Open source web app to publish documentation or books.
We've used this builderbook project to build:
- Async - communication tool for small teams of software developers
- Builder Book - learn how to build full-stack web apps from scratch
- SaaS Boilerplate - open source web app to build your own SaaS product
- As learning material for React/Material-UI/Next/Express/Mongoose/MongoDB stack
- As learning material for Google/Github/AWS SES/Mailchimp/Stripe APIs.
- As starting point for your own project. Use the code in book/1-begin or book/1-end as a lean boilerplate or modify the final app.
- As a production-ready web app to publish documentation or sell content on your own website (we sell our own book).
- Showcase
- Run locally
- Add a new book
- Add your own styles
- Deploy
- Deploy to Heroku
- Scaling
- Screenshots
- Built with
- Docker
- Contributing
- Team
- License
- Project structure
Check out projects built with the help of this open source app. Feel free to add your own project by creating a pull request.
- Retaino by Earl Lee : Save, annotate, review, and share great web content. Receive smart email digests to retain key information.
- SaaS boilerplate app: Open source web app that saves you weeks of work when building your own SaaS product.
- Harbor: Open source web app that allows anyone with a Gmail account to automatically charge for advice sent via email.
- Async: asynchronous communication and project management tool for small teams of software engineers.
- Clone the project and run
yarnto add packages. - Before you start the app, create a
.envfile at the app's root. This file must have values for some env variables specified below.-
To get
MONGO_URL_TEST, we recommend a free MongoDB at MongoDB Atlas (to be updated soon with MongoDB Atlas, see issue). -
Get
Google_clientIDandGoogle_clientSecretby following official OAuth tutorial.Important: For Google OAuth app, callback URL is: http://localhost:8000/oauth2callback
Important: You have to enable Google+ API in your Google Cloud Platform account. -
Specify your own secret key for Express session
SESSION_SECRET: https://github.com/expressjs/session#secret
-
To use all features and third-party integrations (such as Stripe, Google OAuth, Mailchimp), add values for all of the following env variables in your .env file:
.env :
# Used in server/app.js
MONGO_URL="xxxxxx"
MONGO_URL_TEST="xxxxxx"
SESSION_SECRET="xxxxxx"
# Used in server/google.js
Google_clientID="xxxxxx"
Google_clientSecret="xxxxxx"
# Used in server/aws.js
Amazon_accessKeyId="xxxxxx"
Amazon_secretAccessKey="xxxxxx"
Amazon_region="xxxxxx"
# Used in server/models/User.js
EMAIL_SUPPORT_FROM_ADDRESS="xxxxxx"
----------
# All environmental variables above this line are required for successful sign up
# Used in server/github.js
Github_Test_ClientID="xxxxxx"
Github_Test_SecretKey="xxxxxx"
Github_Live_ClientID="xxxxxx"
Github_Live_SecretKey="xxxxxx"
# Used in server/stripe.js
Stripe_Test_SecretKey="xxxxxx"
Stripe_Live_SecretKey="xxxxxx"
# Used in server/mailchimp.js
MAILCHIMP_API_KEY="xxxxxx"
MAILCHIMP_REGION="xxxxxx"
MAILCHIMP_SIGNUPS_LIST_ID="xxxxxx"
MAILCHIMP_PURCHASED_LIST_ID="xxxxxx"
MAILCHIMP_TUTORIALS_LIST_ID="xxxxxx"
-
Start the app with
GA_TRACKING_ID=xxxxxx StripePublishableKey=xxxxxx yarn dev.- To get
GA_TRACKING_ID, set up Google Analytics and follow these instructions to find your tracking ID. - To get
StripePublishableKey, set up Stripe and find your key here.
Env keys
GA_TRACKING_IDandStripePublishableKeyare universally available (client and server). Env keys inside.envfile are used in server code only. - To get
-
The first registered user in the app becomes an Admin user (user document gets parameters
"isAdmin": true).
-
Create a new Github repo (public or private).
-
In that repo, create an
introduction.mdfile and write some content. -
At the top of your
introduction.mdfile, add metadata in the format shown below. See this file as an example.--- title: Introduction seoTitle: title for search engines seoDescription: description for search engines isFree: true --- -
Go to the app, click "Connect Github".
-
Click "Add Book". Enter details and select the Github repo you created.
-
Click "Save".
When you add new .md files or update content, go to the BookDetail page of your app and click Sync with Github.
Important: All .md files in your Github repo must have metadata in the format shown above.
Important: All .md files in your Github repo must have name introduction.md or chapter-N.md.
To make the content of a .md file private (meaning a person must purchase the content to see it), remove isFree:true and add excerpt:"". Add some excerpt content - this content is public and serves as a free preview.
To change the color scheme of this app, modify the primary and secondary theme colors inside lib/context.js. Select any colors from Material UI's official color palette.
Recommended ways to add your own styles to this app:
- Inline style for a single element
- Reusable style for multiple elements within single page or component
- Reusable/importable style for multiple pages or components
- Global style for all pages in application
USE CASE: apply a style to one element on a single page/component
For example, in our book page, we wrote this single inline style:
<p style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>
...
</p>
USE CASE: apply the same style to multiple elements on a single page/component.
For example, in our tutorials page, we created styleExcerpt and applied it to a <p> element within the page:
const styleExcerpt = {
margin: '0px 20px',
opacity: '0.75',
fontSize: '13px',
};
<p style={styleExcerpt}>
...
</p>
USE CASE: apply the same style to elements on multiple pages/components.
For example, we created styleH1 inside components/SharedStyles.js and exported the style at the bottom of the file:
const styleH1 = {
textAlign: 'center',
fontWeight: '400',
lineHeight: '45px',
};
module.exports = {
styleH1,
};
We then imported styleH1 into our book page, as well as our index page, and applied the style to a <h1> element:
import {
styleH1,
} from '../components/SharedStyles';
<h1 style={styleH1}>
...
</h1>
USE CASE: apply the same style to elements on all pages of your app.
Create your style in pages/_document.js. For example, we specified a style for all hyperlinks that use the <a> element:
<style>
{`
a, a:focus {
font-weight: 400;
color: #1565C0;
text-decoration: none;
outline: none
}
`}
</style>
We also specified styles for all content inside a <body> element:
<body
style={{
font: '16px Muli',
color: '#222',
margin: '0px auto',
fontWeight: '400',
lineHeight: '1.5em',
backgroundColor: '#F7F9FC',
}}
>
</body>
IMPORTANT: Now v1 is depreciated for new users. See the next section about deploying to Heroku.
- Install now:
npm install -g now. - Point your domain to Zeit world nameservers: three steps.
- Create
now.jsonfile. Make sure to add actual values forGA_TRACKING_ID,StripePublishableKey(production-level) andalias. Read more about how to configure now.
