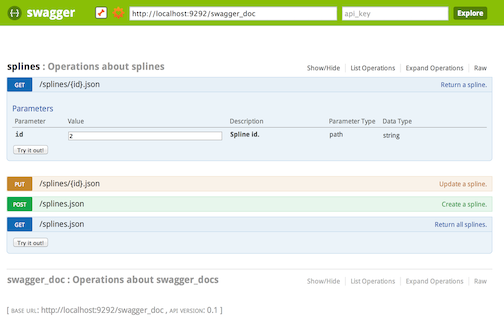
The grape-swagger gem provides an autogenerated documentation for your Grape API. The generated documentation is Swagger-compliant, meaning it can easily be discovered in Swagger UI. You should be able to point the petstore demo to your API.
Grape-swagger generates documentation per Swagger Spec 1.2.
Add to your Gemfile:
gem 'grape-swagger'
Please see UPGRADING when upgrading from a previous version.
Mount all your different APIs (with Grape::API superclass) on a root node. In the root class definition, include add_swagger_documentation, this sets up the system and registers the documentation on '/swagger_doc'. See example/api.rb for a simple demo.
require 'grape-swagger'
module API
class Root < Grape::API
mount API::Cats
mount API::Dogs
mount API::Pirates
add_swagger_documentation
end
endTo explore your API, either download Swagger UI and set it up yourself or go to the online swagger demo and enter your localhost url documentation root in the url field (probably something in the line of http://localhost:3000/swagger_doc).
If you use the online demo, make sure your API supports foreign requests by enabling CORS in Grape, otherwise you'll see the API description, but requests on the API won't return. Use rack-cors to enable CORS.
require 'rack/cors'
use Rack::Cors do
allow do
origins '*'
resource '*', headers: :any, methods: [ :get, :post, :put, :delete, :options ]
end
end
```
Alternatively you can set CORS headers in a Grape `before` block.
``` ruby
before do
header['Access-Control-Allow-Origin'] = '*'
header['Access-Control-Request-Method'] = '*'
endYou can pass a hash with optional configuration settings to add_swagger_documentation.
The API class to document, default self.
The path where the API documentation is loaded, default is /swagger_doc.
API class name.
Allow markdown in detail/notes, default is nil. (disabled) See below for details.
Translations scope (or array of scopes) default is :api. See below for details.
Don't add .(format) to the end of URLs, default is false.
Version of the API that's being exposed.
Base path of the API that's being exposed. This configuration parameter accepts a proc to evaluate base_path, useful when you need to use request attributes to determine its value.
This value is added to the authorizations key in the JSON documentation.
Add basePath key to the JSON documentation, default is true.
A list of entities to document. Combine with the grape-entity gem. See below for details.
Don't show the /swagger_doc path in the generated swagger documentation.
Documentation response format, default is :json.
A hash merged into the info key of the JSON documentation. This may contain:
:title: The API title to be displayed on the API homepage.:description: A description of the API.:contact: Contact email.:license: The name of the license.:license_url: The URL of the license.:terms_of_service_url: The URL of the API terms and conditions.
Customize the Swagger API documentation route, typically contains a desc field. The default description is "Swagger compatible API description".
add_swagger_documentation \
api_documentation: { desc: 'Reticulated splines API swagger-compatible documentation.' }Customize the Swagger API specific documentation route, typically contains a desc field. The default description is "Swagger compatible API description for specific API".
add_swagger_documentation \
specific_api_documentation: { desc: 'Reticulated splines API swagger-compatible endpoint documentation.' }Swagger also supports the documentation of parameters passed in the header. Since grape's params[] doesn't return header parameters we can specify header parameters seperately in a block after the description.
desc "Return super-secret information", {
headers: {
"XAuthToken" => {
description: "Valdates your identity",
required: true
},
"XOptionalHeader" => {
description: "Not really needed",
required: false
}
}
}You can hide an endpoint by adding hidden: true in the description of the endpoint:
desc 'Hide this endpoint', hidden: trueEndpoints can be conditionally hidden by providing a callable object such as a lambda which evaluates to the desired state:
desc 'Conditionally hide this endpoint', hidden: lambda { ENV['EXPERIMENTAL'] != 'true' }You can specify a swagger nickname to use instead of the auto generated name by adding `:nickname 'string'``` in the description of the endpoint.
desc 'Get a full list of pets', nickname: 'getAllPets'You can define an endpoint as array by adding is_array in the description:
desc 'Get a full list of pets', is_array: trueThe Grape DSL supports either an options hash or a restricted block to pass settings. Passing the nickname, hidden and is_array options together with response codes is only possible when passing an options hash.
Since the syntax differs you'll need to adjust it accordingly:
desc 'Get all kittens!', {
:hidden => true,
:is_array => true,
:nickname => 'getKittens',
:entity => Entities::Kitten, # use entity instead of success
:http_codes => [[401, 'KittenBitesError', Entities::BadKitten]] # use http_codes instead of failure
}
get '/kittens' doTo specify further details for an endpoint, use the detail option within a block passed to desc:
desc 'Get all kittens!' do
detail 'this will expose all the kittens'
end
get '/kittens' doYou can override paramType in POST|PUT methods to query, using the documentation hash.
params do
requires :action, type: Symbol, values: [:PAUSE, :RESUME, :STOP], documentation: { param_type: 'query' }
end
post :act do
...
endUse the nested: false property in the swagger option to make nested namespaces appear as standalone resources.
This option can help to structure and keep the swagger schema simple.
namespace 'store/order', desc: 'Order operations within a store', swagger: { nested: false } do
get :order_id do
...
end
end
All routes that belong to this namespace (here: the GET /order_id) will then be assigned to the store_order route instead of the store resource route.
It is also possible to expose a namspace within another already exposed namespace:
namespace 'store/order', desc: 'Order operations within a store', swagger: { nested: false } do
get :order_id do
...
end
namespace 'actions', desc: 'Order actions' do, nested: false
get 'evaluate' do
...
end
end
end
Here, the GET /order_id appears as operation of the store_order resource and the GET /evaluate as operation of the store_orders_actions route.
Auto generated names for the standalone version of complex nested resource do not have a nice look.
You can set a custom name with the name property inside the swagger option, but only if the namespace gets exposed as standalone route.
The name should not contain whitespaces or any other special characters due to further issues within swagger-ui.
namespace 'store/order', desc: 'Order operations within a store', swagger: { nested: false, name: 'Store-orders' } do
get :order_id do
...
end
end
Grape allows for an additional documentation hash to be passed to a parameter.
params do
requires :id, type: Integer, desc: 'Coffee ID'
requires :temperature, type: Integer, desc: 'Temperature of the coffee in celcius', documentation: { example: 72 }
end
The example parameter will populate the Swagger UI with the example value, and can be used for optional or required parameters.
Grape uses the option default to set a default value for optional parameters. This is different in that Grape will set your parameter to the provided default if the parameter is omitted, whereas the example value above will only set the value in the UI itself. This will set the Swagger defaultValue to the provided value. Note that the example value will override the Grape default value.
params do
requires :id, type: Integer, desc: 'Coffee ID'
optional :temperature, type: Integer, desc: 'Temperature of the coffee in celcius', default: 72
end
Add the grape-entity gem to our Gemfile.
The following example exposes statuses. And exposes statuses documentation adding :type and :desc.
module API
module Entities
class Status < Grape::Entity
expose :text, documentation: { type: 'string', desc: 'Status update text.' }
expose :links, using: Link, documentation: { type: 'link', is_array: true }
expose :numbers, documentation: { type: 'integer', desc: 'favourite number', values: [1,2,3,4] }
end
class Link < Grape::Entity
def self.entity_name
'link'
end
expose :href, documentation: { type: 'url' }
expose :rel, documentation: { type: 'string'}
end
end
class Statuses < Grape::API
version 'v1'
desc 'Statuses index', entity: API::Entities::Status
get '/statuses' do
statuses = Status.all
type = current_user.admin? ? :full : :default
present statuses, with: API::Entities::Status, type: type
end
desc 'Creates a new status', entity: API::Entities::Status, params: API::Entities::Status.documentation
post '/statuses' do
...
end
end
endYou may safely omit type from relationships, as it can be inferred. However, if you need to specify or override it, use the full name of the class leaving out any modules named Entities or Entity.
