Scramb.py is a region based JPEG Image Scrambler and Descrambler written in Python for End-to-End-Encrypted (E2EE) Image distribution through unaware channels.
New: Cloak mode! Try it out!
New: Scramp.py Studio - create masks with a GUI!
Start now:
How it works:
Upcoming Features:
Examples:
- Offend the easily offended less: Upload pictures to sites like Twitter, Facebook, DeviantArt etc. (esp. Social Media) that normally trigger people to report these despite being okay and according to TOS of the site.
- Upload a pic as a teaser but give away the password only to a small section of people
- Have a gallery with images showing no sign of a second meaning and distribute the patch images separatly.
- Use as End-to-End-Encryption E2EE method for websites, messaging systems, chats, email, etc.
- Image Hosts / Websites / Chat & Messaging services are left unaware of image content
- Prevent and circumvent automated scanning / image hashing / photo hashing and machine learning / AI recognition of images. Scramb.py helps bringing back the effort of scanning and analysing images to a manual and thus expensive, labor intensive level. It thus helps to prevent mass surveillance. Scramb.py builds another layer of encryption if E2EE of messaging services should be crippled or broken by new laws.
- In comparison to encryption on binary level (ZIP with Password, VeraCrypt Container, PGP), Scramb.py retains a JPEG / an image that can be uploaded to a lot of websites and messaging platforms. Binary encrypted content cannot be uploaded there.
- Scramb.py can scramble images regions. So you can e.g. scramble only the face of a person.
- All you need to descramble the image is encoded in a data „snake“ around the image. The scrambled image is thus a bit wider as the original.
- You can select different scramble modes.
- When you slightly scramble a region, a thumbnail of the image can still be recognized.
- If you use the ultra scrambler, you cannot guess the content.
- You can set a password
- You can scramble and descramble images using GnuPG PKI public key infrastructure
- You can include short text messages that will show up upon descramble
- Easy to use: Windows Drag & Drop descramble
- Survives multiple re-encodings of an image down to JPEG quality around 30 something, when the image gets ugly and blocky still chances that they decode
- You can create patch images to separate transported images from their recreation metadata
- Does not depend on any binary meta data within the JPEG file (EXIF, XMP, IPTC), as these are normally completly stripped by all major social media sites.
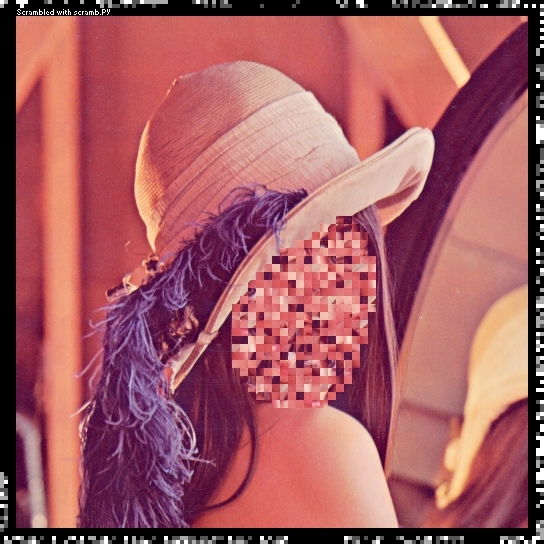
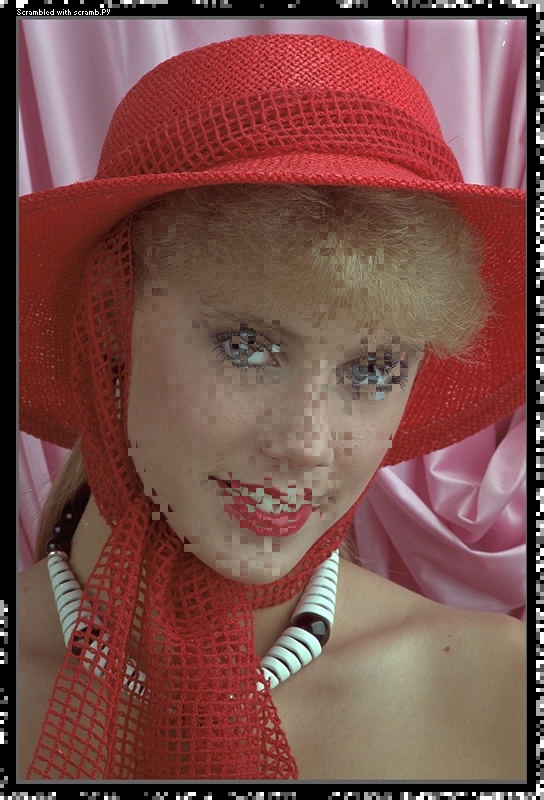
In this example, only Lenna's face was scrambled and the scrambled image is password protected. You can actually try the example images in this repo with scramb.py yourself! Also, people get offended when Lenna is used (although, now we also have Fabio, which I use as a Black/White Test Image!... so, Lenna is scrambled here in this repo :-)
You can host your scrambled images out of sight, out of censorship and out of reporting systems and automated scanning on different online image services!
