Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners
This project is a pytorch implementation of OpenAI GPT-2 model. It provides model training, sentence generation, and metrics visualization. It is considered to be both understandable and optimized. We designed the codes to be comprehensible. Also we use some techniques to improve performance.
- regex
- tqdm
- torch
- numpy
- matplotlib
Using apex for training
While training, you can use NVIDIA apex to use fused CUDA layers and mixed-precision optimization. The option --use_amp enables automatic mixed precision in training. Before using these performance boosting, you should install NVIDIA apex library by following the repository, or run belows:
$ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex
$ cd apex
$ pip install -v --no-cache-dir --global-option="--cpp_ext" --global-option="--cuda_ext" ./
If you cannot install the library or your GPU device does not support fast mixed-precision training (precisely, GPU should support mixed-precision acceleration through Tensor Cores), you can train the model in single-precision mode. Mixed-precision training is an option.
Before training GPT-2 model, corpus dataset should be prepared. We recommmend to build your own corpus by using Expanda. Instead, training module requires tokenized training and evaluation datasets with their vocabulary file.
After preparing your datasets, you can train GPT-2 by using as follows:
$ python -m gpt2 train --train_corpus build/corpus.train.txt \
--eval_corpus build/corpus.test.txt \
--vocab build/vocab.txt \
--checkpoint ckpt \
--batch_train 96 \
--batch_eval 128 \
--seq_len 64 \
--layers 12 \
--heads 16 \
--dims 1024 \
--rate 4 \
--dropout 0.1 \
--base_lr 0.0001 \
--iterations 1000000 \
--warmup_iters 10000 \
--eval_iters 500 \
--save_iters 5000 \
--use_amp
To resume training from last checkpoint file, use --restore [last checkpoint file] option.
If you want to train GPT-2 with multiple GPUs, use --gpus [1st gpu id] [2nd gpu id] ... option.
After training GPT-2, you can generate sentences with your trained model in interactive mode.
$ python -m gpt2 generate --vocab build/vocab.txt \
--checkpoint ckpt \
--seq_len 64 \
--layers 12 \
--heads 16 \
--dims 1024 \
--rate 4 \
--temp 0.8 \
--topk 40 \
--samples 20
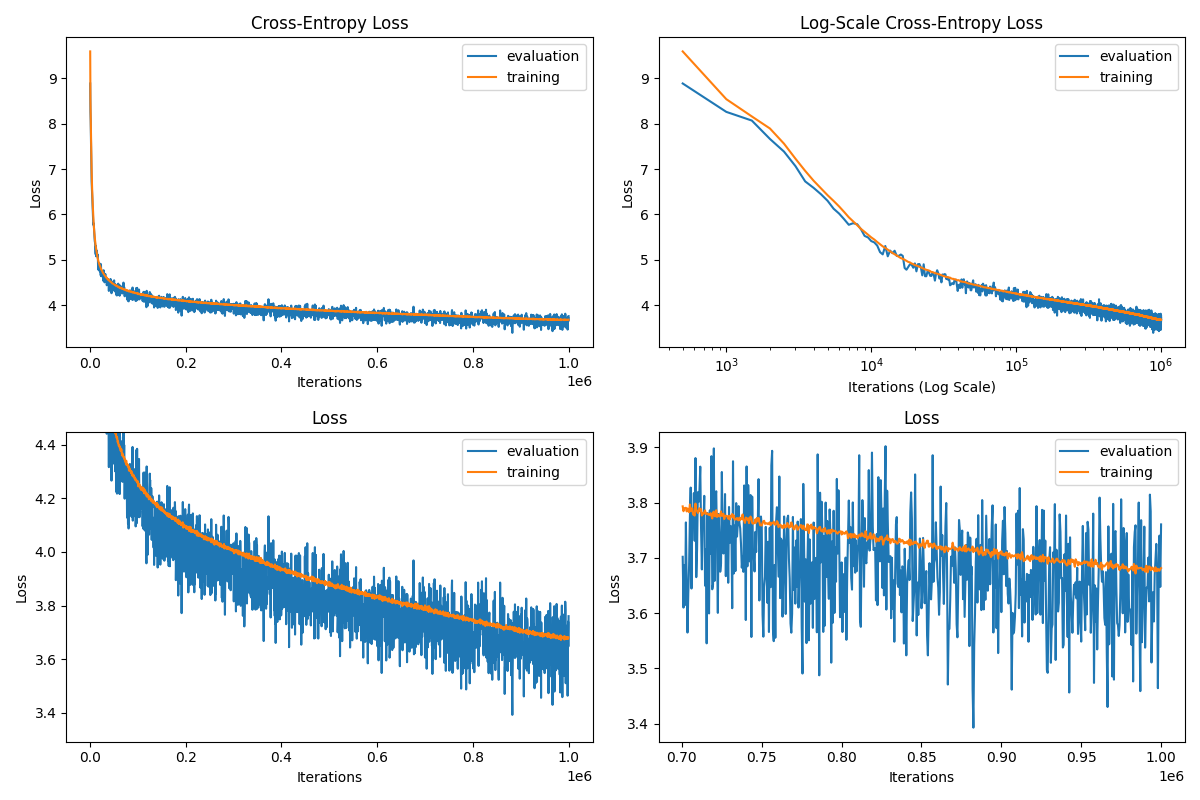
Moreover, there is a module to visualize training metrics.
$ python -m visualize --figure figure.png --checkpoint ckpt
The example figure is as bellow: