An implementation of Almazan's 2013 ICCV paper
The project’s focus is to provide an approach to multi-writer word spotting, where the goal would be to find a query word in a dataset comprised of document images. It is an attributes-based approach that leads to a low-dimensional, fixed-length representation of the word images that is fast to compute and, especially, fast to compare. This approach would lead to a unified representation of word images and strings, which seamlessly allow one to indistinctly perform query-by-example, where the query is an image, and query-by- string where the query is a string.
- Out of Vocabulary words(words not there in training images, but exist in the test images)
- Time taken for the image retrieval
- Same word, different handwriting
To find all instances of a given word in a potentially large dataset of document images. The various types of Queries to be handled are:
- Query by example (Image)
- Query by string (Text)
- A Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) is used to model the distribution of features (e.g. SIFT) extracted all over the image
- The Fisher Vector (FV) encodes the gradients of the log-likelihood of the features under the GMM, with respect to the GMM parameters.
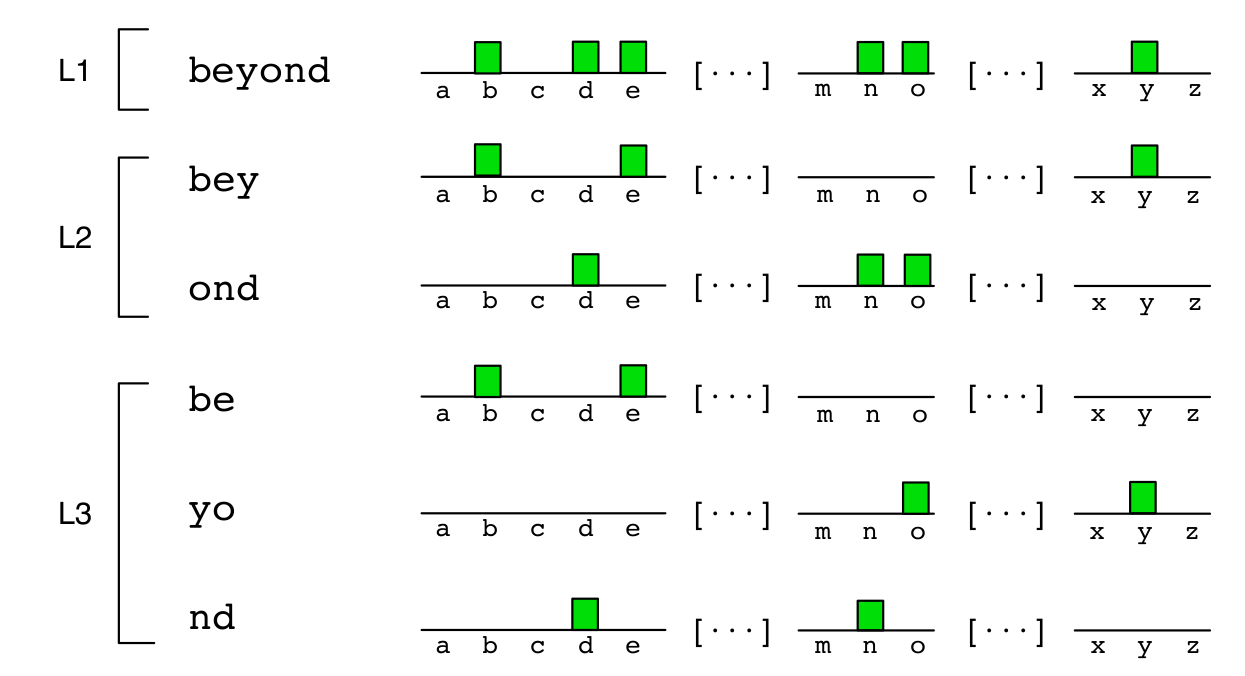
- This binary histogram encodes whether a particular character appears in the represented word or not.
- Spatial pyramid representation ensures that the information of the characters order is preserved.
- PHOC representation is the concatenation of the partial histograms.