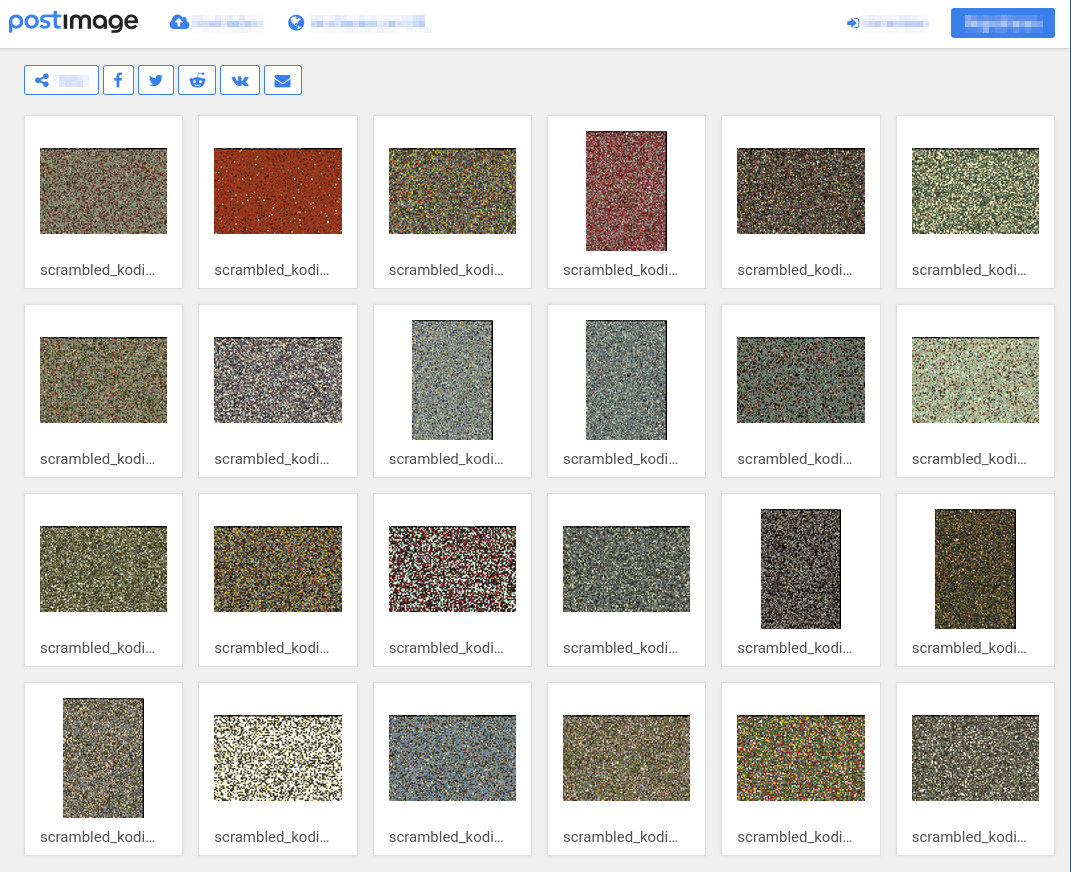
As an example, some images are hosted on PostImages Image Hosting Service.
Head over to this gallery https://postimg.cc/gallery/bh5Zf9J to see all of the Kodak Example Images scrambled with scramb.py!
This is a patch image. Scramb.py can create these to separate transported images from their recreation metadata. The patch image is then used to "patch in" the scrambled image blocks next to the thumbnail you see here.
As long as it is hacking-fun to circumvent scanning and reporting, you are invited to try out scramb.py!
BUT
Scramb.py should not be used in real-world situations that require encryption and your life or personal wealth rely on it. It is only intended for demonstration and experimentation. If you need strong message and image encryption, do not use Scramb.py! Use a well-regarded, open-source OpenPGP implementation such as GnuPG or encryption systems like VeraCrypt.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
scramb.py is written and runs in Python, so you have to install the Python interpreter and one Python module (Pillow).
- Install Python 3 for Windows https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
- Download scramb.py Script, it should look like this:
-
(Optional) Download scrambpystudio.py, if you want to use a GUI for scramb.py. Place scrambpystudio.py in the same directory as scramb.py.
-
Install Pillow module, you can do this manually or let the scramb.py Script do this:
- via Script: Run scramb.py with a double click and if prompted, press
yto install Pillow - manually locate
pip.exein your Python installation folder and runpip.exe install Pillowin a commandline
- via Script: Run scramb.py with a double click and if prompted, press
- Install Python 3 if not already present (Ubuntu, Raspberry OS etc should have Python 3 installed already).
- Download scramb.py Script
- (Optional) Download scrambpystudio.py, if you want to use a GUI for scramb.py. Place scrambpystudio.py in the same directory as scramb.py.
- If not present, install Pillow with
pip install Pillow - Make the script executable
chmod +x scramb.py
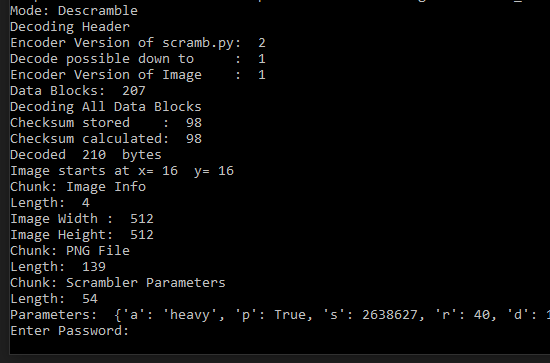
To descramble an image, download it in full resolution and drag & drop it onto the script.
- If the image is password protected, the console window will stay open and ask you for a password:
- At this point you cannot descramble patch-mode images with drag & drop (the one where you input 2 images). You then have to use the commandline.
To descramble an image, download it in full resolution and use its path as one of the arguments
python.exe scramb.py <inputfile.jpg>
python.exe scramb.py -i <inputfile.jpg> -o <outputfile.jpg>
To descramble an image, download it in full resolution and use its path as one of the arguments
./scramb.py <inputfile.jpg>
./scramb.py -i <inputfile.jpg> -o <outputfile.jpg>
python.exe scramb.py -i <patchfile> -d <disguisefile> -o <outputfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
./scramb.py -i <patchfile> -d <disguisefile> -o <outputfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
Note that Scramb.py Studio is in its first release and pretty much featureless. If you want more than basic scramble, you as of now have to use the commandline.