{
"version": 1
"env": {
"NODE_ENV": "production",
"GA_TRACKING_ID": "xxxxxx",
"StripePublishableKey": "xxxxxx"
},
"dotenv": true
"alias": "mydomain.com",
"scale": {
"sfo1": {
"min": 1,
"max": 1
}
}
}
- Make sure you updated
ROOT_URLvalue inpackage.jsonandlib/getRootURL.js. - Check that you have all production-level env variables in
.env. - In your terminal, deploy the app by running
now. - Now outputs your deployment's URL, for example:
builderbook-zomcvzgtvc.now.sh. - Point successful deployment to your domain with
now aliasornow ln NOW_URL mydomain.com(NOW_URLis URL of your deployment).
In this section we will learn how to deploy our app to Heroku cloud. We will deploy our React-Next-Express app to lightweight Heroku container called dyno.
Instructions are for app located at /book/8-end.
Adjust route if you are deploying app from the root of this public repo.
We will discuss the following topics in this section:
- installing Heroku on Linux-based OS
- creating app on Heroku dashboard
- preparing app for deployment
- configuring env variables
- deploying app
- checking logs
- adding custom domain
Let's go step by step.
- Install Heroku CLI (command-line interface) on your OS. Follow the official guide. In this book we provide instructions for Linux-based systems, in particular, a Ubuntu OS. For Ubuntu OS, run in your terminal:
sudo snap install --classic heroku
To confirm a successful installation, run:
heroku --version
As example, my output that confirms successful installation, looks like:
