This is a guide on how to work effectively together using GitHub.
After setup, here's how you manage the repo
cd professional-services/tools/anthosbm-ansible-module/
git fetch upstream
git checkout customer-lab-live
git rebase upstream/customer-lab-live
Use repo, tweaking files along the way. Then commit them and open a PR.
git add .
git commit -m "adding these great improvements"
git push -u origin customer-lab-live
Once pushed, navigate to the upstream repo: https://github.com/jimangel/professional-services and open a PR.
This repo, jimangel/professional-services forked from GoogleCloudPlatform/professional-services is the center / source of truth.
Team members will fork my fork and work from their own local forks.
Why this approach?
By allowing everyone to work out of their own local forks, it reduces the amount of permissions that need to be granted. It also reduces the likelihood of error on the main repo. Lastly, you can create your own branches for experimenting / testing without concern of impacting others.
mainbranch should never be used. That is only to pull changes from the upstream repo if needed.- Work out of your respective branch and I can merge as needed.
- Don't merge breaking changes
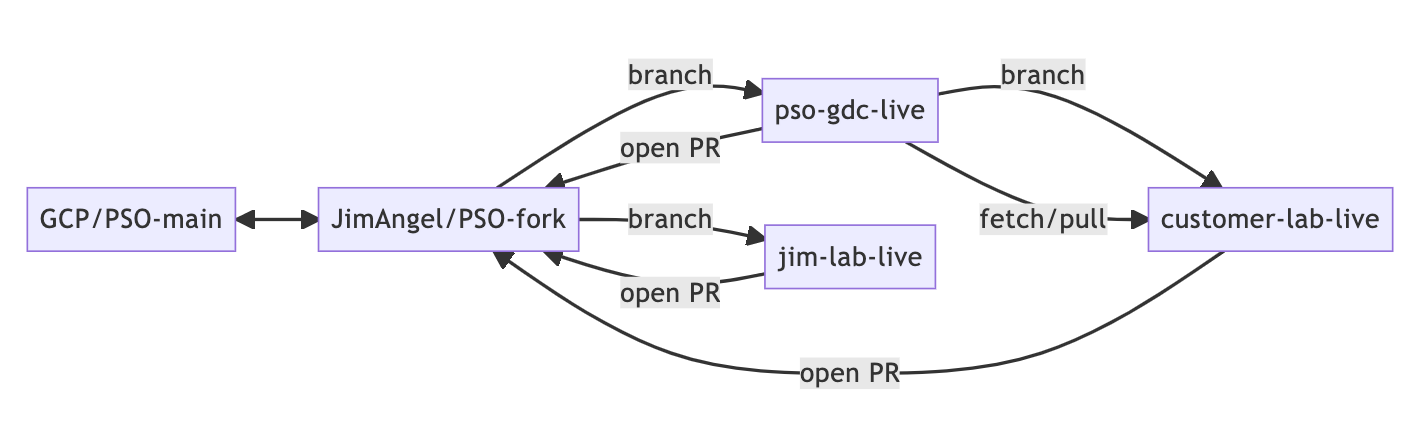
The following shows the upstream and my fork and how they relate to the 3 branches. The 3 branches exist in everyone's repo.
3 branches for our work:
pso-gdc-live- All changes from PSO GDC team
jim-lab-live- All changes from Jim, to be merged into
pso-gdc-liveASAP
- All changes from Jim, to be merged into
customer-lab-live- All changes from Broadcom team, based off of
pso-gdc-live
- All changes from Broadcom team, based off of
This is written from the customer perspective. How to use this repo effectively. Each cloned repo is configured to have an origin and an upstream repo.
origin is always your clone and the only repo we care about. upstream is used to pull in changes. You can check these settings at anypoint with git remote -v
-
Fork my repo to your own personal GitHub.
-
Setup your local working environment by cloning your fork to your working environment
# replace YOUR_USER with your username git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USER/professional-services.git cd professional-services -
Setup push/pull locations (upstream)
git remote add upstream https://github.com/jimangel/professional-services git remote set-url --push upstream no_push
Before doing any work navigate to the working repository and fetch the latest changes from upstream.
cd professional-services
- Ensure you're working with the latest information
# capture all upstream branches git fetch upstream # checkout working branch git checkout customer-lab-live # ensure no changes from pso git rebase upstream/customer-lab-live
After changes are made to the repository, we need to save (commit) them to your fork and open a PR against my upstream repo. It sounds more complex than it is.
-
View your changes
git statusYou should see only the files you've adjusted and nothing else. This is a good chance to check for any data / files you don't intend to commit.
-
Add your changes to single commit
# you can replace "." with specific files if concerned git add . -
Create a commit message
git commit -m "adding these great improvements" -
Push your commit to your fork
git push -u origin customer-lab-live
Once complete, open a PR in the GitHub UI.
There's a lot of examples / tools here, we only really care about:
professional-services/tools/anthosbm-ansible-module/