- Start scrambpystudio.py with double click or via commandline.
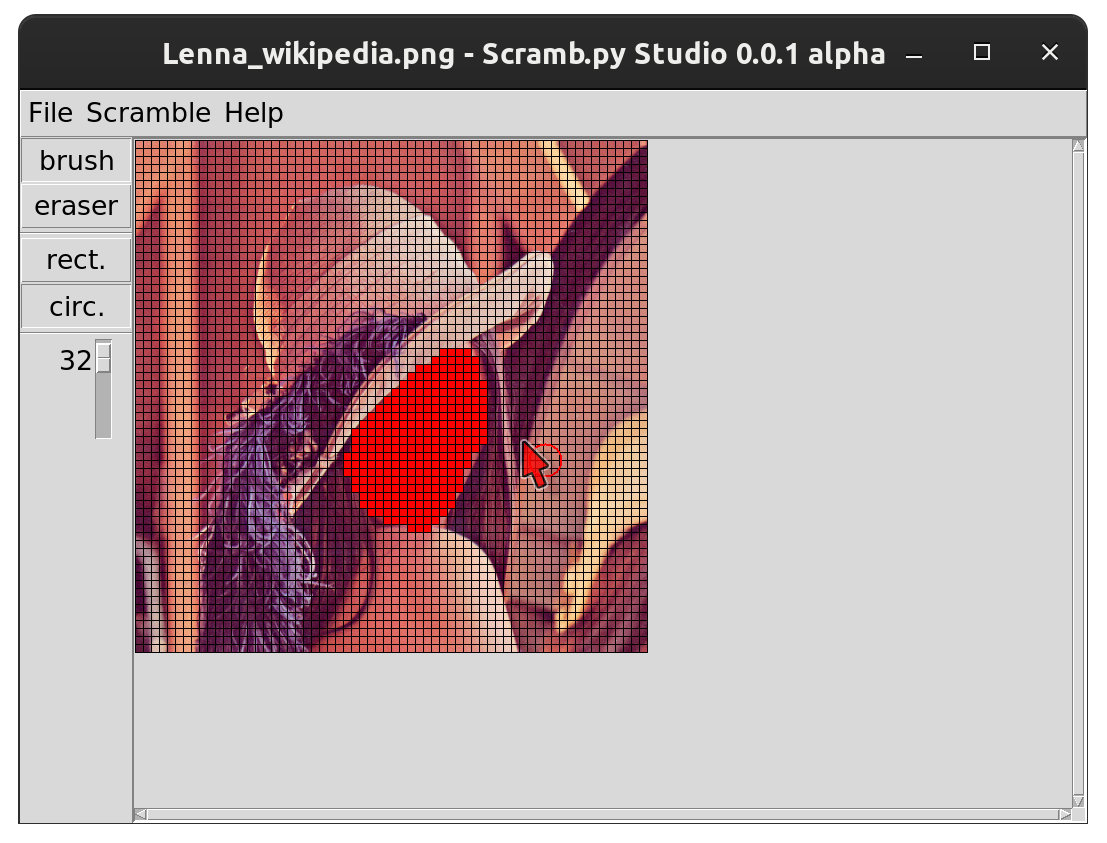
- Open the image to be scrambled
- Draw masked area. It will appear red. You can change brush type (circle / rectangle) and its size. Left mouse button draws, right mouse button erases but you can switch that around with the brush and eraser buttons.
- Select Scramble/Export scrambled image...
Two Images will be saved in the same directory as the loaded image :
- ORIGINALFILENAME_scst_mask.png
- ORIGINALFILENAME_scst_scrambled.jpg
As of now you cannot change these filenames nor is any error given if somehow something (within scramb.py) fails.
The image is scrambled using ultra scrambler and the -2 option. You again cannot change that as of now.
python.exe scramb.py -i <inputfile> [-m <mask.png/.jpg>] -o <outputfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
You must use -m and/or -s for scramb.py to detect that you want to scramble.
./scramb.py -i <inputfile> [-m <mask.png/.jpg>] -o <outputfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
You must use -m and/or -s for scramb.py to detect that you want to scramble.
./scramb.py -i <inputfile> [-m <mask.png/.jpg>] -o <outputfile.jpg> -s pki -k <key-id> [OPTIONS]
./scramb.py --export-public-key <key-id> -i <center-image> -o <outputfile.jpg>
Creates a "business card" image that features <center-image> in the middle surrounded by your public key within the data snake.
The public key is exactly the same type as the one you would use for an encrypted email correspondance.
./scramb.py <publicKeyImageFile.jpg>
A menu will ask you what you want to do with the public key (import in keyring, export into .asc file).
python.exe scramb.py -i <inputfile> -d <disguisefile> -m <maskfile> -o <patchfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
./scramb.py -i <inputfile> -d <disguisefile> -m <maskfile> -o <patchfile.jpg> [OPTIONS]
Note that Scramb.py Studio is in its first release and pretty much featureless.
