Selection in big companies requires an aspirant to be proficient in coding as well as fluent in his words. The latter sometimes becomes a major anchor for various students with the ability to achieve high otherwise. This is a problem that our current interface looks at resolving. We are building an interface that helps users with a situation by the use of an AI that asks questions on the basis of a code which the aspirant has written, asked from a diverse pack of frequently asked coding questions. Then the AI asks the aspirant questions related to his code and some staple questions. At the end of this experience, the user receives his interview profile showing him his flaws in answering questions, his fluency, and his ability to handle the situation verbally. This can be done on various levels and be stored for future scrutiny by the user. We can also provide a growth curve that helps the aspirant to judge his progress.
We developed a AI interview emotion recognition platform to analysis the emotions of job candidates.
The tool can be accessed from the WebApp repository, by installing the requirements and launching main.py.
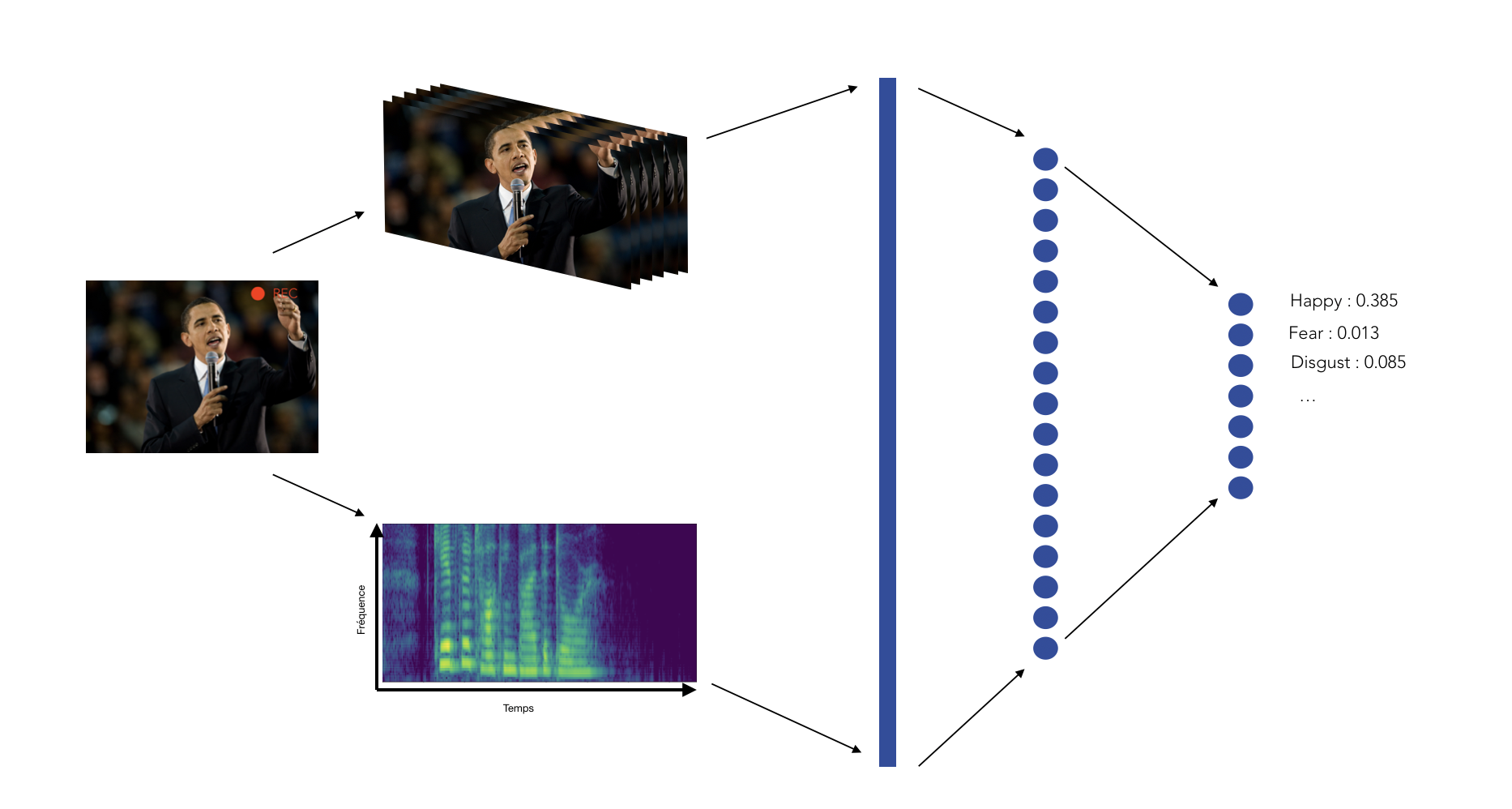
Our aim is to develop a model able to provide a live sentiment analysis with a visual user interface.Therefore, we have decided to separate two types of inputs :
- Textual input, such as answers to questions that would be asked to a person from the platform
- Video input from a live webcam or stored from an MP4 or WAV file, from which we split the audio and the images
The speech emotion recognition pipeline was built the following way :
- Voice recording
- Audio signal discretization
- Log-mel-spectrogram extraction
- Split spectrogram using a rolling window
- Make a prediction using our pre-trained model
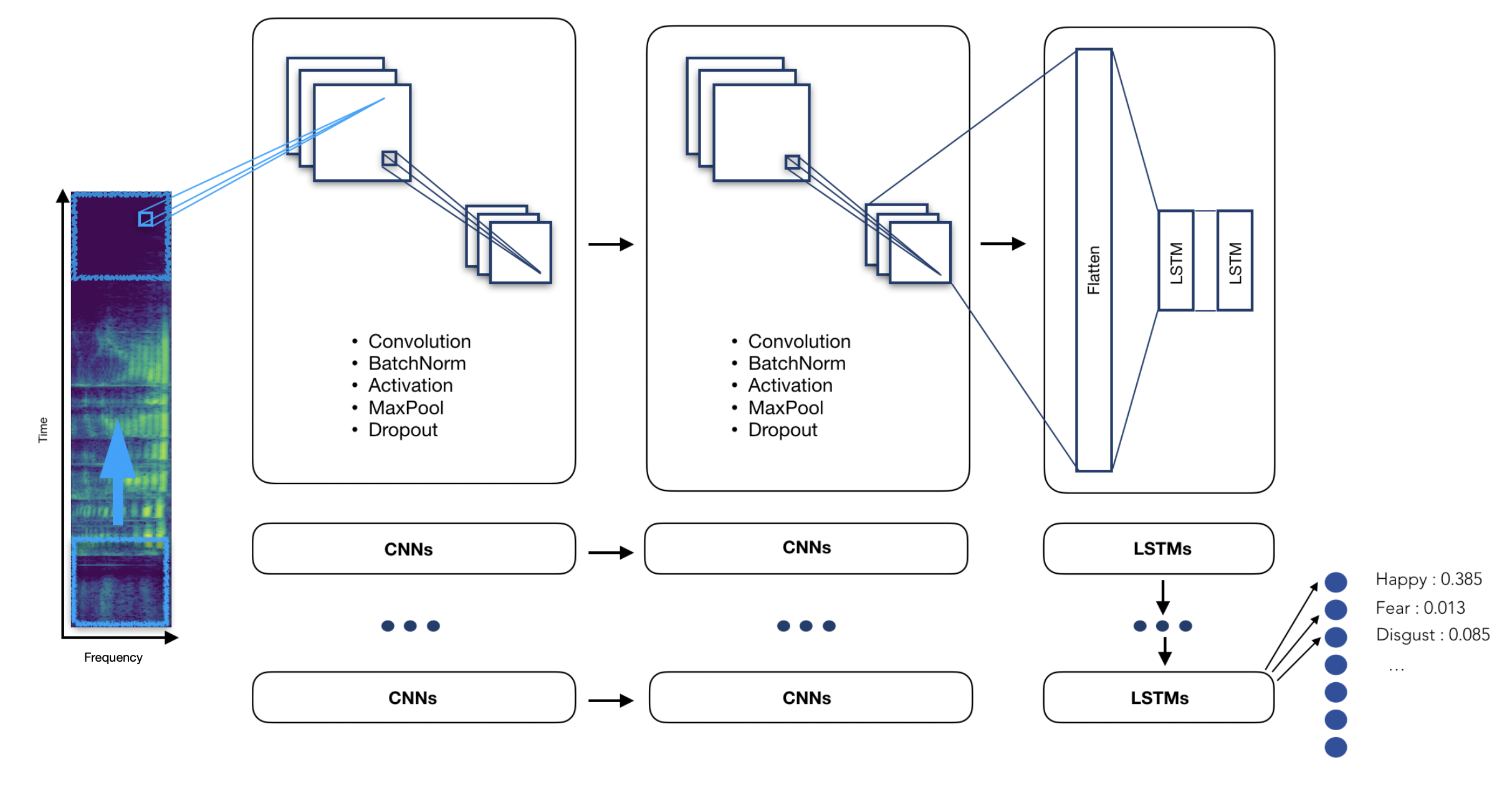
The model we have chosen is a Time Distributed Convolutional Neural Network.
