This is a Pytorch implementation of TriAAN-VC: Triple Adaptive Attention Normalization for any-to-any Voice Conversion. TriAAN-VC is a deep learning model for any-to-any voice conversion. TriAAN-VC can maintain the linguistic contents of source speech and represent target characteristics, unlike previous methods. Experimental results on the VCTK dataset suggest that TriAAN-VC achieves state-of-the-art performance.
We recommend you visit our demo site.
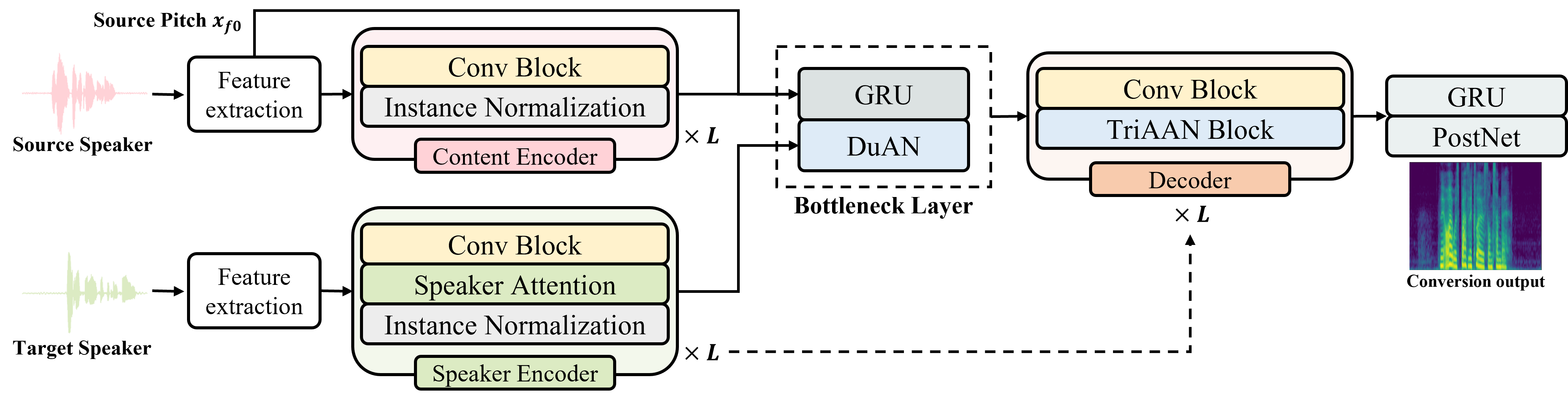
The overall architecture of TriAAN-VC is as below:
The OS, Python, and PyTorch version are as below (You can also use other versions.):
- Windows
- Linux
- python == 3.8
- pytorch == 1.9.1
- torchaudio == 0.9.1
You can install requirements through git and requirements.txt except for pytorch and torchaudio.
git clone https://github.com/winddori2002/TriAAN-VC.git
cd TriAAN-VC
pip install -r requirements.txtWe use the VCTK dataset consisting of 110 speakers with 400 utterances per speaker.
- The dataset can be downloaded here.
- We divide the dataset depending on seen-to-seen and unseen-to-unseen scenarios for evaluation.
We use the pre-trained ParallelWaveGAN as vocoder and CPC extractor as feature extractor. You can use the pre-trained weights in this repository. The vocoder is trained on the VCTK dataset and CPC extractor is trained on the LibriSpeech dataset.
- This repository provides pre-trained ParallelWaveGAN provided by here and CPC extractor provided by here.
- Or you can train ParallelWaveGAN and CPC.
The preprocess stages contain dataset split, feature extraction, making data paths, and eval pairs.
The steps are for VCTK dataset and if you want to use other dataset, you need to modify the details.
- To split dataset and get mel-spectrograms, lf0, and metadata, run the following code and modify the directories in the
./config/preprocess.yaml.
python preprocess.py
- To get CPC features and represent the paths on the metadata, run the following code. (You need pre-trained weights for CPC)
python preprocess_cpc.py
- To get evaluation pairs for conversion, run the following code.
python generate_eval_pair.py
The dataset split and eval pairs are for evaluation and investigation, they are not actually necessary to train models.
You can train TriAAN-VC by running the following code.
If you want to edit model settings, you can run python main.py train with other arguments.
In config/base.yaml, you can find other arguments, such as batch size, epoch, and so on.
python main.py train
Model arguments:
encoder:
c_in: 256 (cpc:256, mel:80)
c_h: 512
c_out: 4
num_layer: 6
decoder:
c_in: 4
c_h: 512
c_out: 80
num_layer: 6
Train arguments:
epoch: 500
batch_size: 64
siam: True (if not, siamese path is excluded)
cpc: True (if not, TriAAN-VC uses mel inputs)
The logs are uploaded on neptune.ai
python main.py train --logging True
Logging arguments:
--logging : True/False
After training, you can evaluate the model in terms of lingustic content (WER and CER) and target characteristic (SV).
You need to keep the model arguments in the training phase. The code only supports the version in which the number of target utterances is 1.
python main.py test
evaluation arguments:
--checkpoint: Checkpoint path
Or, you can use the below code for testing with multi-target utterances.
python test.py --n_uttr 1 --eval True
evaluation arguments:
--eval: Option for evaluation
--n_uttr: Number of target utterances
--checkpoint: Checkpoint path
The pretrained weights of TriAAN-VC is uploaded on the github release here.
We provide two versions of models depending on input types (mel, cpc).
For custom conversion, you can run the code with convert.py.
The codes include data processing, predicting, and vocoding.
python convert.py
Conversion arguments:
--src_name: Sample source names
--trg_name: Sample target names
--checkpoint: Checkpoint path
You can find converted examples in ./samples or please visit our demo site.
The experimental results are from the provided pre-trained weights, and the results can be slightly different from the paper. "VCTK Split" indicates the pre-trained weight with dataset split as in the paper.
Below, the results are summarized with the "TriAAN-VC-Split". Each score is the average of seen-to-seen and unseen-to-unseen scenarios.
| Model | Pre-trained Ver. | # uttr | WER AVG (%) | CER AVG (%) | SV AVG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TriAAN-VC-Mel | VCTK Split | 1 | 27.61 | 14.78 | 89.42 |
| TriAAN-VC-Mel | VCTK Split | 3 | 22.86 | 12.15 | 95.92 |
| TriAAN-VC-CPC | VCTK Split | 1 | 21.50 | 11.24 | 92.33 |
| TriAAN-VC-CPC | VCTK Split | 3 | 17.42 | 8.86 | 97.75 |
@article{park2023triaan,
title={TriAAN-VC: Triple Adaptive Attention Normalization for Any-to-Any Voice Conversion},
author={Park, Hyun Joon and Yang, Seok Woo and Kim, Jin Sob and Shin, Wooseok and Han, Sung Won},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09057},
year={2023}
}
This repository is released under the MIT license. We adapted CPC codes and weights from facebookresearch/CPC_audio, released under the MIT license. We used vocoder codes from kan-bayashi/ParallelWaveGAN, released under the MIT license. For the pre-trained vocoder, we used the weights from Wendison/VQMIVC which is released under the MIT license. We also modified preprocess codes from Wendison/VQMIVC.