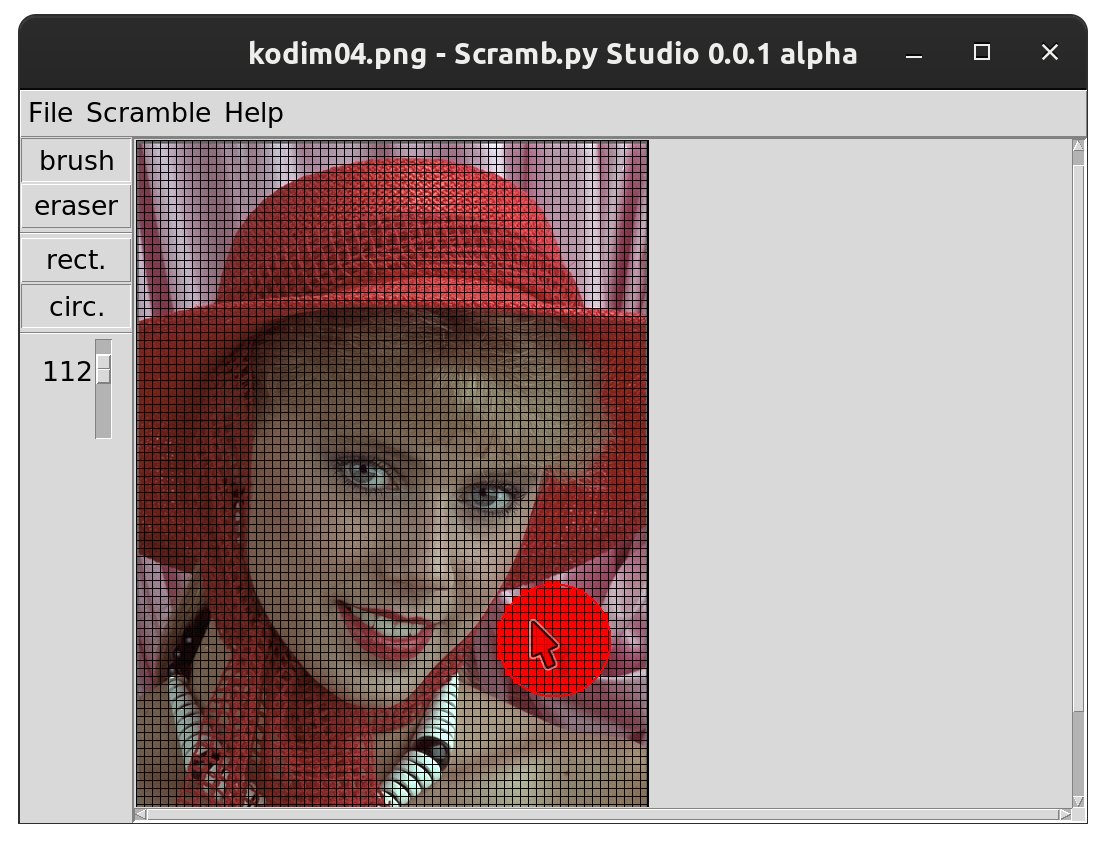
- Start scrambpystudio.py with double click or via commandline.
- Open the image to be scrambled
- (Optional) Open an existing mask png image
- Draw masked area. It will appear red. You can change brush type (circle / rectangle) and its size. Left mouse button draws, right mouse button erases but you can switch that around with the brush and eraser buttons.
- Select File/Save mask image as... to save the PNG mask file
scramb.py -r <imagefile1.jpg> <imagefile2.jpg>
Specific parameter for the chosen scrambler, see table below.
The scrambler to be used
| scrambler | x | y | z | What it does |
|---|---|---|---|---|
matrix |
seed | turn percentage (10=10%, 100=100%, 170=170%) | - | turns a group of 2x2 blocks clockwise. Does not work on lonely pixels. |
medium |
seed | rounds | distance | moves a block a maximum of distance left or right. Runs over all blocks rounds times. |
heavy |
seed | rounds | - | moves every block somewhere else rounds times within a broad neighbourhood |
ultra |
seed | rounds | - | moves every block somewhere else rounds times totally random |
pki |
seed | rounds | - | uses GnuPG public key to scramble. Needs also -k for the key-id. Uses random user input and ultra scrambler |
- matrix rotates 2x2 blocks
- medium & heavy switch two blocks
- ultra & pki copy blocks onto a new surface
-d <disguiseimage.jpg>
With -d scramb.py will take 3 images as input:
- -i original image
- -d disguise image
- -m mask
scramb.py will then generate a patch-image.
Enabled Cloak mode
When scrambling large uniform areas like skin, these areas still have a skin color after scramble. Especially when viewed as a thumbnail or run through automated scanning, these areas may still be recognized as (slightly fuzzy) skin.
Visually (especially as a thumbnail) these images are not that far apart. You still can guess it is naked skin under the scramble.
Cloak mode is ment to lay a "cloak" different colored blocks over the scramble area. It is a distraction feature and not a security feature. When using cloaking, you can change the perception of the overall color of your scrambled area through mixing in different colors. Cloaking works best especially in the perception of the scrambled image's thumbnail (viewed by humans or algorithms).
Now a cloak has been added to the scrambled image.
Several lines of random blocks of pixels taken from the original image are added at the right and bottom side. These duplicated blocks are then also used in scrambling.
These random blocks can be:
- tinted to a specific color
- tinted invers to the original image, so that the scrambled overall image looks 50% grayscale in thumbnails
- replaced by a totally different image alltogether
Works best with ultra scrambler and least with matrix scrambler.
Cannot be used together with -d disguise option.
Subfeatures of cloak mode are:
This mask is used as the source for the randomly copied blocks.
