EPANET file utility planned to read/load different types of EPANET files. The utilities will be provided in two forms:
- command line, text only utilities - one for each file type
- a GUI-based utility providing access to the output of all text based utilities. As text-based utilities are provided for different file types, support for them will also be added to the combined GUI-based utility.
Written for Python 2.6 and 2.7, with GUI using wxPython.
Written and tested on:
- MacOS X 10.9.1 using Python 2.7.5 and GUI using wxPython 3.0.0 (osx-cocoa)
- Windows Vista using Python 2.6.4 and 2.7.5 using wxPython 2.9.5
Requires the following Python packages for the Tables option:
- xlrd (0.9.2 used in development)
- xlwt (0.7.5 used in development)
- xlutils may also be required later (1.7.0 used in development)
To build the language template (.pot) file requires GNU gettext tools available from http://www.gnu.org/software/gettext/. Version 0.18.3.1 has been used on MacOS X.
Scripts for generating language template (.pot) file and testing the utilities are provided for MacOS (.sh) and Windows (.bat).
Functionality for reading other EPANET files is planned for the future, but at the moment, the only type of file read is:
- EPANET toolkit 2.00.12 binary output file (see details below)
A wxPython-based GUI is provided. To use this GUI, wxPython must be installed. Development has been done using versions 2.9.5 and 3.0.0 and it currently is expected to work on both.
Usage: python EPANETFileUtility.py
At startup, the user will currently be prompted to select an EPANET output
file which will then be loaded and its contents displayed. Three example files
are included in the test/data directory. These are the output files generated
for the Net1, Net2 and Net3 examples included with the EPANET software.
Some options are available on the left of the main window, but only the Data
and Export options have any contents.
The Data option displays a PropertyGridManager with 4 pages, viz:
- Prolog: properties read from the prolog of the output file
Node and link information is displayed in two
TreeListCtrls below - Energy Usage: a single property
Information for each pump is shown in a
TreeListCtrlbelow - Dynamic Results: a property grid containing analysis information
and summary information loaded by the demo plugin
Node and link information for each timestep is lazy-loaded and
displayed in two
TreeListCtrlsbelow - Epilog: a property grid
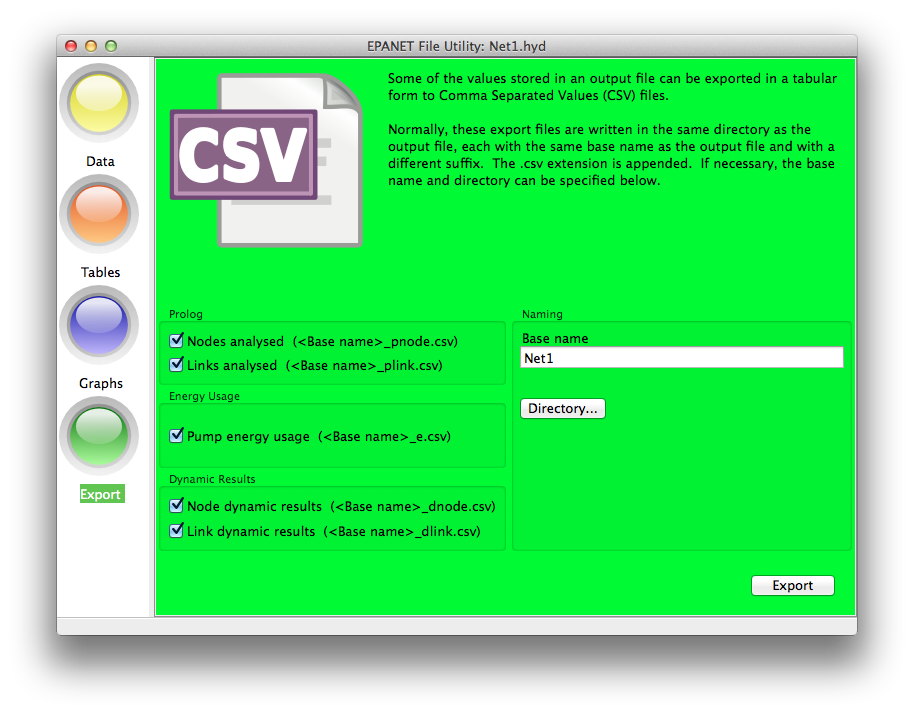
The Export option allows the tabular data from the various sections
of the output file to be exported to Comma Separated Value (CSV) files.
