTML_THEME provide custom theme directory for HTML Report -f {csv,json,json2,console,html,pdf}, --format {csv,json,json2,console,html,pdf} update output format (default: console) specify multiple output formats by using comma (',') as a separator note: don't use spaces between comma (',') and the output formats. --generate-config {yaml,toml,yaml,toml,toml,yaml} generate config file for cve bin tool in toml and yaml formats. -c CVSS, --cvss CVSS minimum CVSS score (as integer in range 0 to 10) to report (default: 0) -S {low,medium,high,critical}, --severity {low,medium,high,critical} minimum CVE severity to report (default: low) --metrics check for metrics (e.g., EPSS) from found cves --epss-percentile EPSS_PERCENTILE minimum epss percentile of CVE range between 0 to 100 to report. Automatically enables `--metrics` --epss-probability EPSS_PROBABILITY minimum epss probability of CVE range between 0 to 100 to report. Automatically enables `--metrics` --no-0-cve-report only produce report when CVEs are found -A [-], --available-fix [-] Lists available fixes of the package from Linux distribution -b [-], --backport-fix [-] Lists backported fixes if available from Linux distribution --affected-versions Lists versions of product affected by a given CVE (to facilitate upgrades) --sbom-output SBOM_OUTPUT provide software bill of materials (sbom) filename to generate --sbom-type {spdx,cyclonedx} specify type of software bill of materials (sbom) to generate (default: spdx) --sbom-format {tag,json,yaml} specify format of software bill of materials (sbom) to generate (default: tag) Vex Output: Arguments related to Vex output document. --vex-ouptput VEX_OUTPUT Provide vulnerability exploitability exchange (vex) filename to generate --vex-type {cyclonedx, csaf, openvex} specify type of vulnerability exploitability exchange (vex) to generate (default: cyclonedx) --product PRODUCT Product Name --release RELEASE Release Version --vendor VENDOR Vendor/Supplier of Product -rr REVISION_REASON, --revision-reason REVISION_REASON a reason for the update to the vex document should be specified in double quotes --filter-triage Filter cves based on triage data from Vex file Merge Report: Arguments related to Intermediate and Merged Reports -a [APPEND], --append [APPEND] save output as intermediate report in json format -t TAG, --tag TAG add a unique tag to differentiate between multiple intermediate reports -m MERGE, --merge MERGE comma separated intermediate reports path for merging -F FILTER, --filter FILTER comma separated tag string for filtering intermediate reports Checkers: -s SKIPS, --skips SKIPS comma-separated list of checkers to disable -r RUNS, --runs RUNS comma-separated list of checkers to enable Database Management: --import-json IMPORT_JSON import database from json files chopped by years --ignore-sig do not verify PGP signature while importing json data --log-signature-error when the signature doesn't match log the error only instead of halting (UNSAFE) --verify PGP_PUBKEY_PATH verify PGP sign while importing json files --export-json EXPORT_JSON export database as json files chopped by years --pgp-sign PGP_PRIVATE_KEY_PATH sign exported json files with PGP --passphrase PASSPHRASE required passphrase for signing with PGP --export EXPORT export database filename --import IMPORT import database filename Exploits: --exploits check for exploits from found cves Deprecated: --triage-input-file TRIAGE_INPUT_FILE replaced by --vex-file -x, --extract autoextract compressed files --report Produces a report even if there are no CVE for the respective output format
For further information about all of these options, please see the CVE Binary Tool user manual.