heroku/7.22.7 linux-x64 node-v11.10.1
-
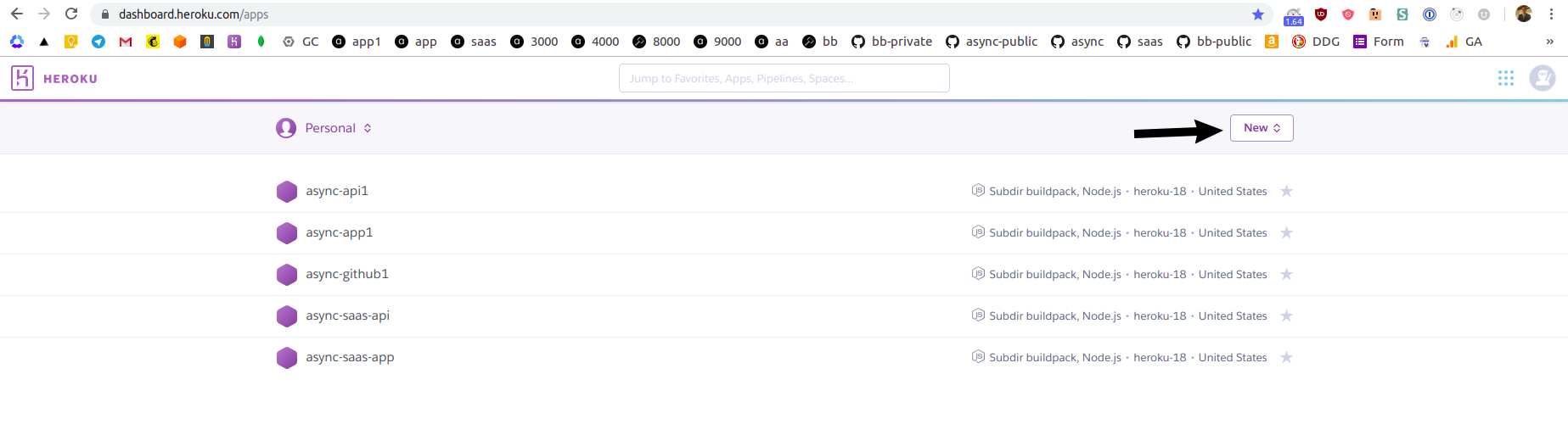
Sign up for Heroku, go to your Heroku dashboard and click purple New button on the right:
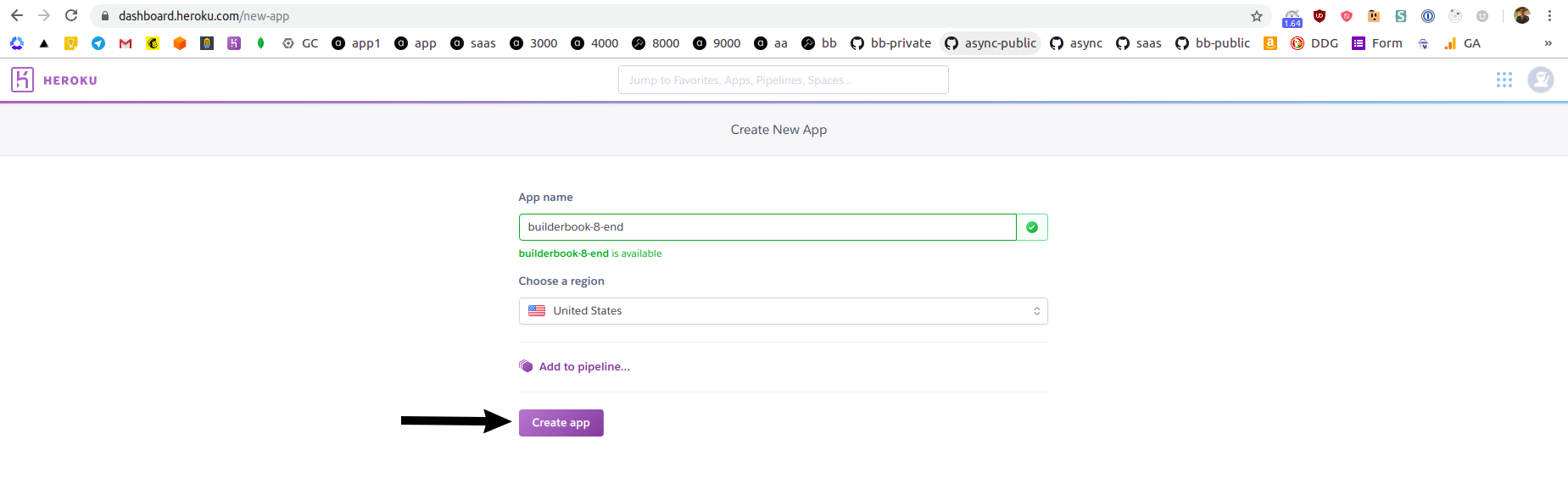
On the next screen, give a name to your app and select a region. Click purple Create app button at the bottom:
You will be redirected to
Deploytab of your newly created Heroku app: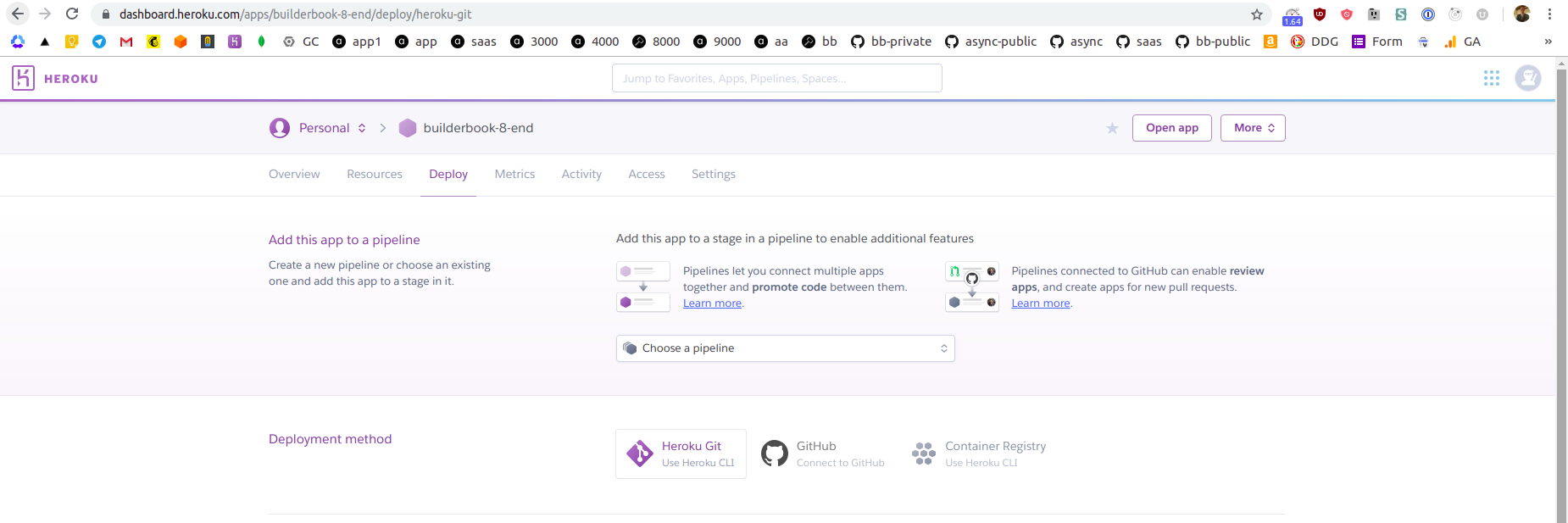
-
As you can see from the above screenshot, you have two options. You can deploy the app directly from your local machine using Heroku CLI or directly from GitHub. In this tutorial, we will deploy a
builderbook/builderbook/book/8-endapp from our public builderbook/builderbook repo hosted on GitHub. Deploying from a private repo will be a similar process.Deploying from GitHub has a few advantages. Heroku uses git to track changes in a codebase. It's possible to deploy app from the local machine using Heroku CLI, however you have to create a Git repo for
builderbook/builderbook/book/8-endwithpackage.jsonfile at the root level. A first advantage is that we can deploy from a non-root folder using GitHub instead of Heroku CLI.A second advantage is automation, later on you can create a branch that automatically deploy every new commit to Heroku. For example, we have a deploy branch for our demo for SaaS boilerplate. When we commit to
masterbranch - there is no new deployment, when we commit todeploybranch - new change is automatically deployed to Heroku app.Let's set up deploying from GitHub. On
