This repository contains the reference code for computing SAM (Saliency Attentive Model) saliency maps based on the following paper:
Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Giuseppe Serra, Rita Cucchiara
Predicting Human Eye Fixations via an LSTM-based Saliency Attentive Model
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018
Please cite with the following Bibtex code:
@article{cornia2018predicting,
author = {Cornia, Marcella and Baraldi, Lorenzo and Serra, Giuseppe and Cucchiara, Rita},
title = {{Predicting Human Eye Fixations via an LSTM-based Saliency Attentive Model}},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Image Processing},
volume={27},
number={10},
pages={5142--5154},
year = {2018}
}
The PDF of the article is available at this link.
Additional experimental results are reported in the following short paper:
Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Giuseppe Serra, Rita Cucchiara
SAM: Pushing the Limits of Saliency Prediction Models
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2018
Please cite with the following Bibtex code:
@article{cornia2018sam,
author = {Cornia, Marcella and Baraldi, Lorenzo and Serra, Giuseppe and Cucchiara, Rita},
title = {{SAM: Pushing the Limits of Saliency Prediction Models}},
journal = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops},
year = {2018}
}
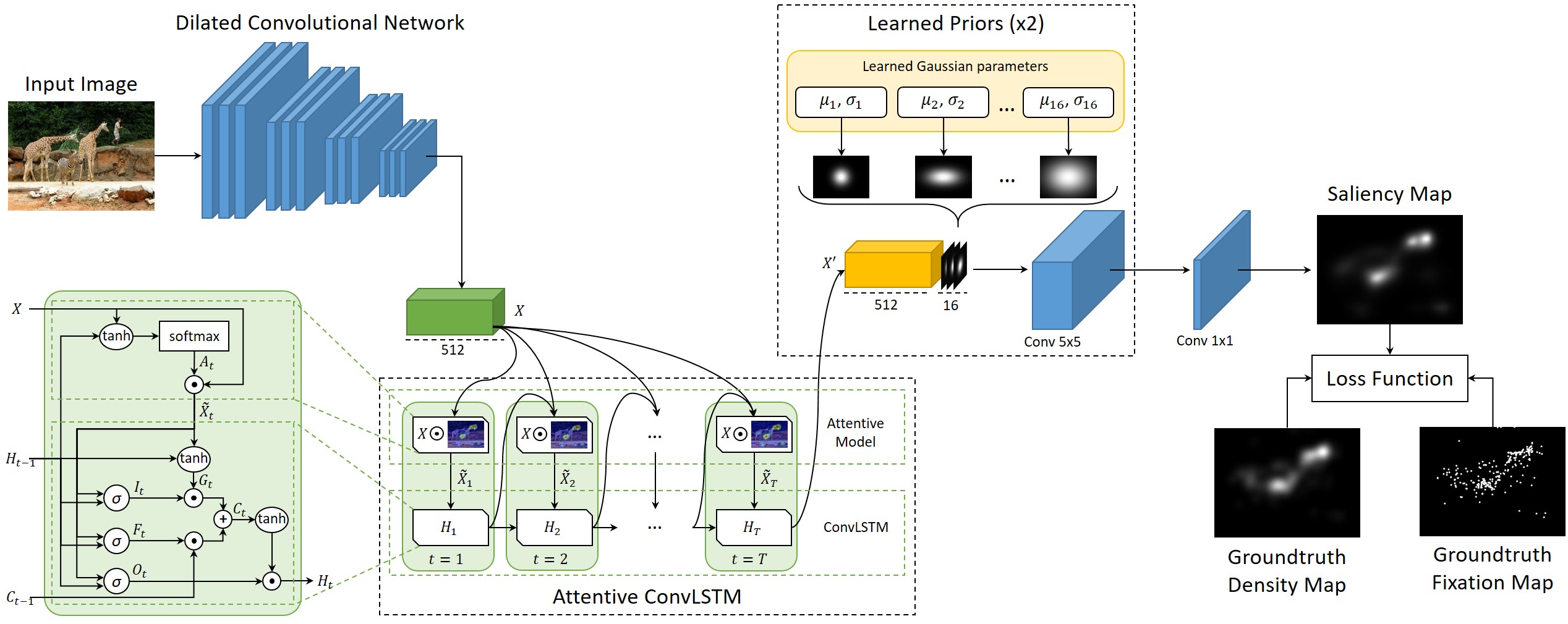
Data-driven saliency has recently gained a lot of attention thanks to the use of Convolutional Neural Networks for predicting gaze fixations. In this paper we go beyond standard approaches to saliency prediction, in which gaze maps are computed with a feed-forward network, and we present a novel model which can predict accurate saliency maps by incorporating neural attentive mechanisms. The core of our solution is a Convolutional LSTM that focuses on the most salient regions of the input image to iteratively refine the predicted saliency map. Additionally, to tackle the center bias present in human eye fixations, our model can learn a set of prior maps generated with Gaussian functions. We show, through an extensive evaluation, that the proposed architecture overcomes the current state of the art on two public saliency prediction datasets. We further study the contribution of each key components to demonstrate their robustness on different scenarios.
Note: Be sure to have "image_dim_ordering": "th" and "backend": "theano" in your keras.json file.
We built two different versions of our model: one based on the VGG-16 (SAM-VGG) and the other based on the ResNet-50 (SAM-ResNet). It is possible use both versions of SAM by changing the version variable in the config.py file (set version = 0 for SAM-VGG or version = 1 for SAM-ResNet).
To compute saliency maps using our pre-trained model:
python main.py test path/to/images/folder/
where "path/to/images/folder/" is the path of a folder containing the images for which you want to calculate the saliency maps.
To train our model from scratch:
python main.py train
It is also necessary to set parameters and paths in the config.py file.
Note: To train our model, both binary fixation maps and groundtruth density maps are required. The current code for loading binary fixation maps supports the format used in SALICON (.mat files). If you want to train our model with other datasets, be sure to appropriately change the loading functions.
Download one of the following pretrained models and save it in the code folder:
- SAM-VGG trained on SALICON (2015 release): sam-vgg_salicon_weights.pkl
- SAM-ResNet trained on SALICON (2015 release): sam-resnet_salicon_weights.pkl
- SAM-ResNet trained on SALICON (2017 release): sam-resnet_salicon2017_weights.pkl
We provide saliency maps predicted by SAM-VGG and SAM-ResNet for three standard datasets (SALICON, MIT1003 and CAT2000):
In addition, we provide saliency maps predicted by SAM-ResNet on the new release of the SALICON dataset:
For more datails about our research please visit our page.
If you have any general doubt about our work, please use the public issues section on this github repo. Alternatively, drop us an e-mail at marcella.cornia@unimore.it or lorenzo.baraldi@unimore.it.