If none is given, the -m mask is used
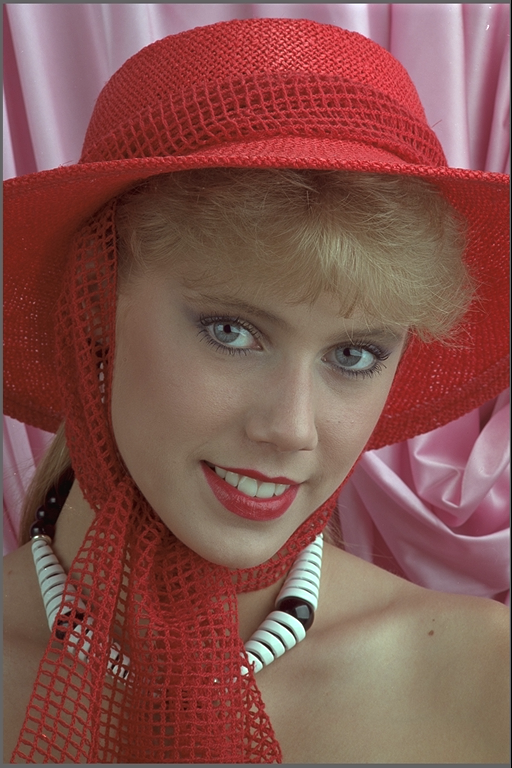
this mask selects only the red hat and scarf for cloaking:
Takes whole -i image as source for random blocks
Inverts the cloak mask (normally used when --cloak-mask is NOT used AND you want to use only blocks OUTSIDE the -m mask (= all blocks, that are not in the area to be scrambled.
CAUTION: This option may look good but makes it super easy to remove all extra blocks used in cloaking the image!
How much percent of the cloak mask blocks should be added to the new lines.
Lines are always fully filled.
default=100
Tints all colors of cloak blocks, with <tint> being:
r,g,ban rgb color value (values=0..255), e.g. for red --cloak-tint=255,0,0rainbowuse random colors
Rainbow works best when used on the whole image:
Inverts all cloak blocks before they are tinted.
This when used with --percent-cloaked=100 results in a 50% grey looking image.
Substitute the random cloak blocks with this image AFTER scrambling. Adjust visibility of this image with --percent-cloaked
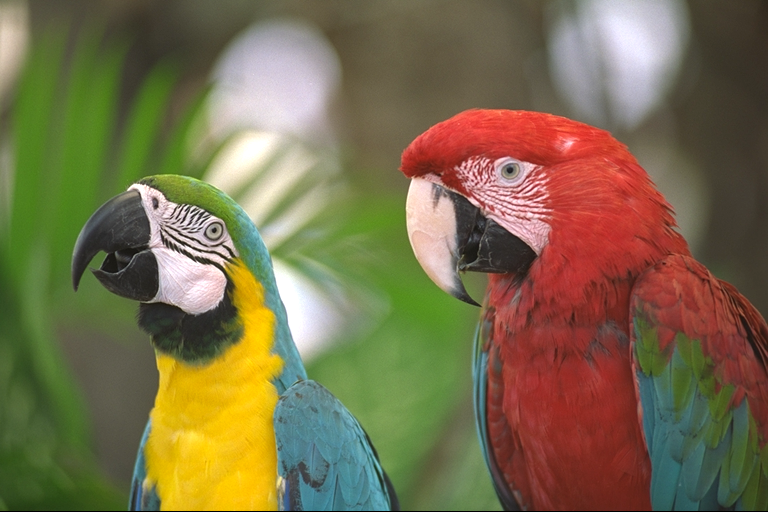
This is still the image of the woman in red, but the image of the parrots has been layed over it as a cloak.
Blowup image by 2x
GnuPG public key-ID within your keyring to scramble with pki scrambler. To descramble this image you need to have the matching private key in your keyring.
--quality=10..100
JPEG Output Quality 0-100, 100=best, default=100
do not include Logo in Image
-t "<Text>"
Embed text to show when descrambling (max. 400 chars)
Do not pause on descramble for displaying text
Also do not pause for user random input when using pki scrambler (not recommended exept testing situations).
Scramble with password (ask for it)
--password=<password>
Scramble with <password>
Caution: it's then in your console history! Use -p instead!
Hide password use from generated image. You must run descrambling with -p or --password option then! Descrambling without these options will otherwise not promt for a password and the descrambled image is still scrambled (in a different way).
Overwrite output file when it exists
Scramb.py was written to showcase how you can use image sharing / posting sites like Twitter, facebook, DeviantArt etc. and not be bothered by their automatic image scanning system. You are also not bothered by people who normally would be offended by your image and report it to the website if they could see it "clearly".
Scramb.py was also written to showcase how to build a new layer of image and data interchange for the situation in which a normally end-to-end encrypted communication channel is broken up by new laws. The European Union is currently (as of June 2022) proposing a new law in which service providers are allowed to break up encryption or scan private communication before it is encrypted under the pretext to countermeasure specific law violations by a minority. This proposal known in the media as "Chatcontrol" does exactly that: It takes away the communication privacy of all European Citizen. Images shared via any online service (which now also includes private chats like WhatsApp or Telegram) are subjected to automated and human scanning.