Deploytab of your Heroku app at Heroku dashboard, click Connect to GitHub, then search for your repo, then click Connect next to the name of the proper repo: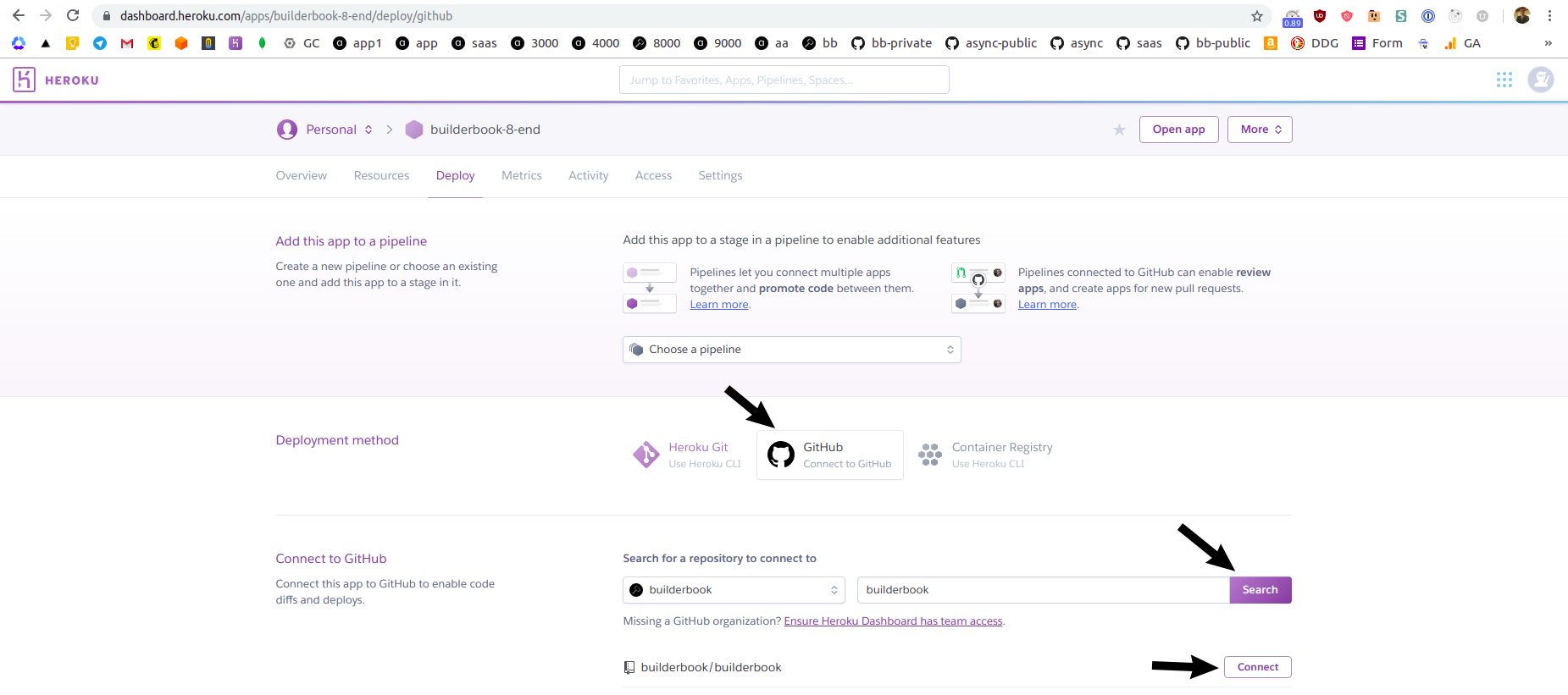
If successful, you will see green text
Connectedand be offered to select a branch and deploy app automatically or manually. Automatic deployment will deploy every new commit, manual deployment requires you to manually click on Deploy Branch button. For simplicity, we will deploy manually frommasterbranch of ourbuilderbook/builderbookrepo.Before we perform a manual deployment via GitHub, we need Heroku to run some additional code while app is being deploying. Firstly, we need to tell Heroku that
8-endapp in thebuilderbook/builderbookrepo is not at the root level, it's actually nested at/book/8-end. Secondly, Heroku needs to know that our app is Node.js app so Heroku findspackage.jsonfile, properly installs dependencies and runs proper scripts (such asbuildandstartscripts frompackage.json). To achieve this, we need to add so calledbuildpacksto our Heroku app. ClickSettingstab, scroll toBuildpackssection and click purple Add buildpack button: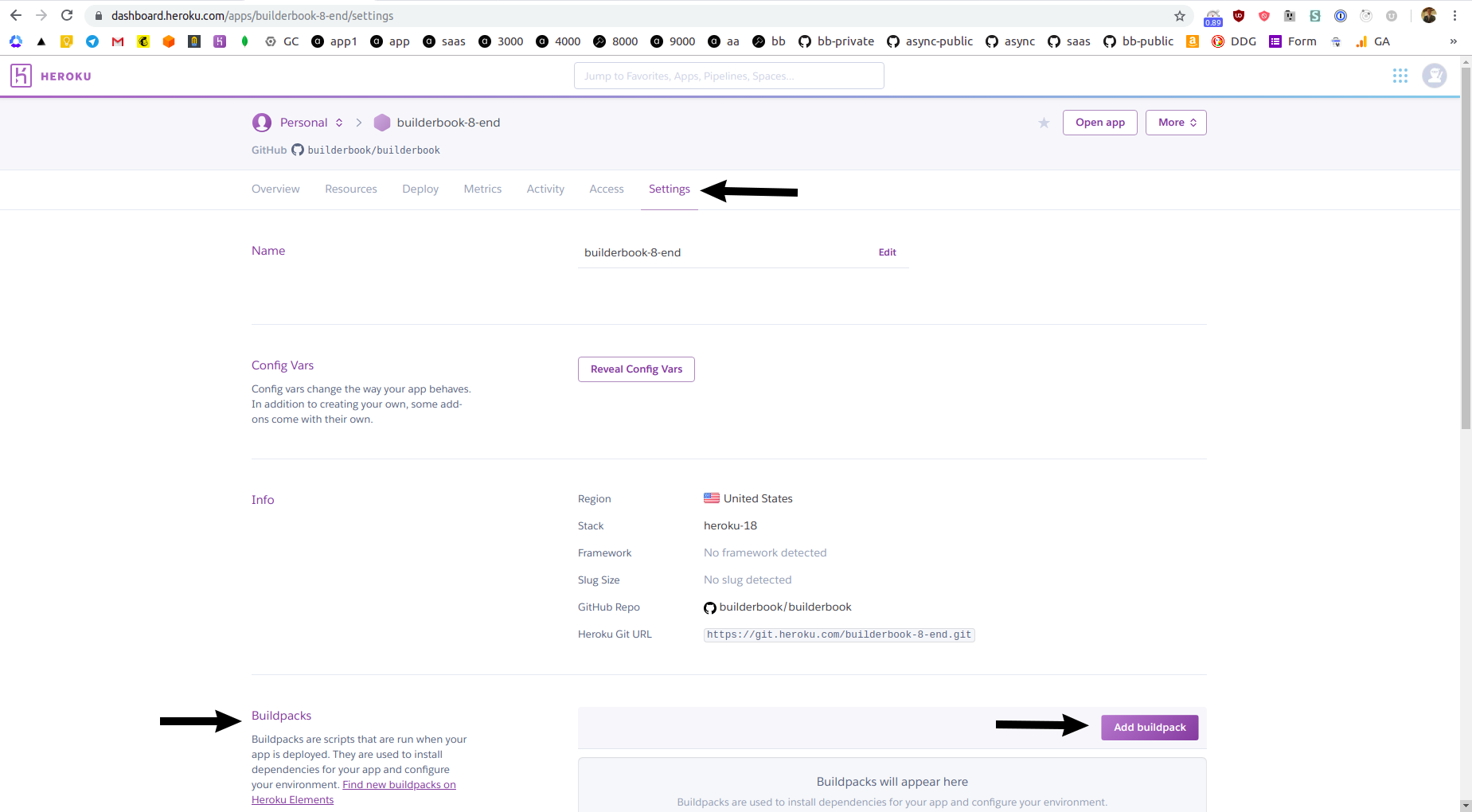
Add two buildpacks, first is
https://github.com/timanovsky/subdir-heroku-buildpackand second isheroku/nodejs: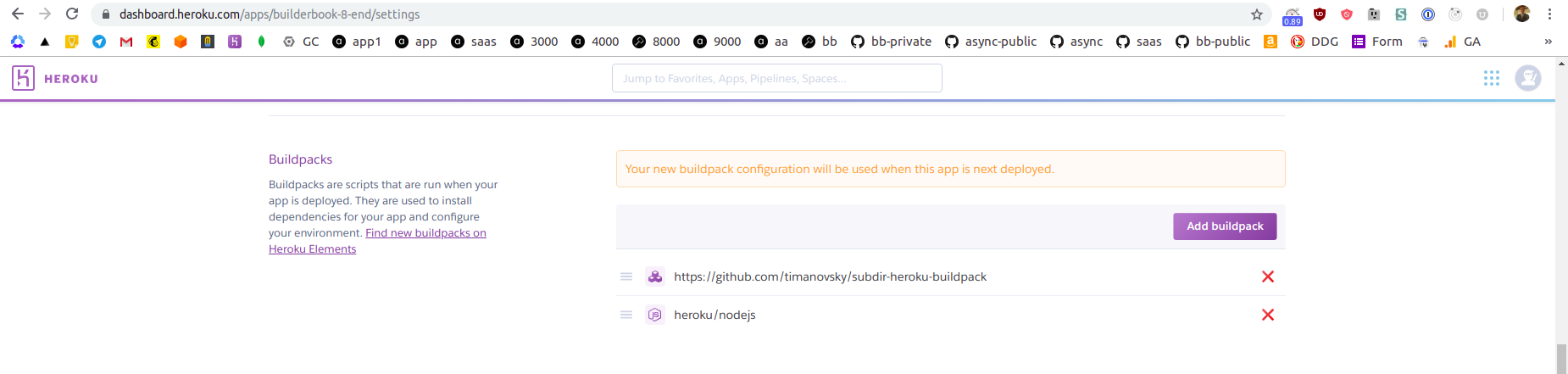
Next, scroll up while on
Settingstab and click purple Reveal Config Vars button, create a new environmental variablePROJECT_PATHwith valuebook/8-end: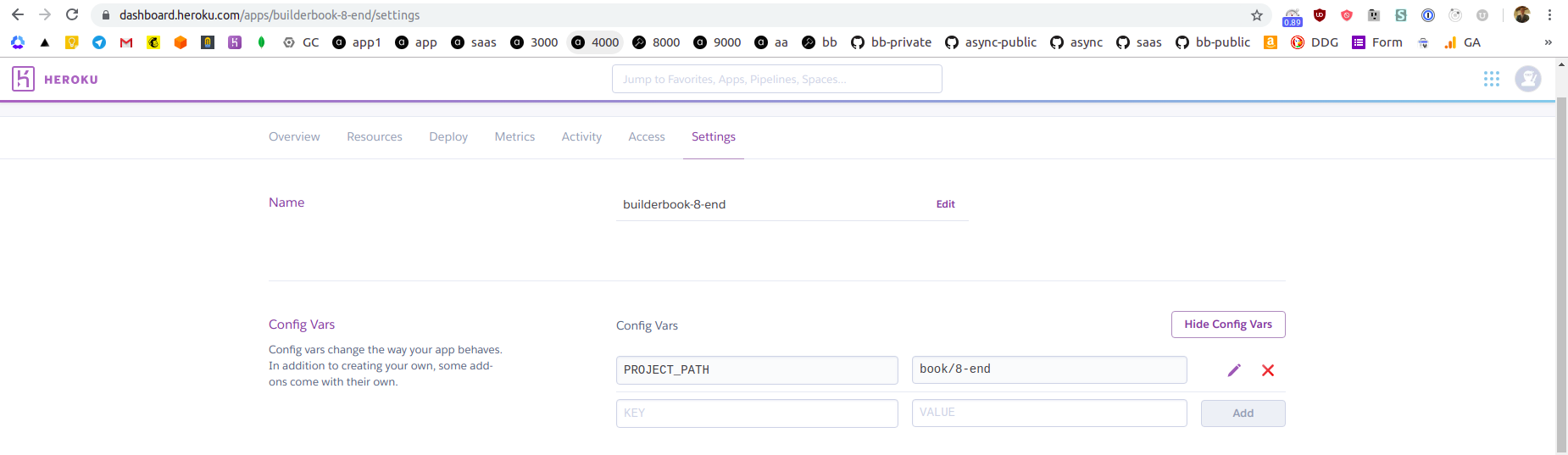
