CNEPS is a tool that can examine dependencies among reused components for a given input C/C++ source code project.
The approaches we used in this tool and the evaluation results are discussed in our paper which will be published in 46th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2024).
CNEPS provides a handy method to set up both CNEPS and the required environment using a docker file including source code.
Anyone interested in CNEPS can reproduce the results provided in the paper and other C/C++ source code projects.
We hope that CNEPS can inspire people who are interested in reused components analysis as well as the Software Bill of Material (SBOM) Generation area.
We provide our executable using Docker images for simple setup including running environments. Run the following command after installing Docker:
docker pull sodium49/cneps:init
After installing the Docker images, you can locate our executable in the "home/cneps" directory. Run the following command to run the CNEPS docker container, the command will automatically run the bash shell in the CNEPS container:
docker run -it --name cneps sodium49/cneps:init /bin/bash
After installing the Docker images, you can locate our executable in the "home/cneps" directory. Run the follwing command to loacate our executables:
cd /home/cneps/
ls
- Install
universalctags:
apt-get install universal-ctags
- After cloning or unzipping the source code of
CNEPS, download the following requirements using pip:
python3 -m pip install python-tlsh
python3 -m pip install networkx
python3 -m pip install matplotlib
python3 -m pip install plotly
CNEPS detects components using the Centris module.
- Using the provided dataset
- Centris is providing its component DB used for evaluation (DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.4514689). You can download it from Zenodo and locate it with the CNEPS.
- Generating new component DB
- You can follow the instructions provided in Centris GitHub (see https://github.com/WOOSEUNGHOON/Centris-public).
CNEPSonly requires thecomponentDB,metaInfosandaveFuncsdirectories generated after running thePreprocessor.
Copy or move the componentDB with the same directory of CNEPS and move aveFuncs to the metaInfos/aveFuncs directory.
After you input any source code project you wants to examine,
Run the following command to run the CNEPS.
Note that the current CNEPS targets C/C++ source code.
python3 cneps.py {Input Project Path}
The output will be saved in cneps-res directory.
-
{Input Project Name}_edgescontains edges discovered byCNEPSandComponent Node -> Component Nodemeans- For example, the following line means the component
c-areshas a dependency oncurlcomponent c-ares@@c-ares_sig@... -> curl@@curl_sig@...
-
{Input Project Name}_nodescontains information on component discovered byCNEPS.- For example, from the following example, a
c-arescomponent is cloned atclones/mongo/src/third_party/cares/dist - Likewise, this component has a dependency on
curlcomponent cloned atclones/mongo/src/third_party/cares/distdirectory
- For example, from the following example, a
c-ares@@c-ares_sig @ clones/mongo/src/third_party/cares/dist
childs:
curl@@curl_sig @ clones/mongo/src/third_party/cares/dist
{Input Project Name}_timecontains the time taken to analyze dependencies for each module in secondscentrisTimemeans the time taken forCentristo analyze componentsmoduleTimemeans the time taken forCNEPSto construct modulesdepsAnalysisTimemeans the time taken forCNEPSto analyze dependencies and generate a graph
- Because
CNEPSsaves Centris results, parsed headers, and definitions atcneps-metadirectory, please deletecneps-metadirectory to accurately evaluate the performance - Because
CNEPSutilizesCentristo identify reused functions, it takes longer time than the result we have shown in the evaluation section, which only presents time taken byCNEPS - Because
CNEPSutilizesCentristo detect the components, any techniques applied to component detection can enhance the results ofCNEPS
In our Docker container, we also included the source code of the representative dataset with the same version: MongoDB in the clones directory.
This is also available from our source code from Zenodo in the testset directory.
-
Run CNEPS using the following command:
python3 cneps.py "clones/mongo"
-
The result will be saved in
cneps-resdirectory{Input Project Name}_edgescontains edges discovered byCNEPS- The Below figure is an example case from
MongoDBwherec-arescloned atthird_party/cares/disthas a dependency oncurlcloned at the same directory as a code reuse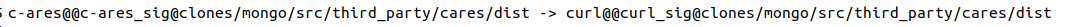
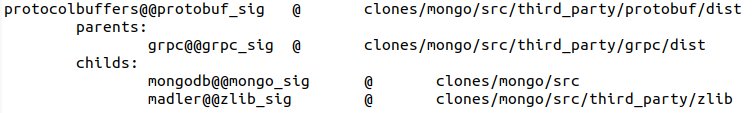
{Input Project Name}_nodescontains information on nodes discovered byCNEPS- The Below figure is an example case from
MongoDBwheregrpchas a dependency onprotobufas a library dependency