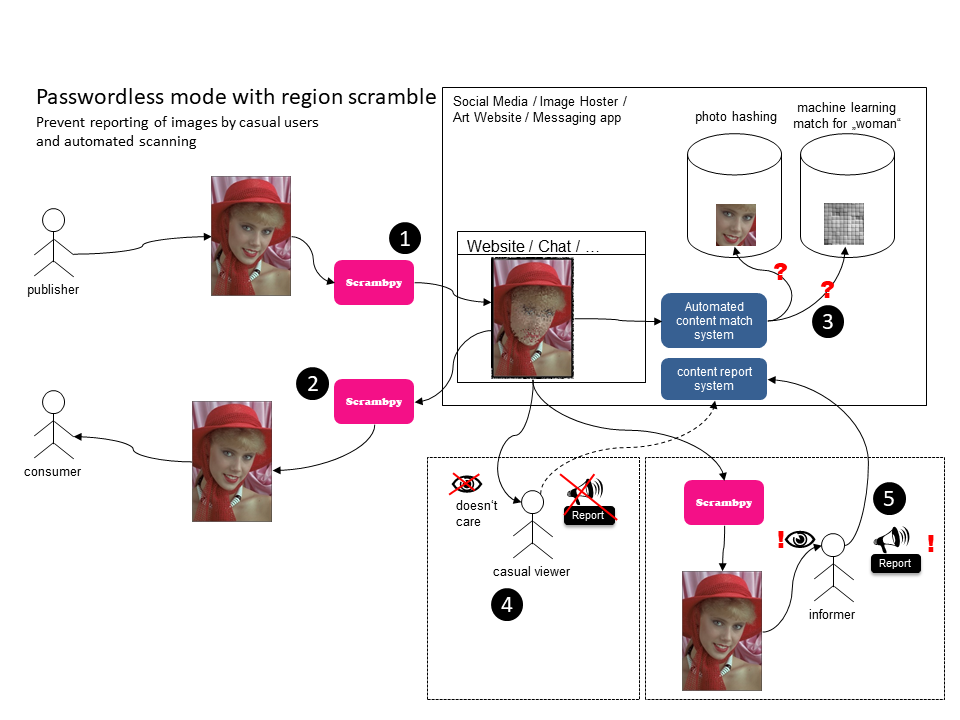
Prevent reporting of images by casual users and automated scanning
-
A publisher wants to distribute an image E2EE and uses scrambpy to regional scramble this image. He uploads the scrambled image to a website
-
A consumer can download this image and descramble it with scrambpy
-
The website uses content match systems to automatically match certain images. Both systems will fail and thus the image is not automatically reported / flagged.
- The photo hashing system fails because the scrambled image creates totally different hashes
- The machine learning system which tries to recognize "a woman" fails for same reason Weak spot: If the content match system uses scrambpy, it can descramble the image and then do hashing and matching
-
A casual viewer scrolls by the image and does not care, thus preventing triggering the user so that he/she reports the image.
-
(Malign Case) An informer can also use scrambpy and now reports the image
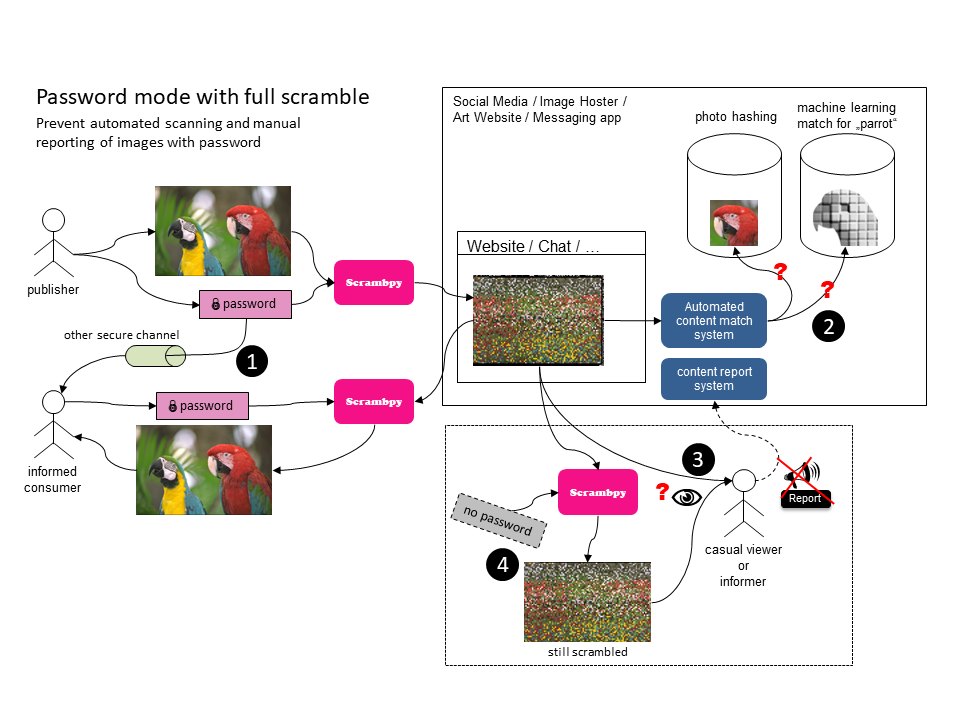
Prevent automated scanning and manual reporting of images with password
-
The publisher scrambles the image with a password and informs the informed consumer about the password through a secure channel. They exchange the image E2EE through a normal website.
-
The website uses content match systems to automatically match certain images. Both systems will fail and thus the image is not automatically reported / flagged. This time, the system will also fail if the system uses scrambpy automatically, because the password is missing.
-
A casual viewer and an informer cannot see the scrambled image.
-
An informer cannot descramble the image without the correct password. He/She then still gets a scrambled image.