The above variable will be used by the first buildpack
subdir-heroku-buildpackto deploy app from repo's subdirectory. -
If we deploy app at this point, our app will deploy with errors since we did not add environmental variables. Similar to how you added
PROJECT_PATHvariable, add all environmental variables frombook/8-end/.envfile to your Heroku app. Remember to add:
MONGO_URL,Google_clientID,Google_clientSecret,EMAIL_SUPPORT_FROM_ADDRESS,Github_Test_ClientID,Github_Test_SecretKey,Github_Live_ClientID,Github_Live_SecretKey,Stripe_Test_SecretKey,Stripe_Live_SecretKey,MAILCHIMP_API_KEY,MAILCHIMP_PURCHASED_LIST_ID,SESSION_SECRET.
-
While on
Settingstab, scroll toDomains and certificatessection and note your app's URL. My app's URL is: https://builderbook-8-end.herokuapp.com Let's deploy, go toDeploytab, scroll toManual deploysection and click Deploy branch button. After deployment process is complete , navigate to your app's URL: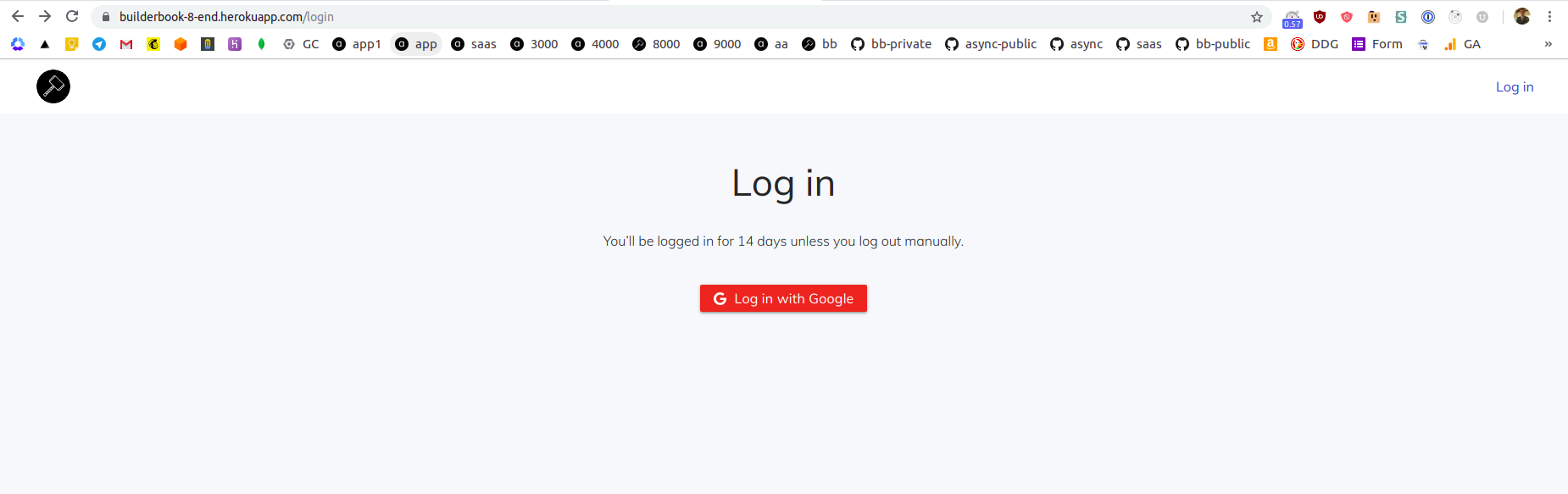
-
Server logs are not available on Heroku dashboard. To see logs, you have to use Heroku CLI. In your terminal, run:
heroku login
Follow instructions to log in to Heroku CLI.
After successful login, terminal will print:
Logged in as email@domain.com
Where
email@domain.comis an email address that you used to create your Heroku account.To see logs, in your terminal run:
heroku logs --app builderbook-8-end --tail
In your terminal, you will see your most recent logs and be able to see a real-time logs.
