Vulnerability scanner for Linux/FreeBSD, agentless, written in golang. We have a slack team. Join slack team Twitter: @vuls_en
| Version | Main Feature | Date |
|---|---|---|
| v0.7.0 | WordPress Vulnerability Scan | 2019/Apr/8 |
| v0.6.3 | GitHub Integration | 2019/Feb/20 |
| v0.6.2 | Add US-CERT/JPCERT Alerts as VulnSrc | 2019/Jan/23 |
| v0.6.1 | BugFix | 2018/Nov/16 |
| v0.6.0 | Add ExploitDB as VulnSrc | 2018/Nov/3 |
| v0.5.0 | Scan accuracy improvement | 2018/Aug/27 |
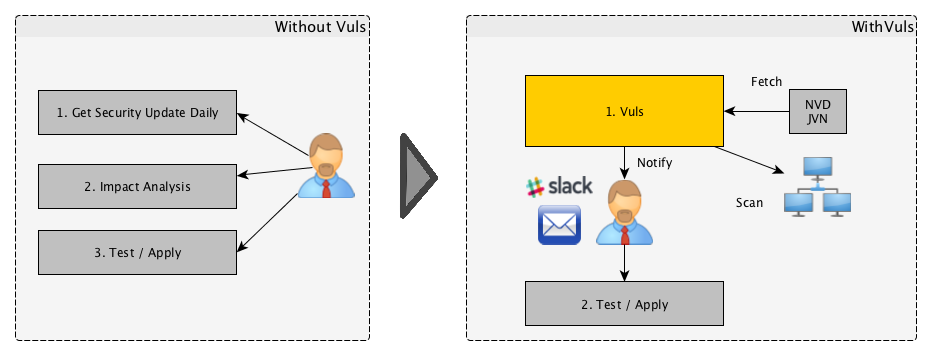
For a system administrator, having to perform security vulnerability analysis and software update on a daily basis can be a burden. To avoid downtime in a production environment, it is common for a system administrator to choose not to use the automatic update option provided by the package manager and to perform update manually. This leads to the following problems.
- The system administrator will have to constantly watch out for any new vulnerabilities in NVD (National Vulnerability Database) or similar databases.
- It might be impossible for the system administrator to monitor all the software if there are a large number of software packages installed in the server.
- It is expensive to perform analysis to determine the servers affected by new vulnerabilities. The possibility of overlooking a server or two during analysis is there.
Vuls is a tool created to solve the problems listed above. It has the following characteristics.
- Informs users of the vulnerabilities that are related to the system.
- Informs users of the servers that are affected.
- Vulnerability detection is done automatically to prevent any oversight.
- A report is generated on a regular basis using CRON or other methods. to manage vulnerability.
- Alpine, Amazon Linux, CentOS, Debian, Oracle Linux, Raspbian, RHEL, SUSE Enterprise Linux, and Ubuntu
- FreeBSD
- Cloud, on-premise, and Docker
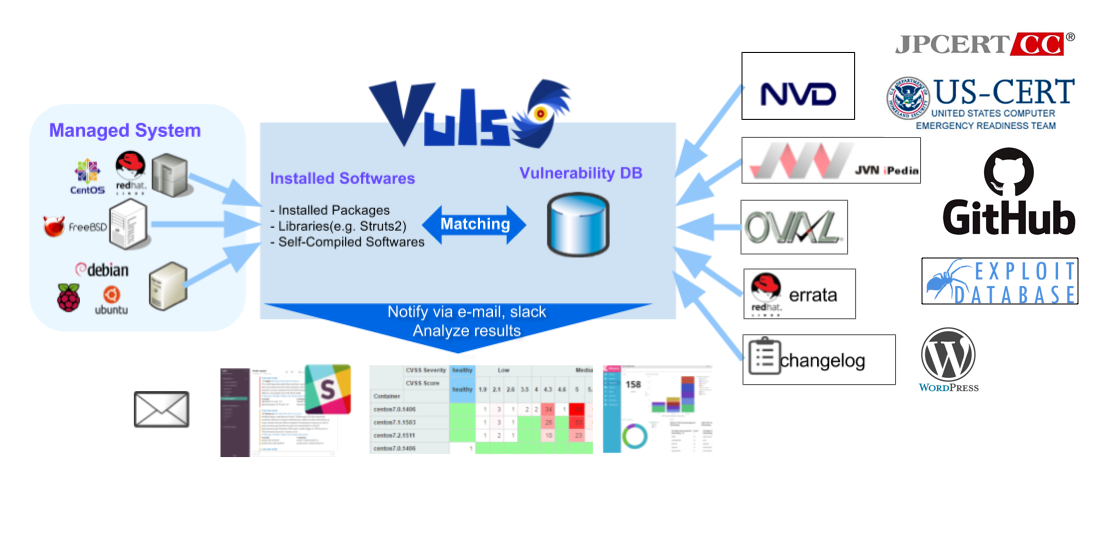
Vuls uses multiple vulnerability databases
-
OVAL
-
Commands (yum, zypper, and pkg-audit)
- RHSA/ALAS/ELSA/FreeBSD-SA
-
Changelog
- Scan without root privilege, no dependencies
- Almost no load on the scan target server
- Offline mode scan with no internet access. (CentOS, Debian, Oracle Linux, Red Hat, and Ubuntu)
- Scan with root privilege
- Almost no load on the scan target server
- Detect processes affected by update using yum-ps (Amazon Linux, CentOS, Oracle Linux, and RedHat)
- Detect processes which updated before but not restarting yet using checkrestart of debian-goodies (Debian and Ubuntu)
- Offline mode scan with no internet access. (CentOS, Debian, Oracle Linux, Red Hat, and Ubuntu)
- Scan with root privilege
- Parses the Changelog Changelog has a history of version changes. When a security issue is fixed, the relevant CVE ID is listed. By parsing the changelog and analysing the updates between the installed version of software on the server and the newest version of that software it's possible to create a list of all vulnerabilities that need to be fixed.