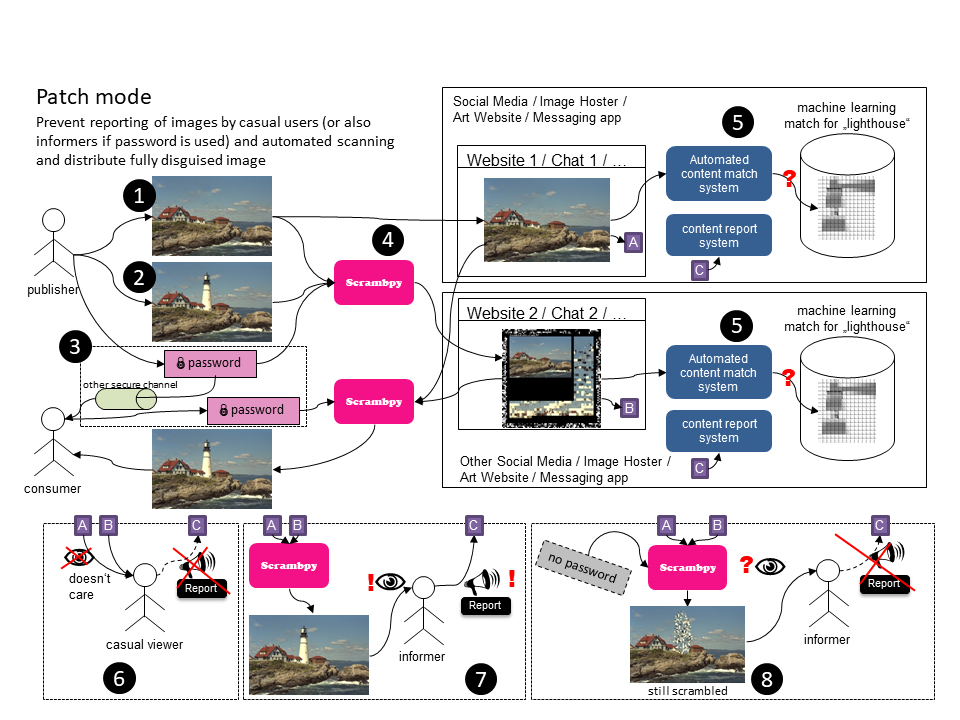
Prevent reporting of images by casual users (or also informers if password is used) and automated scanning and distribute fully disguised image
-
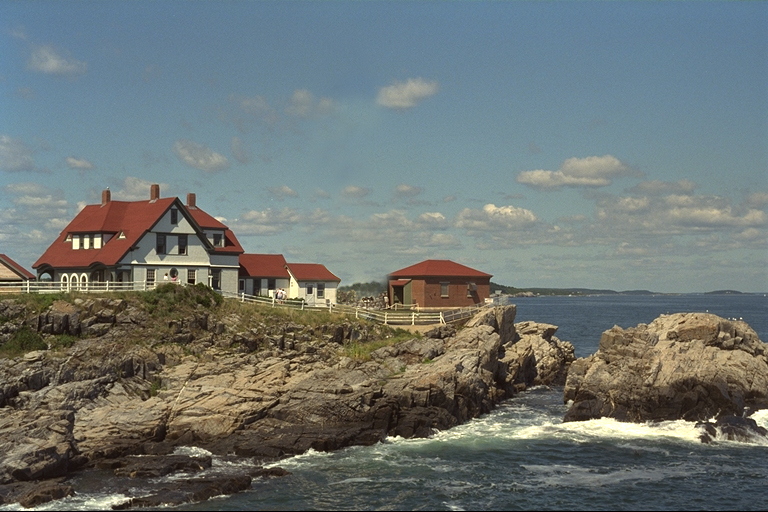
The publisher creates a disguise image without certain content.
-
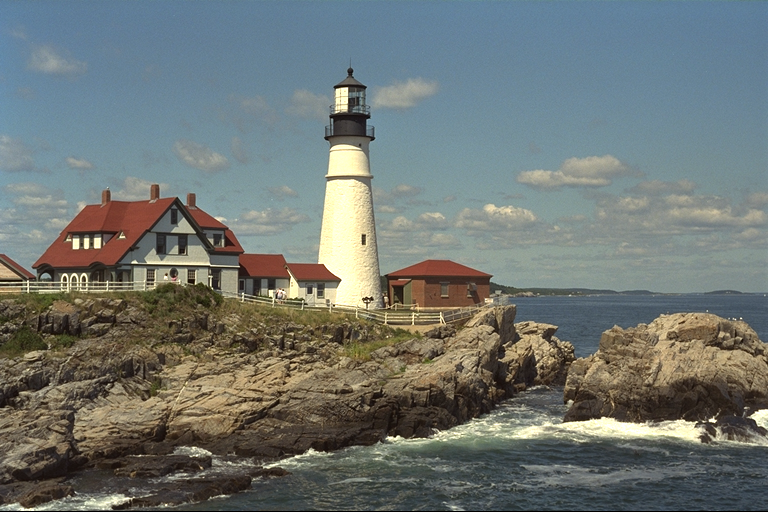
The publisher also creates the hidden image with certain content (a lighthouse in this case).
-
Optional: Publisher and consumer exchage a password via a secure channel
-
The publisher uploads the disguised image in full view and the patch image. He/She may upload both images to different websites.
-
The websites use content match systems to automatically match certain images. Both systems will fail on both websites and thus the image is not automatically reported / flagged.
- The website on top with the disguised image has absolutly no reason to detect anything (100% Save)
- The website on the bottom does not have the full image information to detect anything. There is a weak spot when using the embedded thumbnail and automated scrambpy. If a password is used, this does not work anyway.
-
The casual viewer does not care and thus does not report
-
If no password is used, the informer can collect both images (disguise + patch) and then report the hidden image.
-
If a password is used, the informer cannot descramble the image without the correct password. He/She then still gets the disguise image with scrambled content patched in.
Scramb.py can now use PGP to scramble images with a public key, so that only the person in posession of the private key can descramble the image.
PKI is now included in this version and was not tested under Windows. Help is much appreciated if someone could test it and give hints what to correct (e.g. GPG homedir is a problem under windows).
More information will follow in this whitepaper on scramb.py's PKI usage.