The main idea of a Time Distributed Convolutional Neural Network is to apply a rolling window (fixed size and time-step) all along the log-mel-spectrogram. Each of these windows will be the entry of a convolutional neural network, composed by four Local Feature Learning Blocks (LFLBs) and the output of each of these convolutional networks will be fed into a recurrent neural network composed by 2 cells LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) to learn the long-term contextual dependencies. Finally, a fully connected layer with softmax activation is used to predict the emotion detected in the voice.
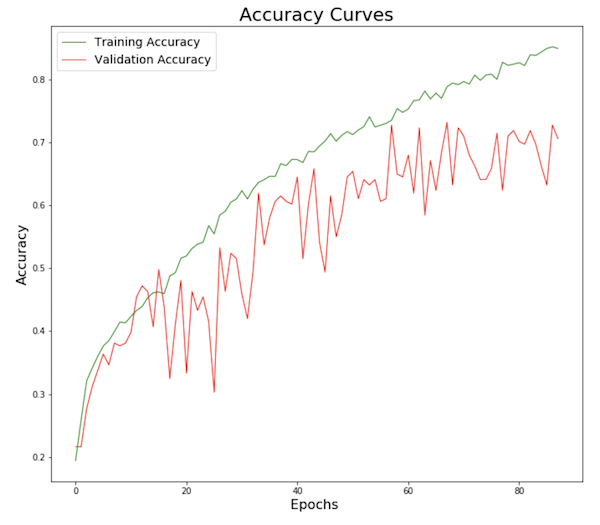
To limit overfitting, we tuned the model with :
- Audio data augmentation
- Early stopping
- And kept the best model
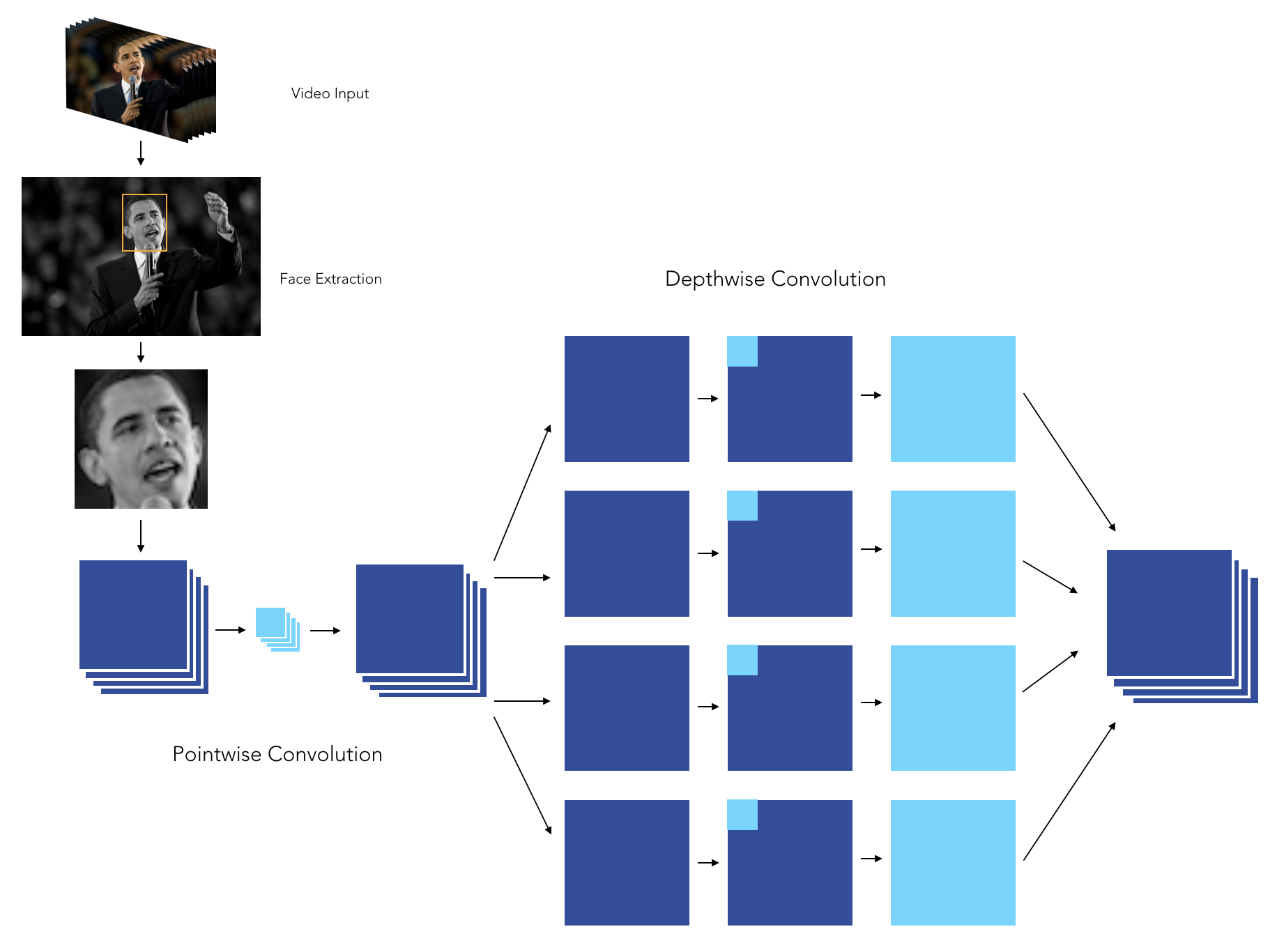
The video processing pipeline was built the following way :
- Launch the webcam
- Identify the face by Histogram of Oriented Gradients
- Zoom on the face
- Dimension the face to 48 * 48 pixels
- Make a prediction on the face using our pre-trained model
- Also identify the number of blinks on the facial landmarks on each picture
The model we have chosen is an XCeption model, since it outperformed the other approaches we developed so far. We tuned the model with :
- Data augmentation
- Early stopping
- Decreasing learning rate on plateau
- L2-Regularization
- Class weight balancing
- And kept the best model
The XCeption architecture is based on DepthWise Separable convolutions that allow to train much fewer parameters, and therefore reduce training time on Colab's GPUs to less than 90 minutes.