- Sometimes load on the scan target server
- User is required to only set up one machine that is connected to other target servers via SSH
- If you don't want the central Vuls server to connect to each server by SSH, you can use Vuls in the Local Scan mode.
- First, start Vuls in server mode and listen as an HTTP server.
- Start Vuls in server mode and listen as an HTTP server.
- Next, issue a command on the scan target server to collect software information. Then send the result to Vuls Server via HTTP. You receive the scan results as JSON format.
- No SSH needed, No Scanner needed. Only issuing Linux commands directory on the scan tareget server.
- It is possible to acquire the state of the server by connecting via SSH and executing the command.
- Vuls warns when the scan target server was updated the kernel etc. but not restarting it.
- Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) based Scan
- Scan middleware, programming language libraries and framework for vulnerability
- Support software registered in CPE
- Nondestructive testing
- Pre-authorization is NOT necessary before scanning on AWS
- Vuls works well with Continuous Integration since tests can be run every day. This allows you to find vulnerabilities very quickly.
- Auto-generation of configuration file template
- Auto-detection of servers set using CIDR, generate configuration file template
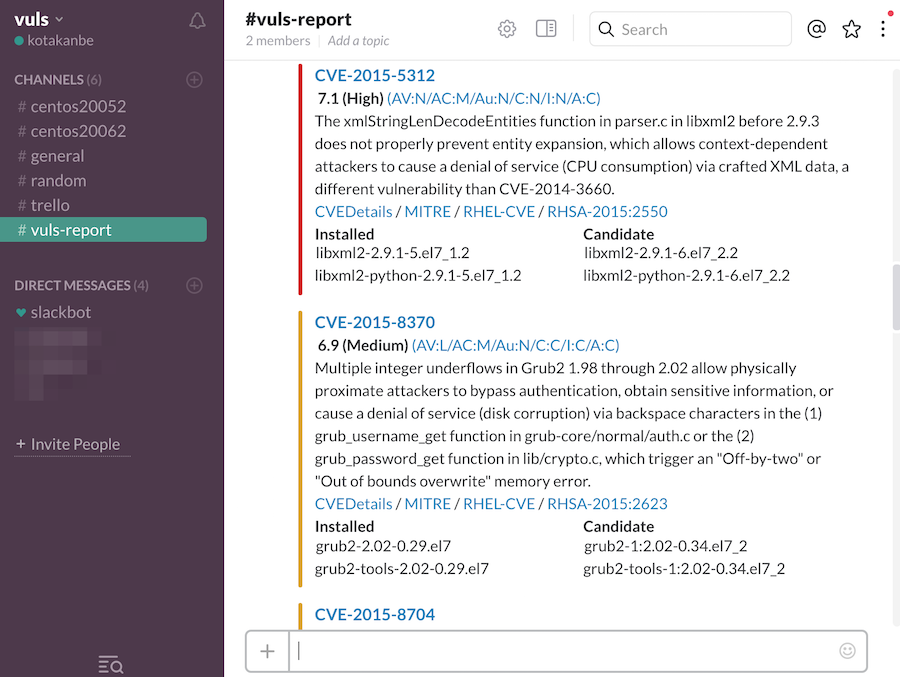
- Email and Slack notification is possible (supports Japanese language)
- Scan result is viewable on accessory software, TUI Viewer in a terminal or Web UI (VulsRepo).
- Vuls doesn't update the vulnerable packages.
For more information such as Installation, Tutorial, Usage, visit vuls.io 日本語翻訳ドキュメント
kotakanbe (@kotakanbe) created vuls and these fine people have contributed.
Please see CHANGELOG.
-----;
Please see LICENSE.