Flycheck checker for Clojure, using eastwood, core.typed and kibit via cider.
See this blog post for more.
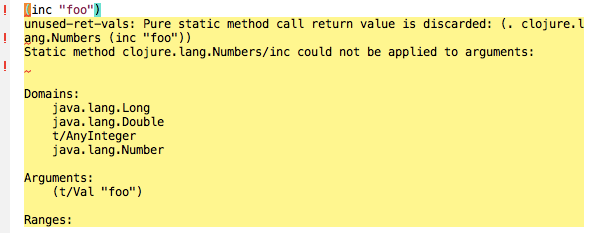
Read these warnings:
- It is assumed that you are familiar with each of these linters, so please read the their documentation. There, you will find additional warnings.
- Do not use
squiggly-clojureunless your code can be reloaded without side effects, as the linters will be reloading it repeatedly. - Eastwood and Kibit are typically run via lein plugins, and use within the REPL vm, as squiggly requires, is not officially supported. (Though in practice it works well.)
The package is available on Melpa:
M-x package-install flycheck-clojure
Alternatively, (1) clone this project and put its elisp/flycheck-clojure/ directory
on your path, or (2) download
this one file,
and install it wherever you like.
Add to your .emacs:
(eval-after-load 'flycheck '(flycheck-clojure-setup))
(add-hook 'after-init-hook #'global-flycheck-mode)Installing flycheck-pos-tip as well is strongly recommended, so that linting and type errors don't clash with cider's eldoc information.
M-x package-install flycheck-pos-tip
And add this to your .emacs:
(eval-after-load 'flycheck
'(setq flycheck-display-errors-function #'flycheck-pos-tip-error-messages))Alternatively to flycheck-pos-tip you can use flycheck-tip
M-x package-install flycheck-tip
In that case add to your .emacs:
(require 'flycheck-tip)
(flycheck-tip-use-timer 'verbose)Either way, you should now get the snazzy yellow post-it messages when the cursor is on a squiggly underline.
If you're used to flycheck but not used to cider, you may want
(add-hook 'cider-mode-hook
(lambda () (setq next-error-function #'flycheck-next-error-function)))to override the binding to ````cider-jump-to-compilation-error`.
The Clojure code used to invoke the various specific linters is in
If you're using a current release of Cider, then this dependency, along with all of Cider's will be injected automatically for you
upon cider-jack-in.
(Specifically, the dependencies will be added to cider-jack-in-dependencies unless you specifically disable it by
setting flycheck-clojure-inject-dependencies-at-jack-in to nil.)
If you want to cider-attach to a running repl, then you'll need to specify the proper dependencies in your
profiles.clj or to the project-specific
project.clj, as part of the :dependencies vector. E.g.
;; profiles.clj
{:repl {:plugins [[cider/cider-nrepl "A.B.C"] ;; subsitute A.B.C from Cider docs
;...
]
:dependencies [[acyclic/squiggly-clojure "x.y.z"] ;; substitute x.y.z from above
;...]}
}squiggly-clojure in turn depends pulls in dependency on
[org.clojure/core.typed "0.3.7"]
[jonase/eastwood "0.2.1" :exclusions [org.clojure/clojure]]
[jonase/kibit "0.1.2"]and core.typed requires clojure 1.7.0 or above, which is therefore a requirement of squiggly clojure; it is not currently possible to use squiggly clojure without
the availability of all three linters, even if you aren't using all of them. (Note that you do not need to list them explicitly.)
See the sample-project subdirectory for examples of the configuration methods
described below.
Squiggly Clojure comprises three Flycheck checkers, clojure-cider-typed,
clojure-cider-kibit and clojure-cider-eastwood. You may exclude one or
more of these by including them in the flycheck-disabled-checkers list.
This can be done via the Local Variables: block at the end of a .clj file,
e.g.
;; Local Variables:
;; flycheck-disabled-checkers: (clojure-cider-kibit)
;; End:but the following two methods are preferable for such persistent settings.
Add or merge
:plugins [[lein-environ "1.0.0"]]and set an :env option map that includes :squiggly , e.g.
{:env {:squiggly {:checkers [:eastwood]
:eastwood-exclude-linters [:unlimited-use]}}}Here, you specify included checkers, as :eastwood, :kibit or :typed. If you
set :eastwood-exclude-linters, it will be passed directly to Eastwood as described
in its documentation. This configuration will apply to all source files in the
project unless overridden by...