You can output certain number of lines (N) for retrieved logs by adding
--num Nto theheroku logscommand. You can print only app's logs by adding--source appor system's logs by adding--source heroku. -
Time to add a custom domain. The Heroku app that we created is deployed on
free dyno. Free dyno plan does not let you to add a custom domain to your app. To add custom domain, go toResourcestab and click purple Change Dyno Type button: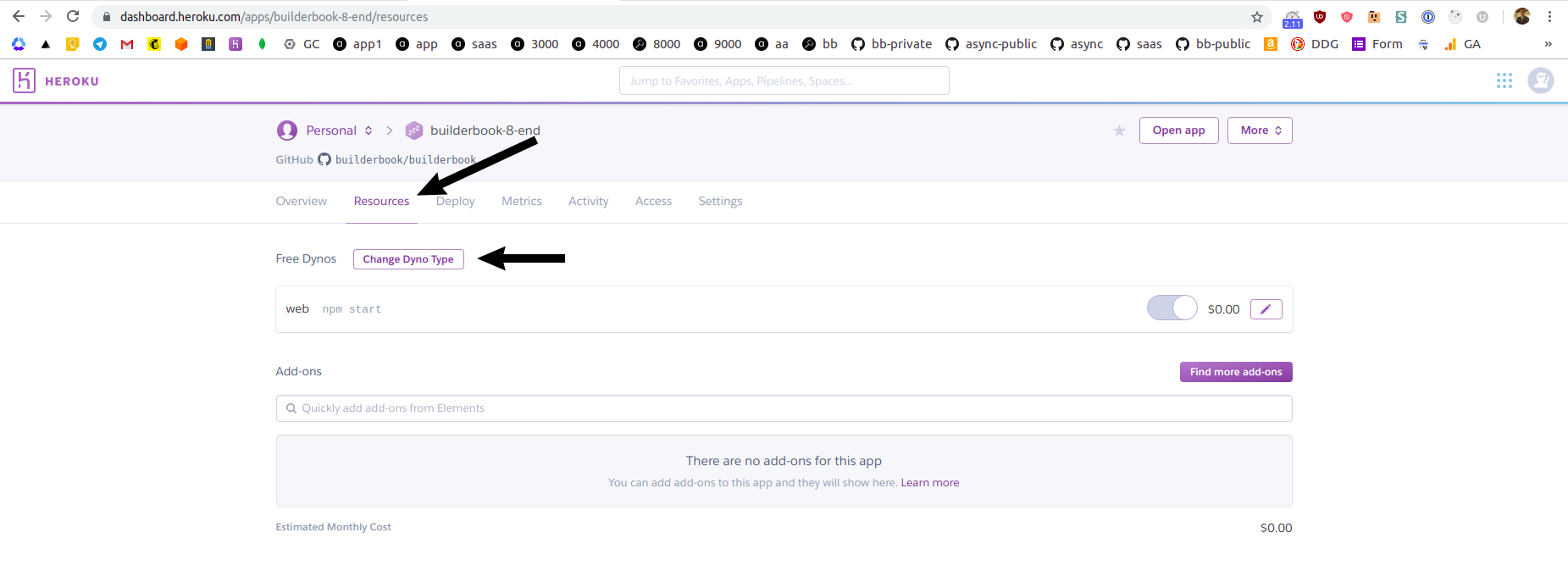
Select a
Hobbyplan and click Save button.Navigate to
Settingstab and scroll to theDomains and certificatesand click purple Add domain button: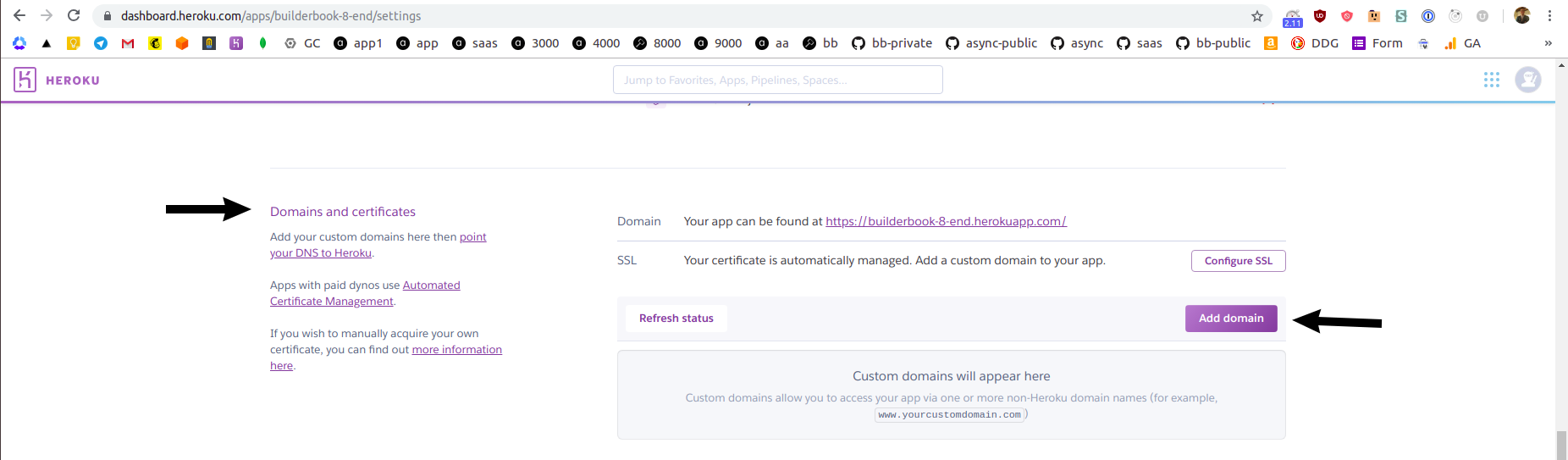
Type your custom domain name, I added
heroku.builderbook.orgas a custom domain, click Save changes button.Heroku will displa you a value for CNAME record that you have to create for your custom domain. For me, custom domain is `heroku.builderbook.org and I manage DNS records at Now by Zeit.
After you create a CNAME, ACM status on Heroku's dashboard will change to
Ok: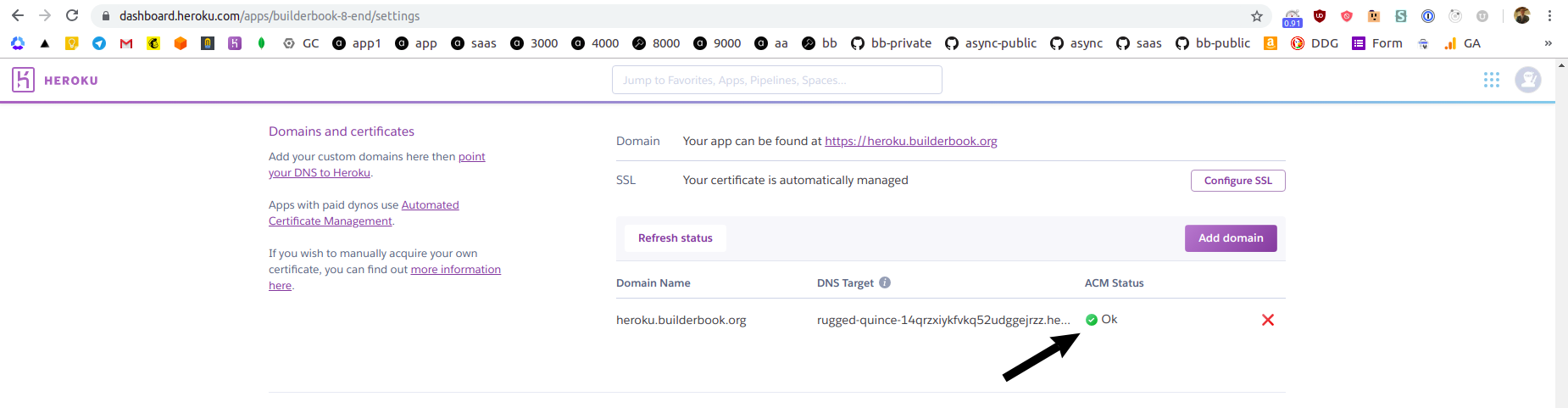
It's important that you remember to manually add your custom domain to the settings of your Google OAuth app (Chapter 3) and GitHub OAuth app (Chapter 6). If you forget to do it, you will see errors when you try to log in to your app or when you try to connect GitHub to your app.