module API
module Entities
class Client < Grape::Entity
expose :name, documentation: { type: 'string', desc: 'Name' }
expose :addresses, using: Entities::Address,
documentation: { type: 'API::Address', desc: 'Addresses.', param_type: 'body', is_array: true }
end
class Address < Grape::Entity
expose :street, documentation: { type: 'string', desc: 'Street.' }
end
end
class Clients < Grape::API
version 'v1'
desc 'Clients index', params: Entities::Client.documentation
get '/clients' do
...
end
end
add_swagger_documentation models: [Entities::Client, Entities::Address]
endNote: is_array is false by default.
module API
module Entities
class Client < Grape::Entity
expose :name, documentation: { type: 'string', desc: 'Name' }
expose :address, using: Entities::Address,
documentation: { type: 'API::Address', desc: 'Addresses.', param_type: 'body', is_array: false }
end
class Address < Grape::Entity
expose :street, documentation: { type: 'string', desc: 'Street' }
end
end
class Clients < Grape::API
version 'v1'
desc 'Clients index', params: Entities::Client.documentation
get '/clients' do
...
end
end
add_swagger_documentation models: [Entities::Client, Entities::Address]
endThe grape-swagger gem allows you to add an explanation in markdown in the detail/notes field. Which would result in proper formatted markdown in Swagger UI. Grape-swagger uses adapters for several markdown formatters. It includes adapters for kramdown (kramdown syntax) and redcarpet. The adapters are packed in the GrapeSwagger::Markdown modules. We do not include the markdown gems in our gemfile, so be sure to include or install the depended gems.
If you want to use kramdown as markdown formatter, you need to add kramdown to your gemfile.
gem 'kramdown'
Configure your api documentation route with:
add_swagger_documentation(
markdown: GrapeSwagger::Markdown::KramdownAdapter
)Finally you can write endpoint descriptions the with markdown enabled.
desc "Reserve a burger in heaven" do
detail <<-NOTE
Veggie Burgers in Heaven
-----------------
> A veggie burger doesn't come for free
If you want to reserve a veggie burger in heaven, you have to do
some crazy stuff on earth.
def do_good
puts 'help people'
end
* _Will go to Heaven:_ Probably
* _Will go to Hell:_ Probably not
NOTE
endAs alternative you can use redcarpet as formatter, you need to include redcarpet in your gemspec. If you also want to use rouge as syntax highlighter you also need to include it.
gem 'redcarpet'
gem 'rouge'
Configure your api documentation route with:
add_swagger_documentation(
markdown: GrapeSwagger::Markdown::RedcarpetAdapter.new(render_options: { highlighter: :rouge })
)Alternatively you can disable rouge by adding :none as highlighter option. You can add redcarpet extensions and render options trough the extenstions: and render_options: parameters.
You can also add your custom adapter for your favourite markdown formatter, as long it responds to the method markdown(text) and it formats the given text.
module API
class MySuperbMarkdownFormatterAdapter
attr_reader :adapter
def initialize(options)
require 'superbmarkdownformatter'
@adapter = SuperbMarkdownFormatter.new options
end
def markdown(text)
@adapter.render_supreme(text)
end
end
add_swagger_documentation markdown: MySuperbMarkdownFormatterAdapter.new(no_links: true)
endYou can also document the HTTP status codes with a description and a specified model that your API returns with the following syntax.
get '/', http_codes: [
[200, 'Ok', Entities::Client],
[400, "Invalid parameter entry"]
] do
...
endGrape-swagger supports I18n for most messages of the JSON documentation, including:
- API info
- Namespaces/resources description
- Endpoints description and detail/notes
- Params (including headers) description
- Models/entities description
By default, grape-swagger will lookup translations inside :api scope. This can be configured by
set i18n_scope to a custom scope (or an array of scopes) when calling
add_swagger_documentation.
To localize your API document, you can add a locale file containing translated messages. Grape-swagger will try to look up translation for each message. If a translation cannot be found, it will use the message specified in the API code, then default to blank.
