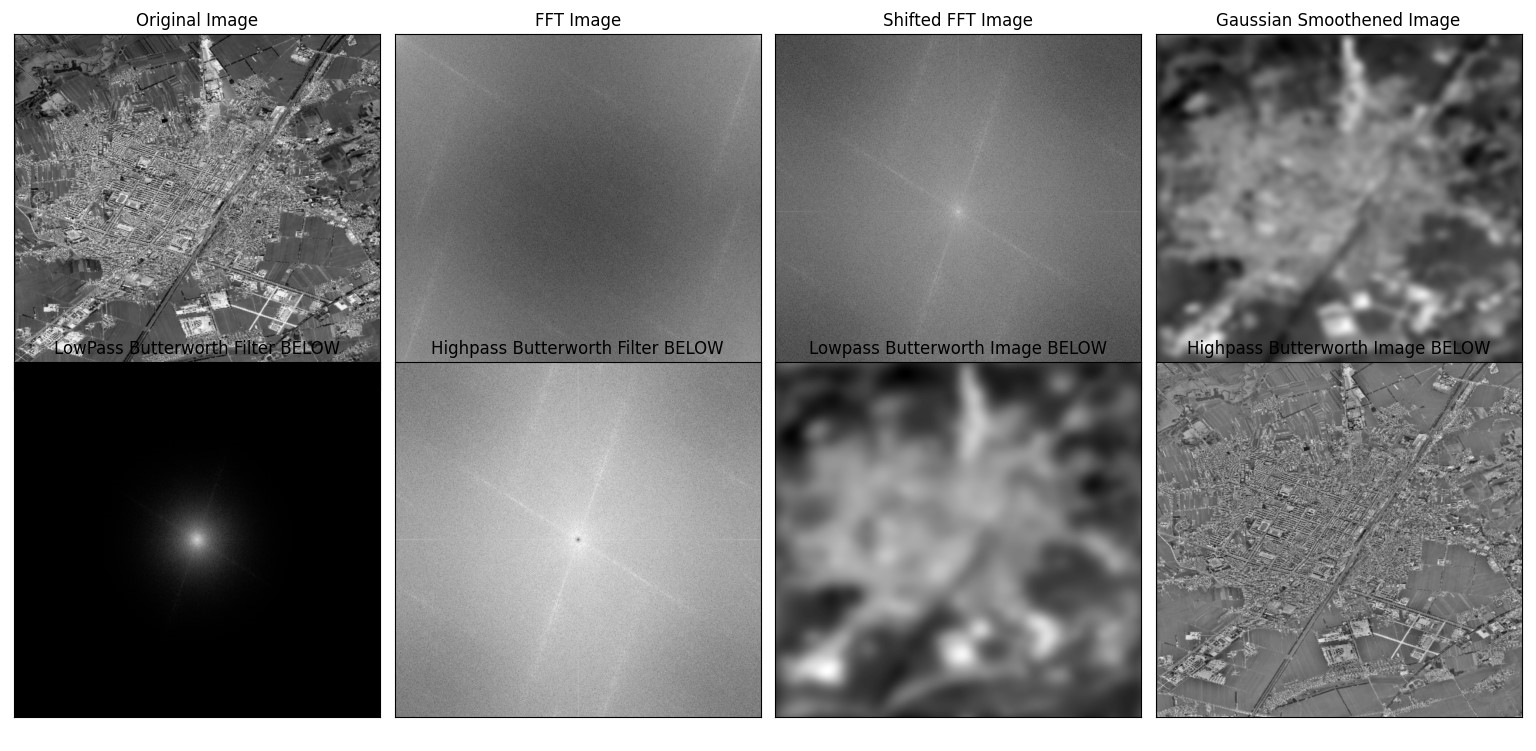
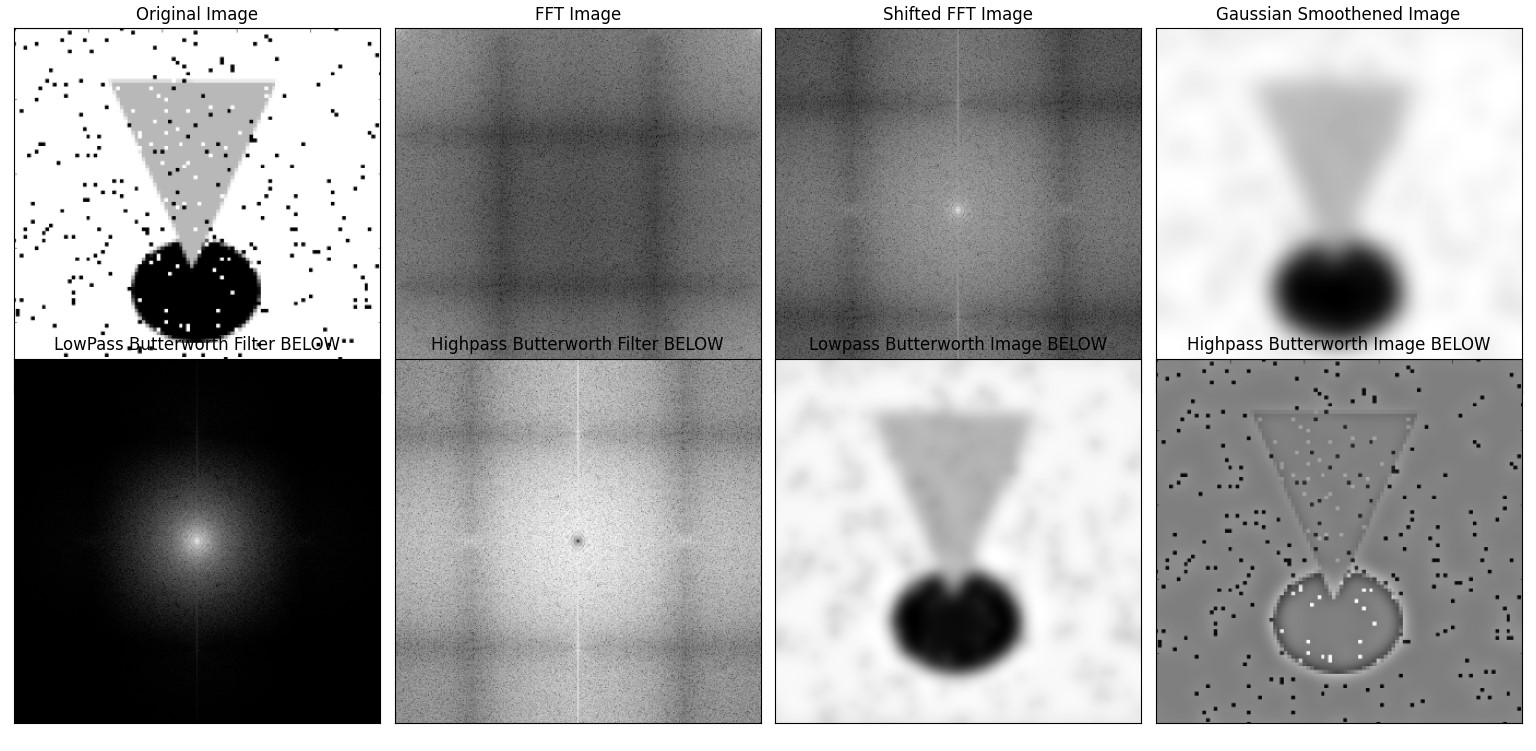
Project : Compute the Fourier transform of an image and generate a low pass filtered image using Gaussian and Butterworth filters.
Installing the dependencies All the required dependencies have been listed in this file, they installed using this command
pip install -r requirements.txtRunning the code
The source code is just contained in this file - which can be run by terminal python gui.py or from text-editors.
Gaussian filter : We have made our own gaussian with equal size as that of the image(in frequency domain). Allowable ranges are sigma_x >= 0 sigma_y >= 0 Depending on the size of the image, lower values of sigma_x and sigma_y can become meaningless. This is because very low values of standard deviation act as uniform smoothing. Since we multiply the Gaussian filter in the frequency domain, it results in significant blurring of the image. Hence we have chosen minimum sigma_x or sigma_y to be 5.
def gaussian_kernel(l, b, sigma_x, sigma_y):
kernel = np.fromfunction(lambda x, y: (1/(2*np.pi*sigma_x*sigma_y)) * np.exp(-((x-(l-1)/2)**2/(2*sigma_x**2) + (y-(b-1)/2)**2/(2*sigma_y**2))), (l, b))
return kernel / np.sum(kernel)Butterwurth Filter
To calculate the allowable ranges for butterworth filter we use the following method:
1. Compute the magnitude spectrum of the Fourier-transformed image.
2. Find the maximum radius in the magnitude spectrum beyond which the frequency weight falls below a specified threshold.
3. Consider this maximum radius as the allowable range for the Butterworth filter.
Code implementation
fft_result_shifted = np.fft.fftshift(fft_result)
magnitude_spectrum = np.log(np.abs(fft_result_shifted) + 1).real
max_magnitude = np.max(magnitude_spectrum)
threshold = 0.5* max_magnitude #Threshold = 0.5*max_magnitude
low_values_indices = np.where(magnitude_spectrum < threshold)
radius_low_values = np.sqrt((low_values_indices[0] - fft_result_shifted.shape[0] // 2)**2 +
(low_values_indices[1] - fft_result_shifted.shape[1] // 2)**2)
max_radius_low_values = np.max(radius_low_values)
cut_off_frequency_max = max_radius_low_valuesSOME SAMPLE IMAGES ARE GIVEN FOR REFERENCE:
- Saurabh Kumar
- Cherish Jain
- Yask Kakade
- Samarth Sirsat