Yutao Tang*
,
Yuxiang Guo*
,
Deming Li
,
Cheng Peng
(*Equal contribution)
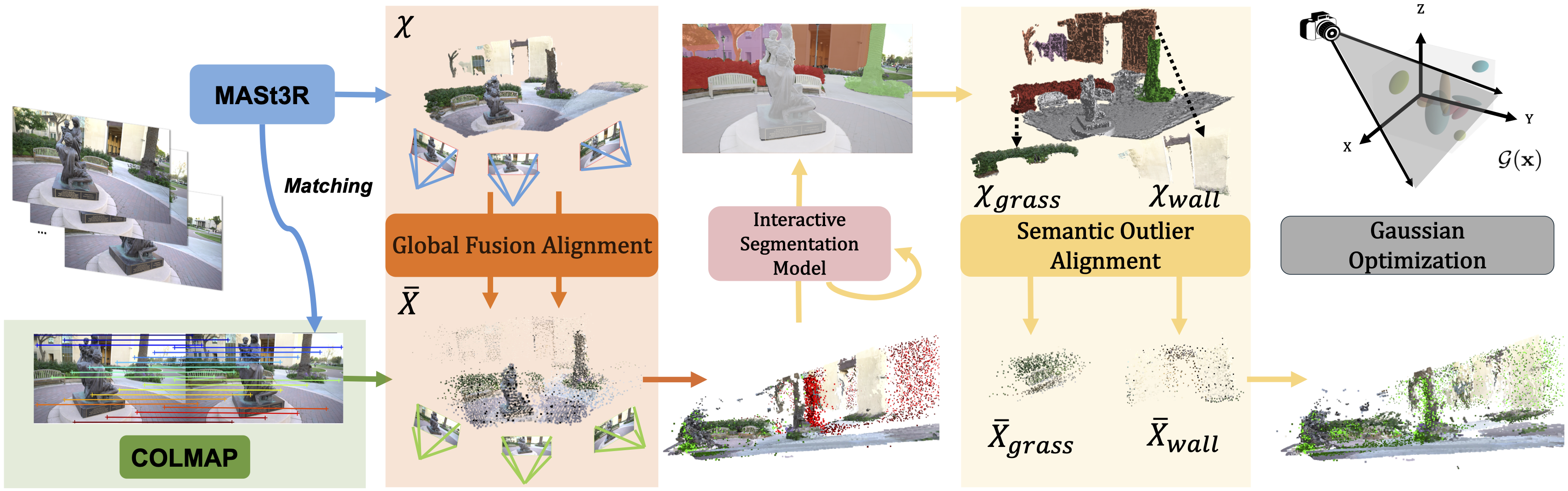 Recent efforts in Gaussian-Splat-based Novel View Synthesis can achieve photorealistic rendering; however, such capability is limited in sparse-view scenarios due to sparse
initialization and over-fitting floaters. Recent progress in
depth estimation and alignment can provide dense point
cloud with few views; however, the resulting pose accuracy
is suboptimal. In this work, we present SPARS3R, which
combines the advantages of accurate pose estimation from
Structure-from-Motion and dense point cloud from depth
estimation. To this end, SPARS3R first performs a Global
Fusion Alignment process that maps a prior dense point
cloud to a sparse point cloud from Structure-from-Motion
based on triangulated correspondences. RANSAC is applied during this process to distinguish inliers and outliers.
SPARS3R then performs a second, Semantic Outlier Alignment step, which extracts semantically coherent regions
around the outliers and performs local alignment in these
regions. Along with several improvements in the evaluation
process, we demonstrate that SPARS3R can achieve photorealistic rendering with sparse images and significantly
outperforms existing approaches
Recent efforts in Gaussian-Splat-based Novel View Synthesis can achieve photorealistic rendering; however, such capability is limited in sparse-view scenarios due to sparse
initialization and over-fitting floaters. Recent progress in
depth estimation and alignment can provide dense point
cloud with few views; however, the resulting pose accuracy
is suboptimal. In this work, we present SPARS3R, which
combines the advantages of accurate pose estimation from
Structure-from-Motion and dense point cloud from depth
estimation. To this end, SPARS3R first performs a Global
Fusion Alignment process that maps a prior dense point
cloud to a sparse point cloud from Structure-from-Motion
based on triangulated correspondences. RANSAC is applied during this process to distinguish inliers and outliers.
SPARS3R then performs a second, Semantic Outlier Alignment step, which extracts semantically coherent regions
around the outliers and performs local alignment in these
regions. Along with several improvements in the evaluation
process, we demonstrate that SPARS3R can achieve photorealistic rendering with sparse images and significantly
outperforms existing approaches
Clone the repository and create an environment using the following commands:
git clone git@github.com:snldmt/SPARS3R.git
cd SPARS3R
conda create -n spars3r -y python=3.8
conda activate spars3r
pip install torch==1.12.1+cu113 torchvision==0.13.1+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
conda install cudatoolkit-dev=11.3 -c conda-forge
pip install ninja git+https://github.com/NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn/#subdirectory=bindings/torch
pip install -e .
pip uninstall gsplat
pip install git+https://github.com/nerfstudio-project/gsplat.git@v0.1.11
pip install git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git
We also provide the sparse sets constructed by us here (to be uploaded).
Perform registration on train and train+test separately, resulting in train_sparse and train+test_sparse folders. Then we align cameras from train+test_sparse onto train_sparse to get train+test_aligned.
python train_test_alignment/align_coordinate.py --true_images ${working_dir}/train_sparse/sfm --guessimages ${working_dir}/train+test_sparse/sfm --output_path ${working_dir}/train+test_aligned
Follow their github to setup the environment and run their model on the train set.
python alignment/spars3r_alignment.py --scene ${scene_name} --source_path ${working_dir} --orig_colmap_path ${train+test_aligned_path}
ns-train splatfacto \
--data ${working_dir} --output-dir results/ \
--timestamp 0 \
colmap --images_path images_train+test \
--colmap-path ${sparse_alignment_output_path}
ns-train splatfacto-tpo \
--data ${working_dir} --output-dir results/ \
--timestamp tpo \
--pipeline.model.test_opt_pose True --pipeline.model.camera_optimizer.mode SO3xR3 \
--load-dir results/splatfacto/0/nerfstudio_models \
colmap --images_path images_train+test \
--colmap-path ${sparse_alignment_output_path} \
--test_opt_pose True
ns-eval --load-config results/splatfacto/tpo/config.yml
This project is built upon NeRFStudio. We thank all the authors for their great work and for providing the code.
If you find it useful for your work please cite:
@article{tang2024spars3r,
title={SPARS3R: Semantic Prior Alignment and Regularization for Sparse 3D Reconstruction},
author={Tang, Yutao and Guo, Yuxiang and Li, Deming and Peng, Cheng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.12592},
year={2024}
}