Application software performs specific task for the user.
System software operates and controls the computer system and provides a platform to run application software
An operating system is a piece of software that manages all the resources of a computer system, both hardware and software, and provides an environment in which the user can execute his / her programs in a convenient and efficient manner by hiding underlying complexity of the hardware and acting as a resource manager.
- Resource exploitation by App.
- No memory protection.
- Bulky and complex app.
- Access to the computer hardware.
- Interface between the user and the computer hardware
- Resource management(Aka, Arbitration)(memory, device, file, security, process etc)
- Hides the underlying complexity of the hardware.(Aka, Abstraction)
- Facilitates execution of application programs by providing isolation and protection.
- Maximum CPU utilization
- Less process starvation(Continuous ruining not giving chance to other processes)
- Higher priority job execution
-
Single Process OS
This type of operating system allows only one process to run at a time. It focuses on completing that process before starting a new one. Once the current process finishes, the operating system selects the next process to execute. It is a straightforward and sequential approach.
-
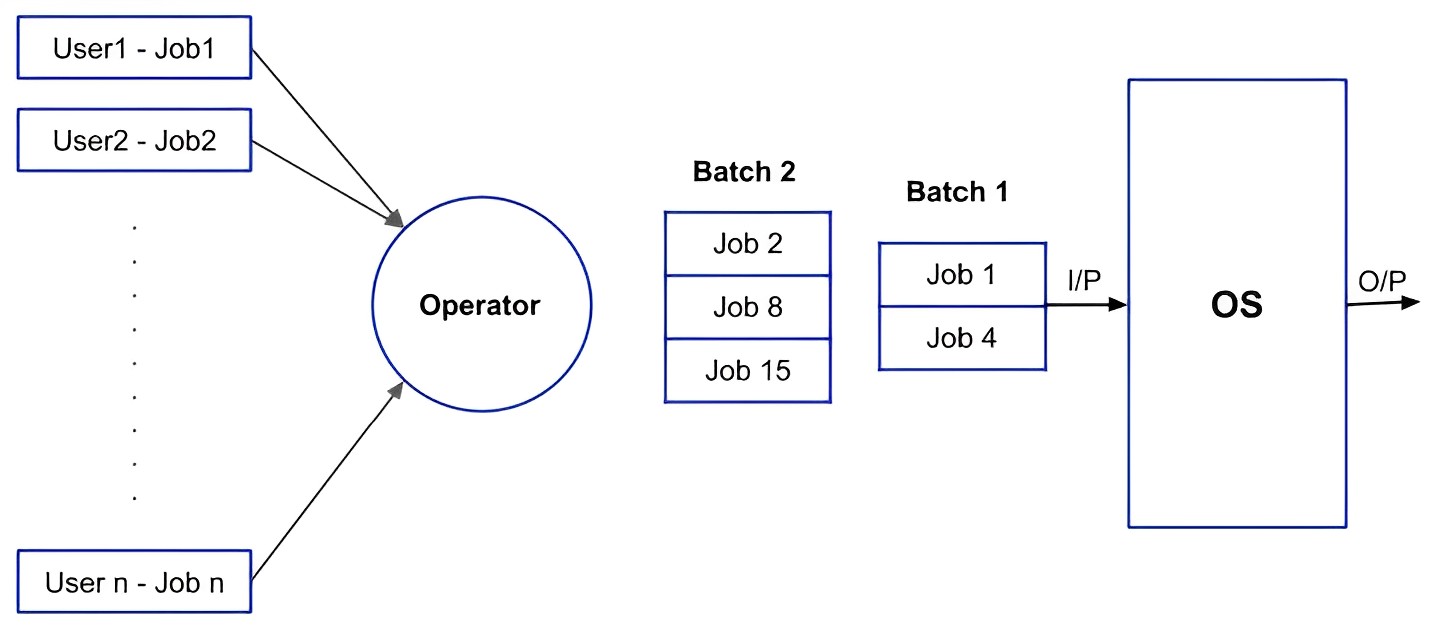
Batch-Processing OS
Batch processing operating systems are designed to efficiently execute a large number of similar tasks without requiring user intervention. They operate by collecting multiple jobs into batches and executing them sequentially, optimizing resource utilization. The operating system automatically schedules and runs these batches, typically in a non-interactive environment. Jobs are processed one after another.
-
Multiprogramming OS
is an ability of an operating system that executes more than one program using a single processor machine. More than one task or program or jobs are present inside the main memory at one point of time.
Buffering and spooling can overlap I/O and CPU tasks to improve the system performance but it has some limitations that a single user cannot always keep CPU or I/O busy all the time.
Context Switching : a procedure that a computer's CPU follows to change from one task (or process) to another while ensuring that the tasks do not conflict.
-
Explain
The OS could pick and start the execution of one of the jobs in memory, whenever the jobs does not need CPU that means the job is working with I/O at that time the CPU is idle at that time the OS switches to another job in memory and CPU executes a portion of it till the job issues a request for I/O and so on.
-
-
Multitasking OS
In multitasking, each job or process is given some time to execute and the operating system switches the jobs after a certain interval of time. This is also known as Time Sharing OS.
-
Multi-processing OS
(More the 1 CPU)
In operating systems, to improve the performance of more than one CPU can be used within one computer system called Multiprocessor operating system.
Multiple CPUs are interconnected so that a job can be divided among them for faster execution. When a job finishes, results from all CPUs are collected and compiled to give the final output. Jobs needed to share main memory and they may also share other system resources among themselves. Multiple CPUs can also be used to run multiple jobs simultaneously.
-
Distributed OS (Loosely Coupled)
It serves multiple real-time applications which require multiple CPUs. Various computers communicate with each other through a network.
-
RTOS (Real Time OS)
RTOS is an operating system intended to serve real time application that process data as it comes in, mostly without buffer delay. The full form of RTOS is Real time operating system.
A thread is a component of a process. It helps a process in doing multiple tasks at a time. A process may contain multiple threads.
There are two types of threads.
- User threads - It is implemented by the user.
- Kernel threads - It is implemented by the Operating System.
A process is any program in execution. It contains more than one thread which helps it in doing multiple tasks at a time.
| Multi-Tasking | Multi-Threading |
|---|---|
| 1. Execution of more than one task simultaneously. | 1. Process is divided into several different sub-tasks called as threads, which has its own path of execution. |
| 2. Concept of more than 1 processes being context switched. | 2. Concept of more than 1 thread. Threads are context switched. |
| 3. Number of CPU is 1. | 3. Number of CPU is more then 1. |
| 4. Isolation and memory protection exists. OS must allocate separate memory and resources to each program that CPU is executing. | 4. No isolation and memory protection, resources are shared among threads of that process. |
It is the scheduling of processes for their execution. It helps in the efficient utilization of the CPU.
Threads are scheduled for execution based on their priority. Even though threads are executing within the runtime, all threads are assigned processor time slices by the operating system.
| Process Scheduling | Thread Scheduling |
|---|---|
| 1. Fast | 1. Slow |
| 2. Doesn’t includes switching of memory address space. | 2. Includes switching of memory address |
| space. | |
| 3. OS saves current state of thread & switches to another thread of same process. | 3. OS saves current state of process & switches to another process by restoring its state. |
| 4. CPU’s cache state is preserved | 4. CPU’s cache state is flushed |
Coming........