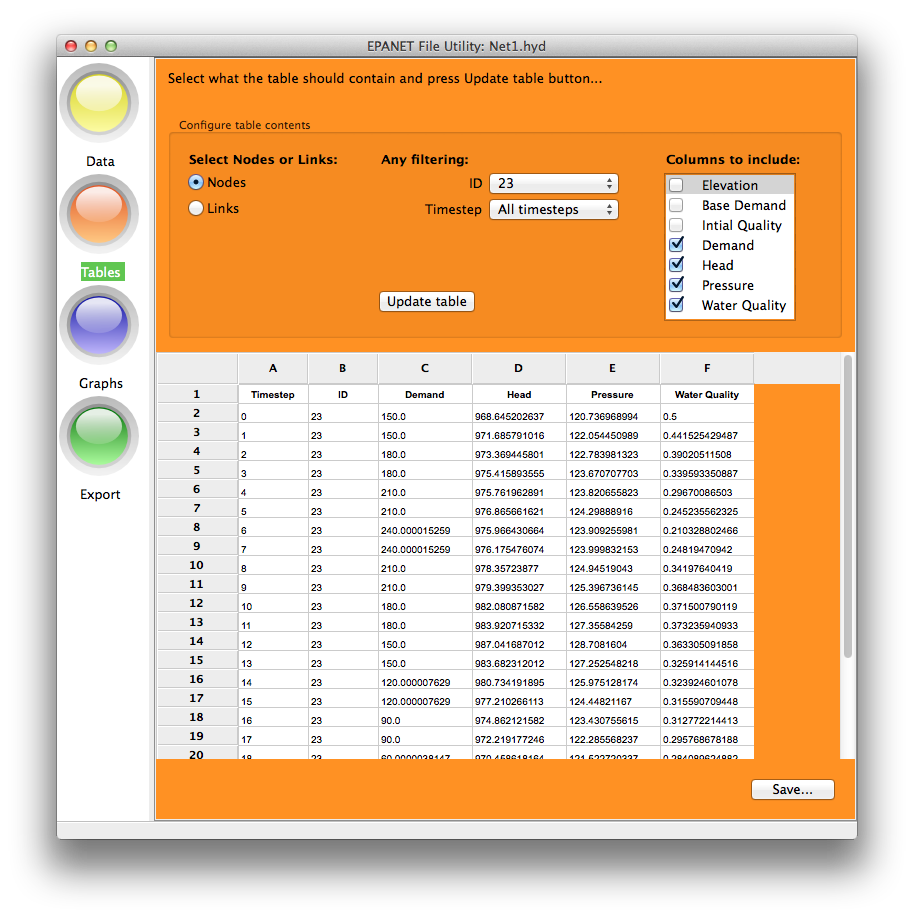
The Tables option allows display of node or link tables for one or all IDs and
one or all timesteps - up to a maximum of 65,536 rows. The Save button does
not work at present.
The Graphs option does not do anything at present.
Please feel free to make suggestions for improvements or to report defects.
-
EPANET toolkit 2.00.12 binary output file reader Loads binary output file (from EPANET toolkit hydraulic analysis) and displays contents or exports contents to CSV files. Supports plugins for extending functionality. Can be run as a standalone program as detailed below or imported to load files into memory for other uses. More details will be available in the doc/ directory soon.
Usage: python ReadEPANETOutputFile.py [Options] <outputfilename> Options: --version show program's version number and exit -h, --help show this help message and exit -a, --all display all output file sections (default) -s, --silent don't display any output file sections -p, --prolog display prolog section, -n PROLOG_NODE_CSV, --prolog_node_csv=PROLOG_NODE_CSV write CSV for nodes from prolog to PROLOG_NODE_CSV -l PROLOG_LINK_CSV, --prolog_link_csv=PROLOG_LINK_CSV write CSV for links from prolog to PROLOG_LINK_CSV -e, --energy_use display energy use section -E ENERGY_CSV, --energy_use_csv=ENERGY_CSV write CSV from energy use section to ENERGY_CSV -d, --dynamic_results display dynamic results section -N DYNAMIC_NODE_CSV, --dynamic_node_csv=DYNAMIC_NODE_CSV write CSV for nodes from dynamic results to DYNAMIC_NODE_CSV -L DYNAMIC_LINK_CSV, --dynamic_link_csv=DYNAMIC_LINK_CSV write CSV for links from dynamic results to DYNAMIC_LINK_CSV -c, --coda, --epilog display file epilog -v, --verbose display verbose outputAn example plugin is included in EPANETOutputFile/plugins/demo/init.py.
Tests can be run with test\runtests.bat on Windows or test/runtests.sh on MacOS X. This contains a typical command line and also shows the setting of the LANG environment variable.
Language can be specified by setting the LANG environment variable to the required locale (eg. en_AU for Australian English - the only translation included at present). This is necessary particularly for Windows where the Window/Python locale names do not match the Posix names, but specifying the Posix name in the LANG variable will make it work properly.
How to get an EPANET output file:
- With EPANET:
analyse the model with the settings required.
Do NOT close EPANET. Look in the%TEMP%directory for the newest file having a name starting withenand ending with.tmp. Copy this file somewhere useful with a meaningful name. - With WaterSums: analyse the model with
the settings required.
The EPANET output file will be written to the same directory
as the network file with the extension changed to
.hyd. This file is overwritten each time the analysis is performed, so if you want to keep a set of results, copy the file somewhere else. - Use the EPANET Toolkit to generate an output file.
EPANET output files can be large files. Their structure is described in the EPANET Toolkit Windows Help File.