Predicting Dynamic Embedding Trajectory in Temporal Interaction Networks (ACM SIGKDD 2019)
Authors: Srijan Kumar, Xikun Zhang, Jure Leskovec
Link to the paper
Link to the slides
Brief video explanation
Introduction
Temporal networks are ubiquitous in e-commerce (users clicking, purchasing, saving items), social networks (users talking with one another and interacting with content), finance (transactions between users and merchants), and education (students taking courses). In all domains, the entities (users, items, content) can be represented as nodes and their interaction as edges.
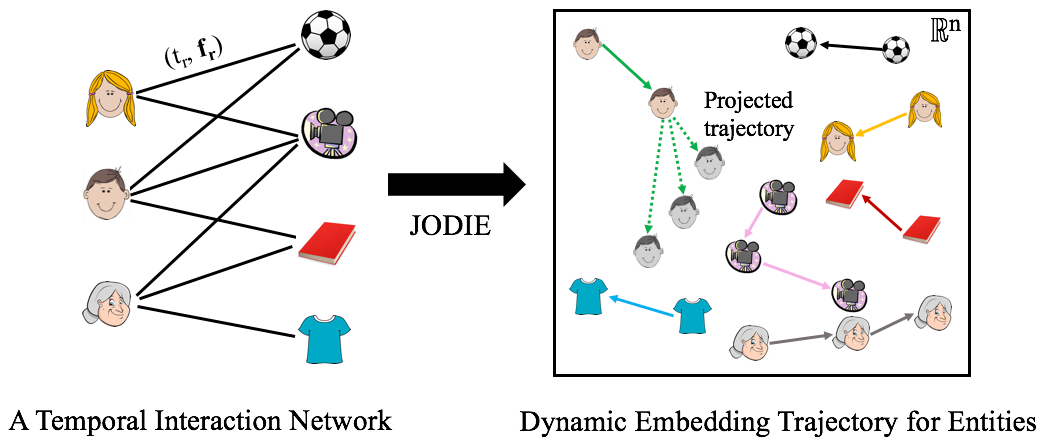
JODIE is a representation learning framework for all nodes in temporal networks. Given a sequence of node actions, JODIE learns a dynamic embedding trajectory for every node (as opposed to a static embedding). These trajectories are useful for downstream machine learning tasks, such as link prediction, node classification, and clustering. JODIE is fast and makes accurate predictions about future interactions and anomaly detection.
In this paper, JODIE has been used for two broad category of tasks:
- Temporal Link Prediction: Which two nodes will interact next? Example applications are recommender systems and modeling network evolution.
- Temporal Node Classification: When does the state of an node change from normal to abnormal? Example applications are anomaly detection, ban prediction, dropout and churn prediction, and fraud and account compromise.
Motivation
Temporal networks provide an expressive language to represent time-evolving and dynamic interactions between nodes. Think of users interacting (click, purchase, view) with items. Representation learning provides a powerful tool to model and reason on networks. However, as networks evolve over time, a single (static) embedding becomes insufficient to represent the changing behavior of the entities and the dynamics of the network.
JODIE is a representation learning framework that embeds every node in a Euclidean space and their evolution is modeled by an embedding trajectory in this space. JODIE learns to forecast the embedding trajectories into the future to make predictions about the entities and their interactions. These trajectories can be trained for downstream tasks, such as recommendations and predictions. JODIE is scalable to large networks by employing a novel data batching algorithm, called t-Batch, that creates batches of independent edges that can be processed simulaneously.
If you make use of this code, the JODIE algorithm, the T-batch algorithm, or the datasets in your work, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{kumar2019predicting,
title={Predicting Dynamic Embedding Trajectory in Temporal Interaction Networks},
author={Kumar, Srijan and Zhang, Xikun and Leskovec, Jure},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining},
year={2019},
organization={ACM}
}
Short Video Explanation of JODIE (External Link to YouTube)
Datasets
Links to datasets used in the paper:
Dataset format
The networks are stored under the data/ folder, one file per network. The filename should be <network>.csv.
The network should be in the following format:
- One line per interaction/edge.
- Each line should be: user, item, timestamp, state label, comma-separated array of features.
- First line is the network format.
- User and item fields can be alphanumeric.