E.g.
(ns sample-project.core
{:squiggly {:checkers [:eastwood :typed]
:eastwood-exclude-linters [:unlimited-use]}}
(:require [clojure.core.typed])
(:use [clojure.stacktrace]) ;; warning suppressed by :eastwood-exclude-linters
)If set in the namespace metadata, the value of :squiggly fully overrides
anything set in the
project.clj: no fancy merging is performed.
And note that, if a checker is in flycheck-disabled-checkers, it will never
be invoked no matter what you set in Clojure code.
:checkers [:eastwood :typed :kibit]
:eastwood-exclude-linters [] # see Eastwood documentation
:eastwood-options {} # See Eastwood documentationNote that :eastwood-exclude-linters is here for backwards compatibility, and
specifying :eastwood-options {:exclude-linter [...]} would override it. If
you have really a lot of Eastwood options you want to specify, you can specify
:config:files in the :eastwood-options map and really go to town.
First, see the warnings above. The general theme is that we depend on three external linters, problems or incompatibilities with any of which might now manifest in emacs.
If something mysterious is happening, you may find it helpful to look at the
*nrepl-messages... buffers, where CIDER silently logs all traffic between EMACS
and Clojure. Among other things, you'll find here the Clojure expressions that
were evaluated to initiate the checking, e.g.
op "eval"
session "5f8764c8-3f2b-4871-9a26-766b4b5af314"
code "(do (require 'squiggly-clojure.core) (squiggly-clojure.core/check-tc 'sample-project.core))"
id "20"
You can see output from this command by looking for messages with the same id, e.g.
id "20"
ns "user"
session "5f8764c8-3f2b-4871-9a26-766b4b5af314"
value "\"[{\\\"line\\\":16,\\\"column\\\":3,\\\"file\\\":\\\"sample_project\\\\/core.clj\\\",\\\"level\\\":\\\"error\\\",\\\"msg\\\":\\\"Static method clojure.lang.Numbers\\\\/inc could not be applied to arguments:\\\\n\\\\n\\\\nDomains:\\\\n\\\\tNumber\\\\n\\\\nArguments:\\\\n\\\\t(clojure.core.typed\\\\/Val \\\\\\\"foo\\\\\\\")\\\\n\\\\nRanges:\\\\n\\\\tNumber\\\\n\\\\n\\\"},{\\\"line\\\":25,\\\"column\\\":13,\\\"file\\\":\\\"sample_project\\\\/core.clj\\\",\\\"level\\\":\\\"error\\\",\\\"msg\\\":\\\"Function range could not be applied to arguments:\\\\n\\\\n\\\\nDomains:\\\\n\\\\tNumber\\\\n\\\\nArguments:\\\\n\\\\tclojure.core.typed\\\\/Any\\\\n\\\\nRanges:\\\\n\\\\t(clojure.core.typed\\\\/ASeq clojure.core.typed\\\\/AnyInteger)\\\\n\\\\n\\\"}]\""
In this case, you can see that type-checking returned a map of results correctly.
If results are correctly returned in the REPL but are not displayed in the Emacs buffer, then there may be an elisp bug to report.
If you see something that looks like an error, you should reproduce it by running the Clojure expression directly from the REPL, e.g. in this case
(do (require 'squiggly-clojure.core) (squiggly-clojure.core/check-tc 'sample-project.core))If this returns an error, you should then try replicating outside the REPL using the linter's lein plugin. In the example above, that would be lein-typed, which must be installed separately.
If all linters work propertly outside of the REPL, there may be a reportable bug in the squiggly clojure
code, though historically it's usually turned out to be related to dependency conflicts between the linters
and the project being linted. Accordingly, when reporting a possible bug, please include the output of lein deps :tree
or lein with-profile something deps, where something is probably repl, as appropriate.
If, due to one of these or other problems, flycheck does not
receive the proper callbacks, it may be stuck in a state where it
will never try to check again. To reset (modulo some memory leaks perhaps)
try turning flycheck-mode off and then on.
- Deal better with catastrophic failure of a checker. Currently, we silently ignore exceptions.
- Performance optimizations: throttling and narrowing.