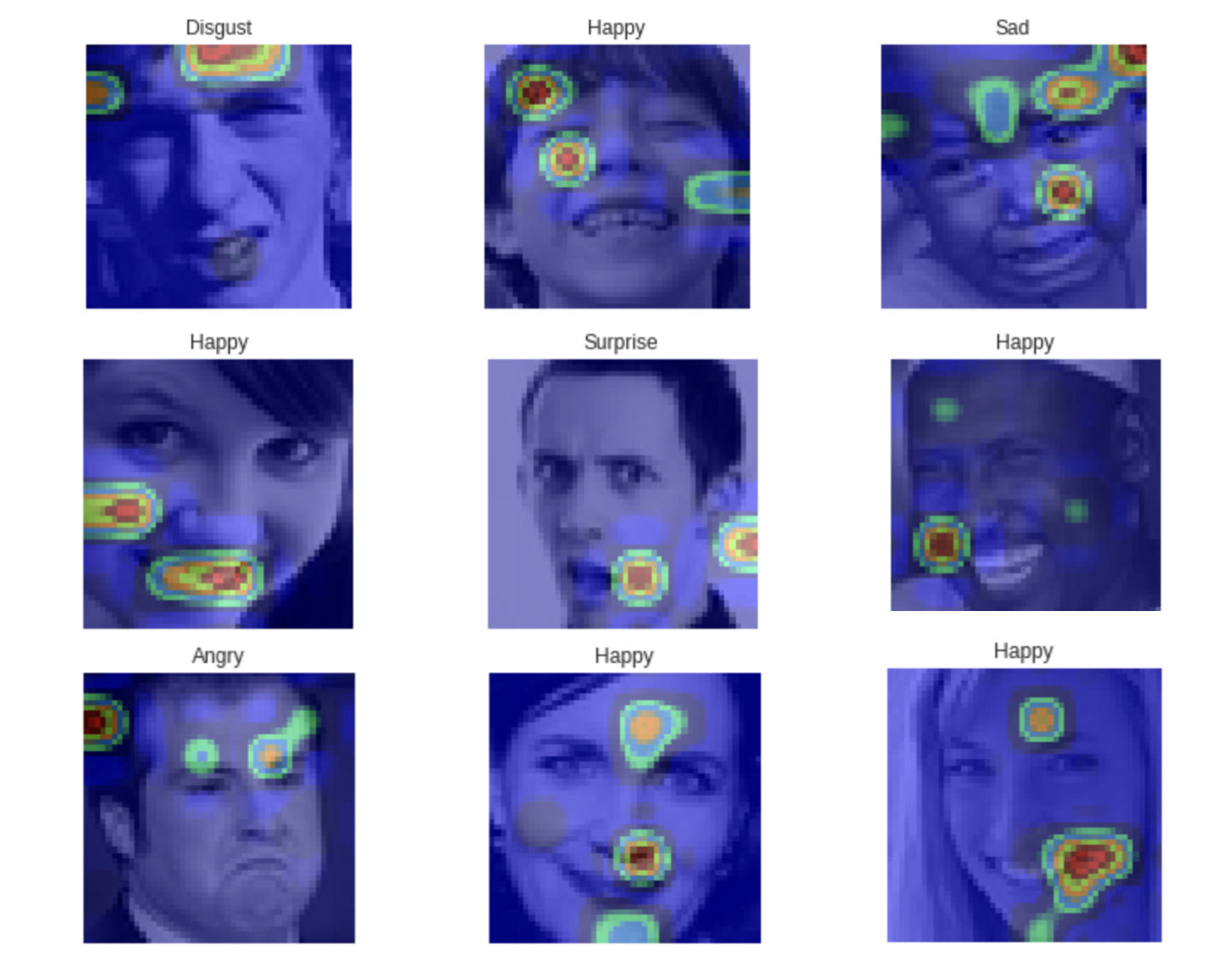
When it comes to applying CNNs in real life application, being able to explain the results is a great challenge. We can indeed plot class activation maps, which display the pixels that have been activated by the last convolution layer. We notice how the pixels are being activated differently depending on the emotion being labeled. The happiness seems to depend on the pixels linked to the eyes and mouth, whereas the sadness or the anger seem for example to be more related to the eyebrows.
The ensemble model has not been implemented on this version.
There are several resources available :
- the working notebooks can be found in the /Video/Audio sections
- the final notebooks can be accessed through the Google Colab link in the table at the beginning
To use the web app :
- Clone the project locally
- Go in the WebApp folder
- Run `$ pip install -r requirements.txt``
- Launch
python app.py
The web app has been dockerized
- First build the image, run
docker-compose build - Then start/run the container, run
docker-compose up
- Take a look at the Existing Issues or create your own Issues!
- Wait for the Issue to be assigned to you.
- Fork the repository
- Have a look at Contibuting Guidelines