- Timestamp should be in cardinal format (not in datetime).
- State label should be 1 whenever the user state changes, 0 otherwise. If there are no state labels, use 0 for all interactions.
- Feature list can be as long as desired. It should be atleast 1 dimensional. If there are no features, use 0 for all interactions.
For example, the first few lines of a dataset can be:
user,item,timestamp,state_label,comma_separated_list_of_features
0,0,0.0,0,0.1,0.3,10.7
2,1,6.0,0,0.2,0.4,0.6
5,0,41.0,0,0.1,15.0,0.6
3,2,49.0,1,100.7,0.8,0.9
Code setup and Requirements
Recent versions of PyTorch, numpy, sklearn, tqdm, and gpustat. You can install all the required packages using the following command:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
To initialize the directories needed to store data and outputs, use the following command. This will create data/, saved_models/, and results/ directories.
$ chmod +x initialize.sh
$ ./initialize.sh
To download the datasets used in the paper, use the following command. This will download four datasets under the data/ directory: reddit.csv, wikipedia.csv, mooc.csv, and lastfm.csv.
$ chmod +x download_data.sh
$ ./download_data.sh
Running the JODIE code
To train the JODIE model using the data/<network>.csv dataset, use the following command. This will save a model for every epoch in the saved_models/<network>/ directory.
$ python jodie.py --network <network> --model jodie --epochs 50
This code can be given the following command-line arguments:
--network: this is the name of the file which has the data in thedata/directory. The file should be named<network>.csv. The dataset format is explained below. This is a required argument.--model: this is the name of the model and the file where the model will be saved in thesaved_models/directory. Default value: jodie.--gpu: this is the id of the gpu where the model is run. Default value: -1 (to run on the GPU with the most free memory).--epochs: this is the maximum number of interactions to train the model. Default value: 50.--embedding_dim: this is the number of dimensions of the dynamic embedding. Default value: 128.--train_proportion: this is the fraction of interactions (from the beginning) that are used for training. The next 10% are used for validation and the next 10% for testing. Default value: 0.8--state_change: this is a boolean input indicating if the training is done with state change prediction along with interaction prediction. Default value: True.
Evaluate the model
Interaction prediction
To evaluate the performance of the model for the interaction prediction task, use the following command. The command iteratively evaluates the performance for all epochs of the model and outputs the final test performance.
$ chmod +x evaluate_all_epochs.sh
$ ./evaluate_all_epochs.sh <network> interaction
To evaluate the trained model's performance for predicting interactions in only one epoch, use the following command. This will output the performance numbers to the results/interaction_prediction_<network>.txt file.
$ python evaluate_interaction_prediction.py --network <network> --model jodie --epoch 49
The file get_final_performance_numbers.py reads all the outputs of each epoch, stored in the results/ folder, and finds the best validation epoch.
State change prediction
To evaluate the performance of the model for the state change prediction task, use the following command. The command iteratively evaluates the performance for all epochs of the model and outputs the final test performance.
$ chmod +x evaluate_all_epochs.sh
$ ./evaluate_all_epochs.sh <network> state
To evaluate the trained model's performance for predicting state change in only one epoch, use the following command. This will output the performance numbers to the results/state_change_prediction_<network>.txt file.
$ python evaluate_state_change_prediction.py --network <network> --model jodie --epoch 49
Run the T-Batch code
To create T-Batches of a temporal network, use the following command. This will save a file with T-Batches in the results/tbatches_<network>.csv file. Note that the entire input will be converted to T-Batches. To convert only training data, please input a file with only the training interactions.
$ python tbatch.py --network <network>
This code can be given the following command-line arguments:
--network: this is the name of the file which has the data in thedata/directory. The file should be named<network>.csv. The dataset format is explained below. This is a required argument.
References
Predicting Dynamic Embedding Trajectory in Temporal Interaction Networks. Srijan Kumar, Xikun Zhang, Jure Leskovec. ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), 2019.
If you make use of this code, the JODIE algorithm, the T-batch algorithm, or the datasets in your work, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{kumar2019predicting,
title={Predicting Dynamic Embedding Trajectory in Temporal Interaction Networks},
author={Kumar, Srijan and Zhang, Xikun and Leskovec, Jure},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining},
year={2019},
organization={ACM}
}