You may want to consider splitting single Next/Express server into two servers:
- Next server for serving pages, server-side caching, sitemap and robots
- Express server for internal and external APIs
Here is an example of web application with split servers: https://github.com/async-labs/saas
Splitting servers will get you:
- faster page loads since Next rendering does not block internal and external APIs,
- faster code reload times during development,
- faster deployment and more flexible scaling of individual apps.
Chapter excerpt with Buy Button for Public/Guest visitor:
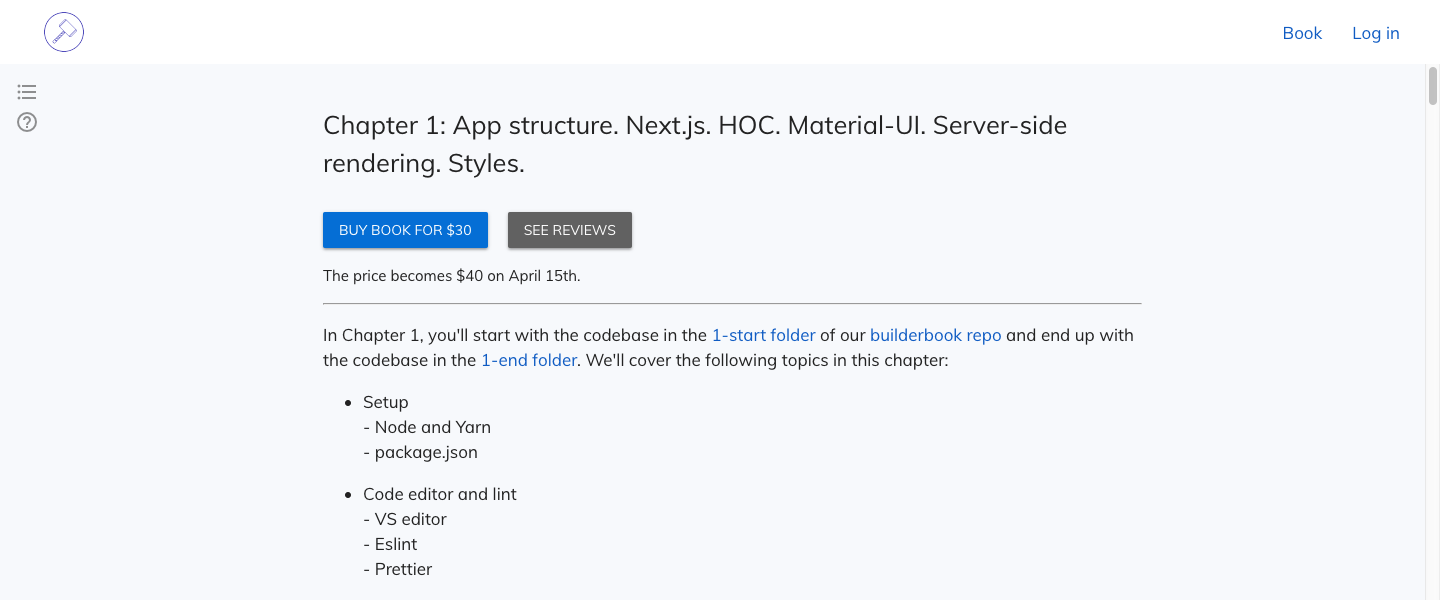
Chapter content and Table of Contents for book Customer:

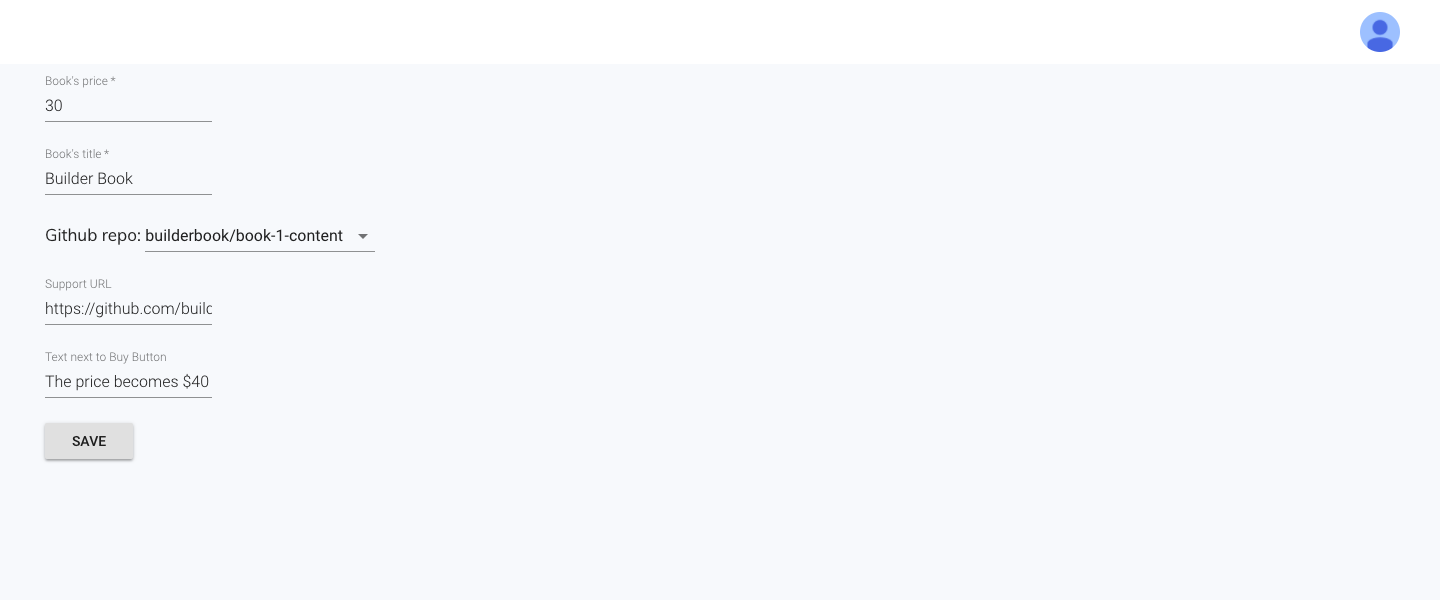
Add-book/Edit-book page for Admin user:
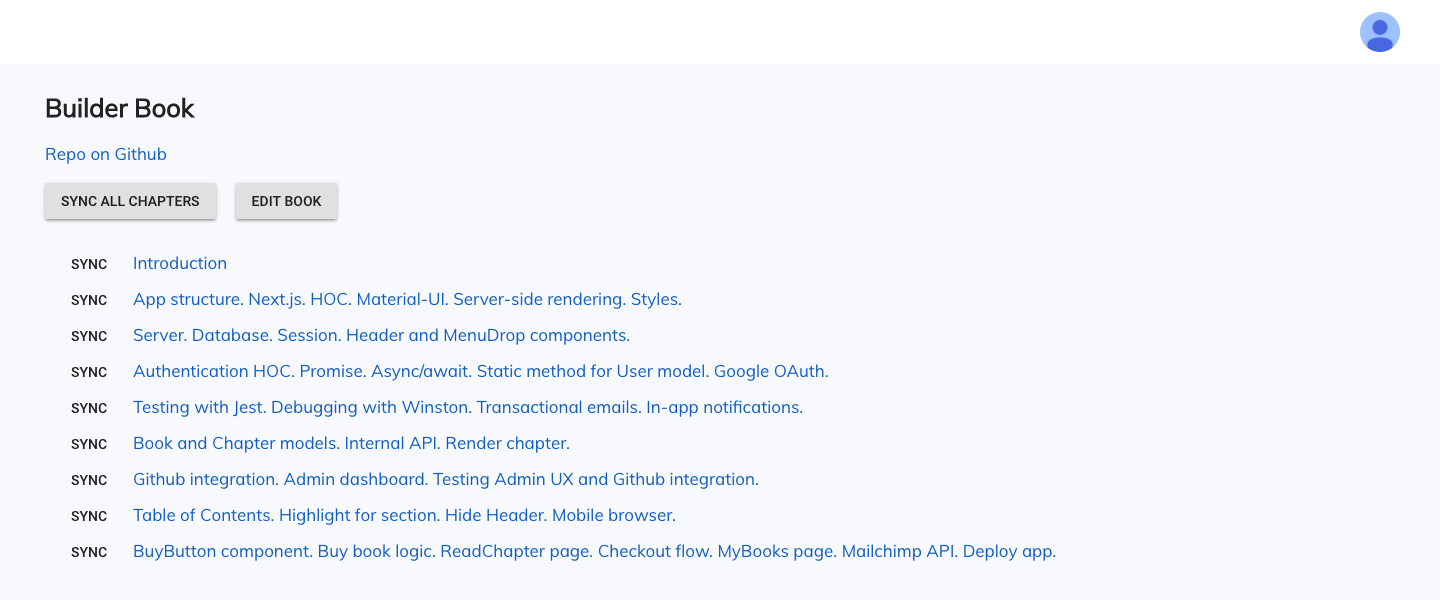
Book-detail page for Admin user:
- Google OAuth
- Github
- AWS SES
- Stripe
- MailChimp
Check out package.json.