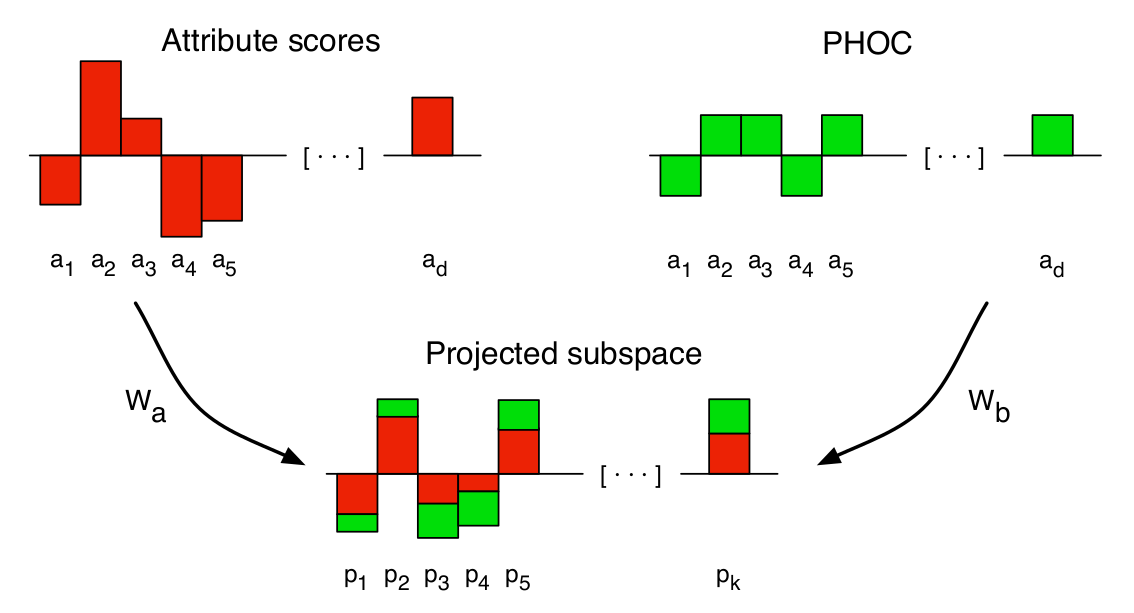
Technique to embed the attribute scores and the binary attributes in a common subspace where they are maximally correlated.
- SIFT features are densely extracted from the images over a 2x6 spatial grid and reduced to 62 dimensions with PCA
- Normalized x and y coordinates are appended to the projected SIFT descriptors
- Predict/train the PHOC attributes using a SVM classifier, given the FV
- Since we have the image and string for a word, actual PHOC attributes can be found by using the string input
- Using CCA (Canonical Correlation Analysis), get the projections of the predicted scores and the ground truth values
- Use cosine similarity to compute the mean average precision
- Used 1 million SIFT features over 2 x 6 spatial grid for training the GMM with 16 gaussians .
- Used PCA to reduce dimensions to 64. Attribute dimensions are 2 × 64 × 192 = 24, 576. Descriptors are then power and L2- normalized.
- Used levels 2, 3 ,4 and 75 common bigrams at level 2, leading to 384 dimensions considering the 26 characters of the English alphabet.
- For learning the attributes we’ve used 39,756 (40%) images to train one vs rest SGD classifier.
- For CCA we’ve used 41,032 images to learn the common subspace. We’ve reduced the 384 dimensions to 196 dimensions in the process.
- Testing was done on 13,329 images
The following are the results on IAM dataset.
| Fisher Vector | Attributes | Attributes + CCA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| QBS | - | 0.42 | 0.48 |
| QBE | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.37 |
- Praveen Balireddy (praveeniitkgp1994@gmail.com)
- Aman Joshi (amanjoshi668@gmail.com)
- Abhijeet Panda (abhijeet.panda@students.iiit.ac.in)
For more details regarding the project, please refer to the "CV project report.pdf" in the repo.

