Recognition, this project wouldn't be here with out the great json-server. I thought to myself that JSON was a little verbose. So I created yaml-server so you can have a Mock REST API based on a YAML file instead.
yaml-server is a command line tool that create a REST server based on a YAML file.
-
RESTful API Do HTTP requests towards a Mock API using GET, PUT, POST and DELETE created off of a
db.ymlfile. -
Filter your GET calls with query parameters
pageandpageSize, example:/products?page=1&pageSize=10
-
JSON support, yes you can have your database in JSON as well. All you need is to specify the
--dialectargument like so:npx yaml-server --dialect=json
The above will look after a
db.jsonfile at the root. You override where it looks for this if you specify--databaselike for example:npx yaml-server --dialect=json --database ./db/db.json
Above you need to ensure the
db.jsonis located in sub directorydbas seen from the root. -
Create new resource, make a POST call with the following format
/<new resource>/new, example:/kittens/new
Ensure you have a payload as well, looking like for example
{ title: 'paw paw' } -
Sorting, by order and key, you can sort a resource response using query parameters
sortOrderandsortKey. Assume we have the resource/kittenswhere one kitten object looks like so{ id: 1, name: 'paws' }and the entire resource looks like so:[{ id: 1, name: 'paws' }, { id: 2, name: 'alpha paw' }]
Use sorting by appending
sortOrderandsortKeylike below:/kittens?sortOrder=ASC&sortKey=name
This would give the response:
[{ id: 2, name: 'alpha paw' }, { id: 1, name: 'paws' }]
-
browser autostart, the Browser auto starts at
http://locallhost:<selected port>/info. Should you not wish to have that behavior, you can shut it off like so:npx yaml-server --autoStart=off
-
Static file server
By default a static file server is starting up to host your files at root directory. You can change that by specifying
--static. Here's how you would do that:npx yaml-server --static=public
The above would start a static file server from the sub folder
public. -
Hot reload
The server will restart if you make changes to your database file. No need for closing and starting the server after a database change. Should you not wish that behavior, you can shut it off with:
npx yaml-server --hotReload=off
Either install it globally with:
npm install -g yaml-serverOR use NPX
npx yaml-server --port 3000 --database ./db.yml-
Create a
db.yml. -
Give
db.ymlan example content, for example:products: - id: 1 name: tomato - id: 2 name: lettuce orders: - id: 1 name: order1 - id: 2 name: order2
-
There are two ways to start:
- Quick start, run
npx yaml-server, this will start a server onhttp://localhost:3000and base it off adb.ymlat the project root that you created. - With parameters, You can also configure like so
npx yaml-server --port 8000 --database ./db/mydb.yml(If you place db file under./db/mydb.yml)
- Quick start, run
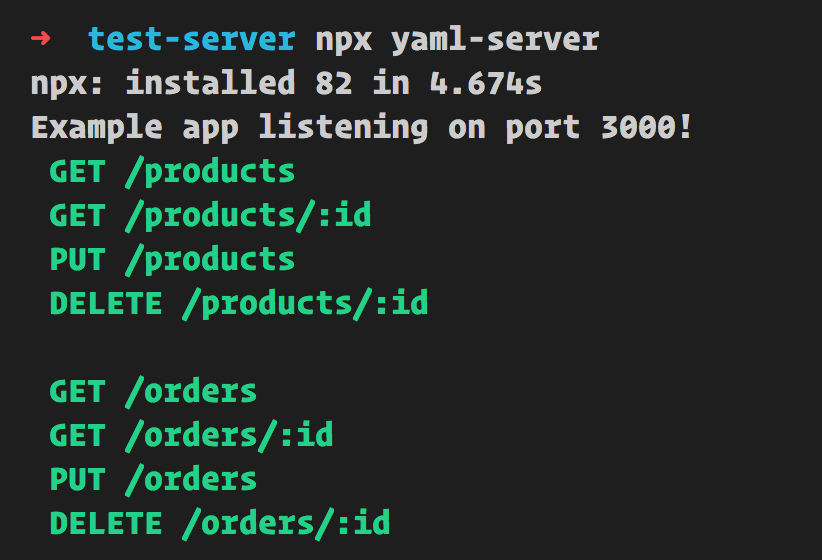
Open up a browser and navigate to http://localhost:<your port>/info. Default port is 3000, if you specified port use that as port instead.
The page at route http://localhost:<port>/info will tell you what routes and operations are available. Here's a typical response for the default page:
Welcome to YAML Server
Routes available are:
GET /products
GET /products/:id
PUT /products
DELETE /products/:id
GET /orders
GET /orders/:id
PUT /orders
DELETE /orders/:id
Routes are created from a YAML file. The default value is db.yml. You can name it whatever you want though.
Routes are first level elements. Consider the following example file:
# db.yml
products:
- id: 1
name: tomato
- id: 2
name: lettuce
orders:
- id: 1
name: order1
- id: 2
name: order2This will produce routes /products, /orders. Below is a table of supported operations with products as example resource. The same operations are also supports for orders/.
| VERB | Route | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /products | None | Array |
| GET | /products/:id | e.g 3 | Object |
| POST | /products | object | Created object |
| PUT | /products | object | Updated object |
| DELETE | /products/:id | e.g 3 | Deleted object |