Slight scramble will produce a near identical descrambler image. Scramb.py scrambles 8x8 blocks to best encounter effects of jpeg artifacts. Nevertheless the heavy scrambler will produce a grid like structure in bright (esp. red/blue) regions of the descrambled image. This happens because of color subsampling in JPEG by the factor 2 and in a scrambled image, blocks of brigthness and darkness now lie next to each other when in the original image they do not.
You can circumvent that with the -2 option, blowing up the image by 2x. While descrambling, it will automatically be reduced to the original size.
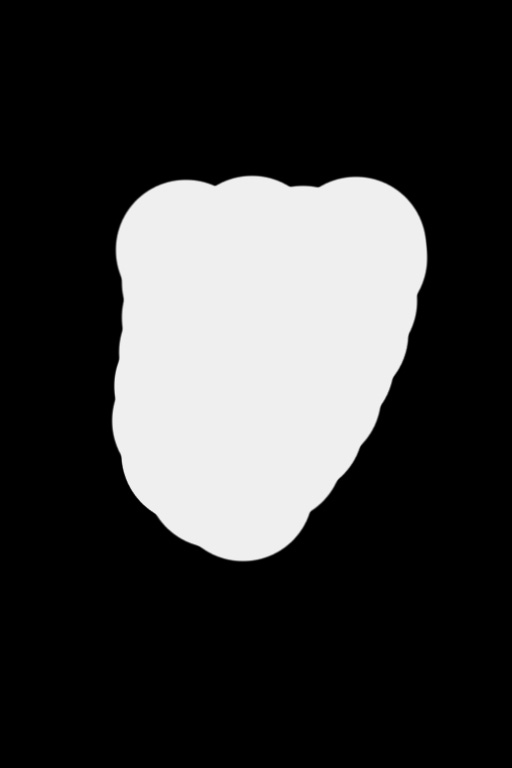
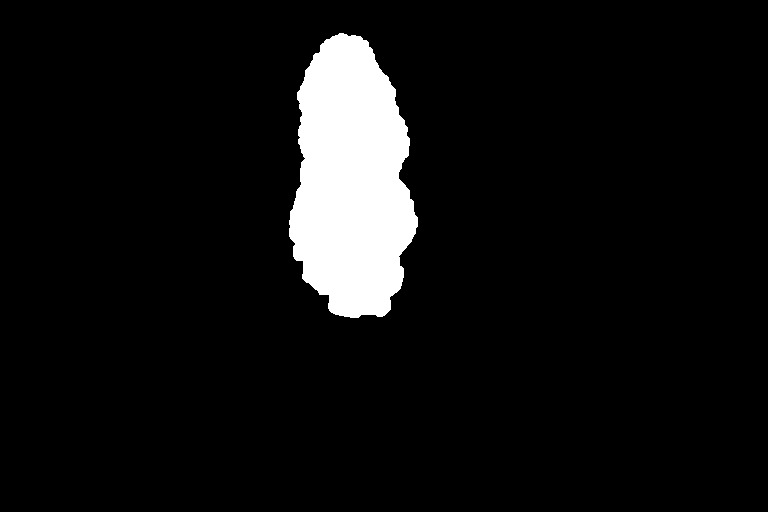
The main advantage of this scrambler in comparison to other image scrambles is that it can scramble only parts of an image. For that you provide the scrambler also a black and white image where you marked the regions you want to scramble in white. You can easily create such an image with Photoshop, GIMP or even Windows Paint. Just be carefull not to overwrite your original image with Paint ;-D
Scramb.py can create a "patch" for an image to hide blocks and corresponding reconstruction data in a second image. This way, a "disguise" image can freely be distributed and later be patched with the patch-image.
In the following example, the lighghouse was edited out with a photo editing software. As a result, we want to distribute the edited version (without the lighthouse) and the patch image, so that Scramb.py users can recreate the original image with the lighthouse.
With parts you want to disguise.
An image where you edited something out or, if e.g. rendered, you changed something.
(No, scramb.py cannot do this for you ;-) it's not an artificial intelligence multitool ;-) you have to use Gimp or Photoshop etc )
Showing what will be switched / what is hidden.
With this patch-image and the disguise image (the one without the lighthouse), scramb.py can recreate the one with the lighthouse.
All of Scramb.py's Scrambling Algorithms use a Seed to generate pseudo random numbers. This is essential so that when descrambling, Scramb.py can create the substitution map that was used for scrambling.
You can set a password which is used to alter the seed of the random number generator. Thus you need the password to retreive the correct seed for descrambling. Providing the wrong password results in a still scrambled image.
Be aware that the password system and the used Random Number Generator are nowhere near security and not tested for that application. Consider the password system to be like a cheap padlock.
Scramb.py scrambles 8x8 Pixel blocks of a JPEG image. Thus, everything within these 8x8 Blocks stays "in clear text". If e.g. the image features a logo / text small as 8 pixels chances are that blocks contain this text in the scrambled version of the image.
You can add a short text to be shown while descramble This text is not password protected
A small logo is added to help people find this descrambler „Scrambled with Scramb.py“.
You can of course switch that off if you wish
Windows use is easy for descramble
(Scramble needs commandline;-)
Code is easy to follow so feel free to check it for backdoors. You can even delete the encoded logo.
- A GUI tool to draw masks and configure scramb.py scrambling (people gave feedback that scramb.py should be easier to use, especially using it without the need for a separate graphic editor like Photoshop)
- Config file for PKI Scrambler
- PKI working under Windows
- JavaScript version for Website and Greasemonkey integration (probably not feasible anymore since scramb.py is too library depened right now)
- 4 or 8 Bytes per Datablock instead of 1 Byte
- ECC Error Correction
View changelog
Sample Images from