- Install Docker and Docker Compose
- Modify
docker-compose-dev.ymlfile - If using Ubuntu, follow these steps: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38775954/sudo-docker-compose-command-not-found
- Start app with
docker-compose -f docker-compose-dev.yml up
We welcome suggestions and pull requests, especially for issues labeled as discussion and contributions welcome.
By participating in this project, you are expected to uphold Builder Book's Code of Conduct.
Want to support this project? Sign up at async and/or buy our books, which teach you how to build web apps from scratch. Also check out our open source SaaS boilerplate.
You can contact us at team@builderbook.org
If you want to hire us to add custom features on top of our SaaS boilerplate, please fill out our form.
All code in this repository is provided under the MIT License.
.
├── book # Codebases for each chapter of our book
├── components # React components
│ ├── admin # Components used on Admin pages
│ │ ├── EditBook.js # Edit title, price, and repo of book
│ │ ├── GiveFreeBook.js # Give free book to user
│ ├── customer # Components used on Customer pages
│ │ ├── Bookmark.js # Bookmark a section within a book chapter
│ │ ├── BuyButton.js # Buy book
│ ├── BookReviews.js # Component that outputs grid of reviews
│ ├── Header.js # Header component
│ ├── HomeFooter.js # Footer component on homepage
│ ├── HomeHeader.js # Header component on homepage
│ ├── MenuDrop.js # Dropdown menu
│ ├── Notifier.js # In-app notifications for app's users
│ ├── SubscribeForm.js # Form to subscribe to MailChimp newsletter
│ ├── TOC.js # Table of Contents
├── lib # Code available on both client and server
│ ├── api # Client-side API methods
│ │ ├── admin.js # Admin user methods
│ │ ├── customer.js # Customer user methods
│ │ ├── getRootURL.js # Returns ROOT_URL
│ │ ├── public.js # Public user methods
│ │ ├── sendRequest.js # Reusable code for all GET and POST requests
│ ├── SharedStyles.js # List of _reusable_ styles
│ ├── context.js # Context for Material-UI integration
│ ├── env.js # Universal config for environmental variables
│ ├── gtag.js # Universal config for Google Analytics
│ ├── notifier.js # Contains notify() function that loads Notifier component
│ ├── withAuth.js # HOC that passes user to pages and more
│ ├── withLayout.js # HOC for SSR with Material-UI and more
├── pages # Pages
│ ├── admin # Admin pages
│ │ ├── add-book.js # Page to add a new book
│ │ ├── book-detail.js # Page to view book details and sync content with Github
│ │ ├── edit-book.js # Page to update title, price, and repo of book
│ │ ├── index.js # Main Admin page that has all books and more
│ ├── customer # Customer pages
│ │ ├── my-books.js # Customer's dashboard
│ ├── public # Public pages (accessible to logged out users)
│ │ ├── login.js # Login page
│ │ ├── read-chapter.js # Page with chapter's content
│ ├── _document.js # Allows to customize pages (feature of Next.js)
│ ├── book.js # Book page
│ ├── index.js # Homepage
│ ├── tutorials.js # Tutorials page
├── server # Server code
│ ├── api # Express routes, route-level middleware
│ │ ├── admin.js # Admin routes
│ │ ├── customer.js # Customer routes
│ │ ├── index.js # Mounts all Express routes on server
│ │ ├── public.js # Public routes
│ │ ├── sync-all-inside-fork.js # Sync all book chapters in forked process
│ │ ├── sync-one-inside-fork.js # Sync single book chapter in forked process
│ ├── models # Mongoose models
│ │ ├── Book.js # Book model
│ │ ├── Chapter.js # Chapter model
│ │ ├── EmailTemplate.js # Email Template model
│ │ ├── Purchase.js # Purchase model
│ │ ├── Review.js # Book Reviews model
│ │ ├── Tutorial.js # Tutorial model
│ │ ├── User.js # User model
│ ├── utils # Server-side util
│ │ ├──slugify.js # Generates slug for any Model
│ ├── app.js # Custom Express/Next server
│ ├── aws.js # AWS SES API
│ ├── github.js # Github API
│ ├── google.js # Google OAuth API
│ ├── logs.js # Logger
│ ├── mailchimp.js # MailChimp API
│ ├── routesWithCache.js # Express routes with cache
│ ├── routesWithSlug.js # Express routes that contain slug
│ ├── sitemapAndRobots.js # Express routes for sitemap.xml and robots.txt
│ ├── stripe.js # Stripe API
├── static # Static resources
│ ├── robots.txt # Rules for search engine bots
├── test/server/utils # Tests
│ ├── slugify.test.js # Unit test for generateSlug() function
├── tutorials # Codebases for our tutorials
├── .eslintrc.js # Config for Eslint
├── .gitignore # List of ignored files and directories
├── .npmignore # Files and directories that are not uploaded to the server
├── now.json # Settings for now from Zeit
├── package.json # List of packages and scripts
├── yarn.lock # Exact versions of packages. Generated by yarn.