Take the following sample API for example:
desc 'Gets all kittens' do
detail 'This will expose all the kittens.'
end
params do
optional :sort
end
get :kittens do
endTo generate I18n documentation, you can add a locale file with translated messages:
api:
kittens:
get:
detail: This will return a full list of kittens, and you can change the way of sorting them.
params:
sort: Specifies the order of resultsThe endpoint description in generated API document will be "Gets all kittens" - specified in source
code - because there is no translation defined. And endpoint details will be overwritten by locale
message - "This will return a full list of kittens, and you can change the way of sorting them.".
Parameter :sort will have a description from locale file too.
The following lookup keys are all within the scope given by i18n_scope.
The default lookup key of a field in API info is info.<field>, i.e.:
info.titlefor:titlefield.info.descorinfo.descriptionfor:descriptionfield.info.contactfor:contactfield.info.licensefor:licensefield.info.license_urlfor:license_urlfield.info.terms_of_service_urlfor:terms_of_service_urlfield.
Grape-swagger will give each root namespace a default description, such as "Operations about
users", where users is a namespace (pluralized). But you can change it by provide your own
message under key <namespace>.desc or <namespace>.description in your locale file. And the
namespace itself is available as a variable for interpolation.
An endpoint's default lookup key is in format of <namespace>.<path>.<http_method>. And if there
are nested namespaces or multi-level path, all parts will be join by .. For example for this
endpoint:
namespace :users do
route_params :id do
get :'password/strength' do
end
end
endIts corresponding lookup key will be users.:id.password.strength.get, let's say that this is
the key of this endpoint.
So an endpoint's description message can be given under <endpoint_key>.desc or
<endpoint_key>.description. And use <endpoint_key>.detail or <endpoint_key>.notes for the
message of its further details.
The first default key of endpoint parameter's description translation is
<endpoint_key>.params.<param_name>. But considering that some endpoints could usually share a
same parameter, it will be a little annoyed to duplicate its description message everywhere. So if
no translation found in the first default key, grape-swagger will try to find all its parent keys.
Take above endpoint for example, it may have a parameter named :id, then the lookup keys are:
users.:id.password.strength.get.params.idusers.:id.password.strength.params.idusers.:id.password.params.idusers.:id.params.idusers.params.idparams.id
A model class' lookup key is by default its class name, without module part, and underscored. Each
property's key is then entities.<class_key>.<property_name>. When not found, grape-swagger will
try to check the its ancestors, up to a class whose name is Entity.
Say if there is model class User inherits Grape::Entity, and another model AdminUser inherits
User, to translate a property named :email of AdminUser, the lookup keys are:
entities.admin_user.emailentities.user.emailentities.default.email
en:
api:
info:
title: My Awesome API
desc: Some detail information about this API.
entities:
default:
id: Resource identifier
user:
name: User's real name
email: User's login email address
sign_up_at: When the user signed up
admin_user:
level: Which level the admin is
password_strength:
level: A 0~4 integer indicates `very_weak` to `strong`
crack_time: An estimated time for force cracking the password, in seconds
params:
locale: Used to change locale of endpoint's responding message
sort: To specify the order of result list, default is %{default_sort}
users:
desc: Operations about not-disabled users
get:
desc: Gets a list of users
detail: You can control how to sort the results.
':id':
params:
id: User id
get:
desc: Finds user by id
email:
put:
desc: Changes a user's email
params:
email: A new email
password:
strength:
get:
desc: Gets the strength estimation of a user's password
detail: The estimation is done by a well-known algorithm when he changed his password
swagger_doc:
desc: Endpoints for API documents
get:
desc: Gets root API document
':name':
get:
desc: Gets specific resource API document
params:
name: Resource nameThe translation can be customized by using different kind/format of message in source code.
- A string or
nil: It will become the default message when a translation is not defined. - A symbol: Looks up translation using the symbol as a key, but will fallback to default key(s).
- A hash with the following keys:
- key: A symbol, defines custom lookup key.
- default: A string, defines the default message when translation can not be found.
- translate: A boolean (default is
true), set tofalseto skip translation for this message. - scope: A symbol, or a string, or an array of them. Used to replace the
i18n_scopeconfig value for a custom lookup scope. - Any other key/value will be sent to the translation function for interpolation.
See CONTRIBUTING.
Copyright (c) 2012-2014 Tim Vandecasteele and contributors. See LICENSE.txt for details.