Unsupervised-Image-Segmentation
Introduction
We have been given a vehicle dataset. The dataset has been retrieved from the IIT Kanpur surveillance cameras and consists of a variety of vehicle classes like, cars, buses, bicycles, motorbikes and pedestrians. This data can be used to implement various computer vision tasks and we have explored the problem of segmenting the dataset. We have used two different methods as described below :-
Approaches
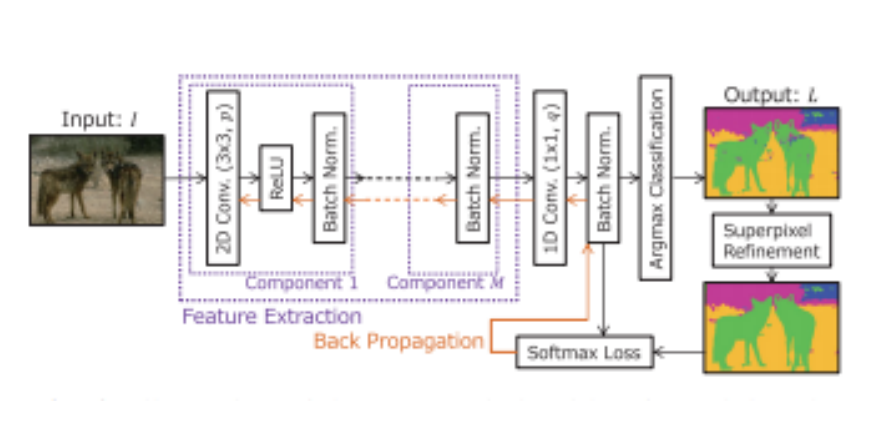
Unsupervised Image Segmentation by BackProapagation
Given an RGB image where each pixel is a 3-dimensional vector, this method computes a feature vector for each pixel by passing it through a convolutional network and then the pixels are assigned labels using the method of k-mean clustering.
Letxnbe the feature vector for thenthpixel in the image andf(xn) be a function which predicts the cluster labelcnfor the particular pixel. Now we have three things,xn,f(xn) andcnwhich need to be trained. We do this by alternately fixing parameters for two things and training the third function. For example, ifcn is being predicted we keepxn andf(xn) constant. The weights are updated by using backpropagation method using stochastic gradi- ent optimizer.
For good segmentation, certain characteristics are required for the cluster labelcn. Instance of any object contains patches of similar texture patterns. This is taken into account while performing the segmentation. Hence, spa- tially continuous pixels that have similar color and texture patterns should be
grouped together. On the other hand, different object instances should be cat- egorized separately. To facilitate this cluster separation, the number of cluster labels is desired to be large. CNN architecture is used to extract the pixel features. This CNN assigns the cluster labels to image pixels and updates the convolutional filters for better separation of clusters. Backpropagation of softmax loss is used to update the network. The model architecture is given below:
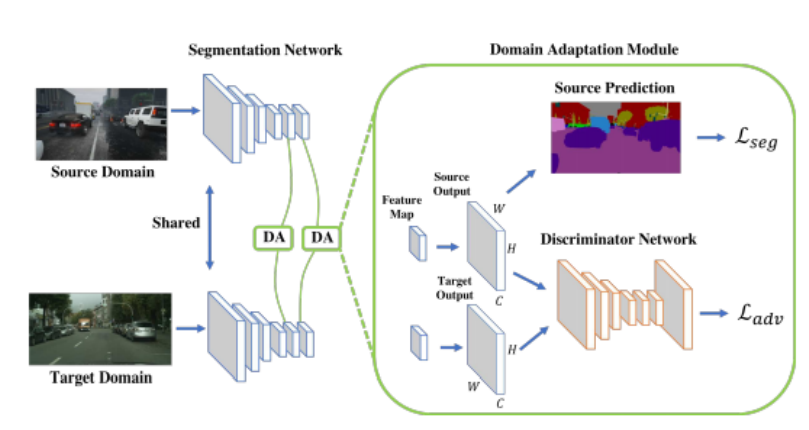
Domain Adaptation for Segmentation
In this method, knowledge transfer or domain adaptation is done to close the gap of distributions of source and target domains. Based on the General Ad- versial Network, this model consits of two parts:
Segmentation Network to predict the segmentation of the images, and Discriminator Network to tell whether the input image is from source do- main or target domain. We first used a pretrained model adapted on Cityscapes dataset through GTA dataset directly to visualise the results which were not significant. Then we used the GTA dataset as the source domain and the IITK dataset as the target domain to train our separate model.
The model architecture is as follows:
On the one hand the loss for the segmentation is minimized while simultane- ously the loss for the discriminator network is maximised so that it becomes hard for the discriminator network to distinguish between the source domain and target domain and thus the segmentation network can easily use the trans- ferred knowledge from GTA dataset(which is labelled) to predict the segmen- tation for the IITK Dataset.
Results Obtained By Both Methods Respectively:
References [1] Richter 2016 ECCV, author = Stephan R. Richter and Vibhav Vineet and Stefan Roth and Vladlen Koltun, title = Playing for Data: Ground Truth from Computer Games, booktitle = European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), year = 2016, editor = Bastian Leibe and Jiri Matas and Nicu Sebe and Max Welling, series = LNCS, volume = 9906, publisher = Springer International Publishing, pages = 102–
[2] @articleKanezaki2018UnsupervisedIS, title=Unsupervised Image Segmen- tation by Backpropagation, author=Asako Kanezaki, journal=2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), year=2018, pages=1543-
[3] https://github.com/kanezaki/pytorch-unsupervised-segmentation
[4] https://github.com/wasidennis/AdaptSegNet
[5] @articleTsai2018LearningTA, title=Learning to Adapt Structured Output Space for Semantic Segmentation, author=Yi-Hsuan Tsai and Wei-Chih Hung and Samuel Schulter and Kihyuk Sohn and Ming-Hsuan Yang and Manmohan Krishna Chandraker, journal=2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, year=2018, pages=7472-