A SageMath package for computation of degree 2 Siegel modular forms
degree2 is a package written in pure Python.
Place it an appropriate directory so that SageMath can find the package.
In the following, we illustrate how we install this package in
"/sage_packages/". Of course the directory name may not be
"/sage_packages/".
-
First install SageMath.
-
Open a terminal.
In SageMathCloud, one can open a terminal by creating a new file whose file type is "Terminal".
-
Create the directory and clone the repository.
mkdir ~/sage_packages cd ~/sage_packages git clone https://github.com/stakemori/degree2.git cd degree2 git submodule init git submodule update
-
Edit the init script file of SageMath to load the package.
touch ~/.sage/init.sage cat ~/sage_packages/degree2/config/example_config.sage >> ~/.sage/init.sage
-
(Optional for vector valued Siegel modular forms) Set
degree2.vector_valued_impl.utils.data_dirto an existing directory. And download cache data for vector valued Siegel modular forms. For example, we use '/home/your_user_name/degree2_data/vector_valued' for the data directory.cd /home/your_user_name/degree2_data # And download vector_valued.tar.gz to this directory. tar xf vector_valued.tar.gz
Put the following lines to
~/.sage/init.sage.import degree2.vector_valued_impl.utils degree2.vector_valued_impl.utils.data_dir= '/home/your_user_name/degree2_data/vector_valued'
-
Siegel-Eisenstein of degree two can be obtained by the function
eisenstein_series_degree2. Siegel-Eisenstein series is normalized so that the constant term is one.sage: es4 = eisenstein_series_degree2(4, 10) sage: es4.prec 10 sage: es4[(2, 1, 3)] 2903040
The last line means that the Fourier coefficient of
es4at the half integral symmetric matrix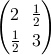 is 2903040.
The third lines means that
is 2903040.
The third lines means that es4knows Fourier coefficients of Siegel-Eisenstein series of weight 4 at half integral matrices whose maximum value of diagonal entries are less than or equal to 10. -
Igusa's weight 10 , 12 and 35 cusp forms can be obtained by the function
x10_with_prec,x12_with_precandx35_with_precrespectively. These functions take one positive integer argument. The meaning of the argument is same as the attributeprecofes4, i.e. it means that the returned value knows the Fourier coefficients at half integral matrices whose maximum value of diagonal entries are less than or equal to the argument.sage: x10 = x10_with_prec(10) sage: x12 = x12_with_prec(10) sage: x35 = x35_with_prec(10) sage: x10[(1, 1, 1)] 1 sage: x12[(1, 1, 1)] 1 sage: x35[(2, -1, 3)] 1 sage: x35[(5, 1, 4)] -759797709
-
One can add and multiply modular forms by
+and*.sage: es4 = eisenstein_series_degree2(4, 10) sage: es8 = eisenstein_series_degree2(8, 10) sage: es4 + es4 Siegel Modular form of weight 4 with prec = 10: {(0, 0, 0) : 2, (0, 0, 1) : 480, (1, 0, 0) : 480, (1, 0, 1) : 60480, ... (10, 0, 0) : 544320} sage: 2*es4 == es4 + es4 True sage: es8 == es4 * es4 True sage: es8 == es4^2 True
-
One can create the space of Klingen-Eisenstein series and cusp forms by the function
KlingenEisensteinAndCuspForms.sage: N47 = KlingenEisensteinAndCuspForms(47, 8) sage: N47.dimension() 3 sage: N47.prec 8
Here
N47is the space of Klingen-Eisenstein series and cusp forms of weight 47, which is equal to the space of cusp forms of weight 47 because 47 is odd. Last line means eachprecof the basis ofN47is 8.One can compute the matrix of Hecke operator T(m) (m: a prime or a square of a prime) by the function
N47.hecke_matrix.sage: A = N47.hecke_matrix(2); A [ -69045420294144 8646128852105428992 -33244506086178816000] [ 7688192 -53094861766656 17259429888000] [ -16719872 26329615958016 -58220441763840] sage: f = A.charpoly(); f x^3 + 180360723824640*x^2 + 9700267079136838378586112000*x + 157899144590481648119705809591468032000000 sage: f.is_irreducible() True sage: K.<a> = NumberField(f); K Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^3 + 180360723824640*x^2 + 9700267079136838378586112000*x + 157899144590481648119705809591468032000000
Here
fis the characteristic polynomial of T(2) acting onN47andKis the number field generated by a rootaoff.One can obtain an eigenform of weight 47 by the function
N47.eigenform_with_eigenvalue_t2.sage: x47 = N47.eigenform_with_eigenvalue_t2(a)
Here
x47is the weight 47 cusp form whose eigenvalue of T(2) isa.sage: x47[(2, 1, 3)] 9031680*a + 526277673739804999680 sage: x47._construction (-16719872*a - 685312149824691240960)*es4^3*x35 + (7688192*a + 159034476084886241280)*es6^2*x35 + (a^2 + 111315303530496*a + 2636772146839387523556311040)*x12*x35
The attribute
_constructionshows howx47is constructed as a polynomial of Siegel-Eisenstein series of weight 4, 6 and cusp forms of weight 10, 12 and 35. -
To construct the space of vector valued Siegel modular forms of weight det^* Sym(j), where j = 2, 4, 10, one can use the function
vector_valued_siegel_modular_formsin the moduledegree2.vector_valued_smfs. This function uses structure theorems of weights det^* Sym(j) for j = 2, 4, 10. Structure theorems are known if j = 6, 8, but I have not implemented them yet.The following code illustrate how one can construct a basis of the space of Siegel modular forms of weight det^13 Sym(10).
sage: from degree2.vector_valued_smfs import vector_valued_siegel_modular_forms as vvsmf sage: M = vvsmf(10, 13, prec=6) sage: M.dimension() 2 sage: M.basis() [Vector valued modular form of weight det^13 Sym(10) with prec = diag_max 6, Vector valued modular form of weight det^13 Sym(10) with prec = diag_max 6] sage: f = M.basis()[0] sage: f[(2, 1, 3)] (0, 1574304, 7610976, 33371712, 42535584, -3229632, 47605824, 112992768, -22784544, -10237632, -2096640) sage: f[(2, 1, 3)][1] 1574304
One can construct Hecke eigenforms in a similar way to the scalar valued case.
sage: M.hecke_charpoly(2).factor() (x - 84480) * (x + 52800) sage: g = M.eigenform_with_eigenvalue_t2(84480) sage: g.euler_factor_of_spinor_l(2).factor() (1 - 133632*x + 8589934592*x^2) * (1 + 49152*x + 8589934592*x^2)
The function
vector_valued_siegel_modular_formsuses Python's modulemultiprocessing. Sometimes it consumes much memory. To avoid multi-processing, use the following with statement.sage: with degree2_number_of_procs(1): ....: N = vvsmf(10, 20, prec=10) ....: h = N.basis()[0]
Licensed under the [GPL Version 3][GPL] [GPL]: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html