TLSAssistant v3.1 is the latest version of TLSAssistant, a modular state-of-the-art TLS analyzer, extensible with new features and thus capable of streamlining the mitigation process of known and newly discovered TLS attacks even for non-expert users. The companion page, containing additional details can be found here.
The latest release introduces a redesigned PDF report, a novel module able to perform compliance analyses against five agency-issued technical guidelines:
- AgID ver.2020-01
- ANSSI v1.2
- BSI TR-02102-2 and TR-03116-4
- Mozilla v5.7
- NIST SP 800-52 Rev. 2 (and related)
and the integration of a new state-of-the-art static and extensible app security testing tool called SEBASTiAn. Its presence enhanced existing Android analyses and introduces the possiblity to analyze iOS applications.
Vulnerability analysis
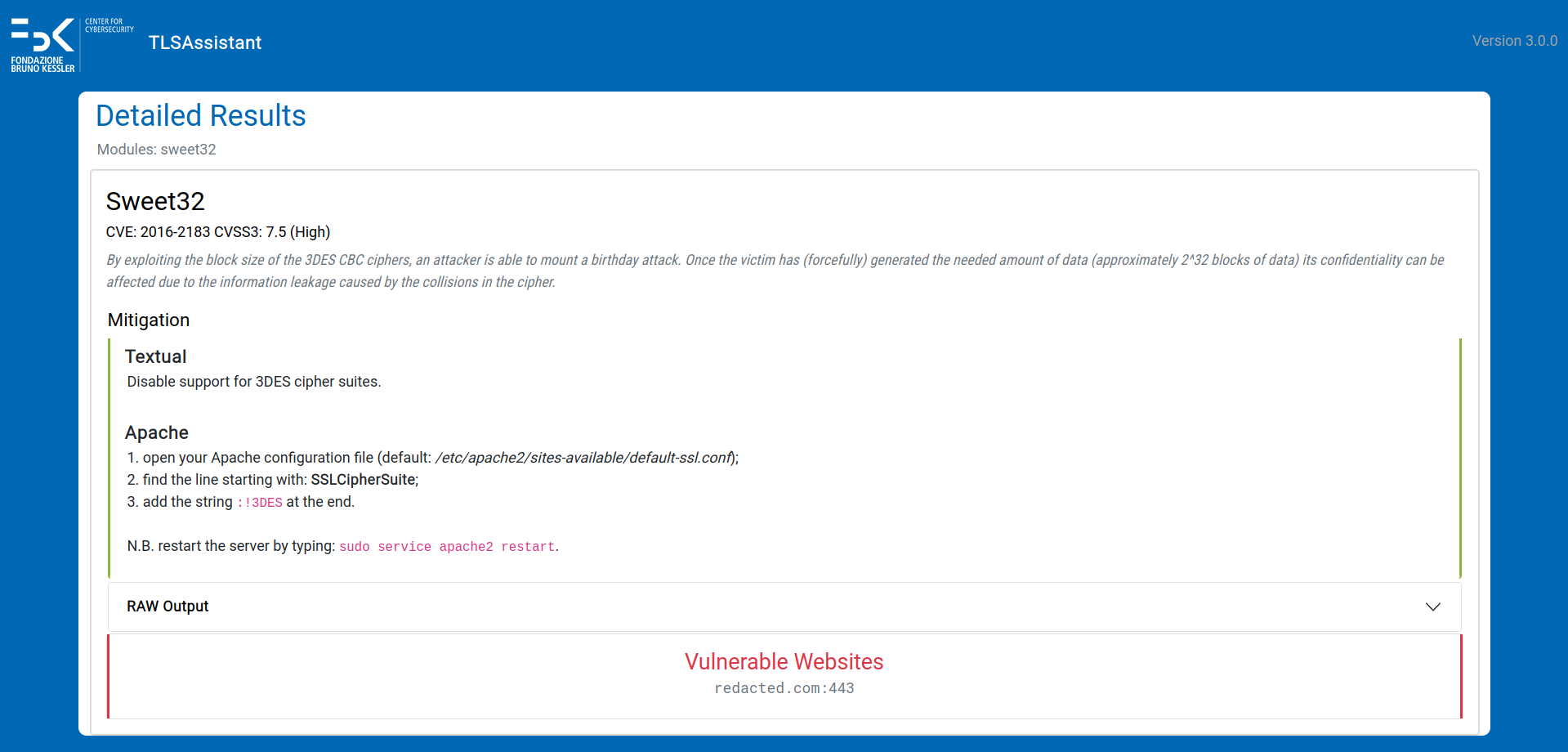
TLSAssistant is capable of identifying a wide range of TLS vulnerabilities and generating actionable reports that can assist the system administrators in correctly and easily fixing their configurations.
The list of detectable issues is:
- Android applications (.apk)
- Accepting all SSL certificates
- Allow all hostname
- Certificate or keyStore disclosure
- Crypto ECB ciphers
- Debuggable application
- Default HTTP scheme
- Insecure connection
- Insecure HostnameVerifier
- Insecure SocketFactory
- Insecure Socket
- Invalid server certificate
- Obfuscated Code
- SSL GetInsecure Method
- Weak Algorithms
- WebView SSL Errors
- iOS applications (.ipa)
- Allow HTTP Plist
- Insecure connection Plist
- Insecure TLS version Plist
- No forward secrecy Plist
- Weak crypto
- Webservers
- 3SHAKE
- ALPACA
- BEAST
- BREACH
- CCS Injection
- Certificate Transparency
- CRIME
- DROWN
- FREAK
- Heartbleed
- HSTS preloading
- HSTS set
- HTTPS enforced
- LOGJAM
- LUCKY13
- BAR MITZVAH
- RC4 NOMORE
- Padding oracle (SSL and TLS POODLE)
- Perfect Forward Secrecy
- RACCOON
- SSL RENEGOTIATION
- ROBOT
- SLOTH
- SWEET32
- TICKETBLEED
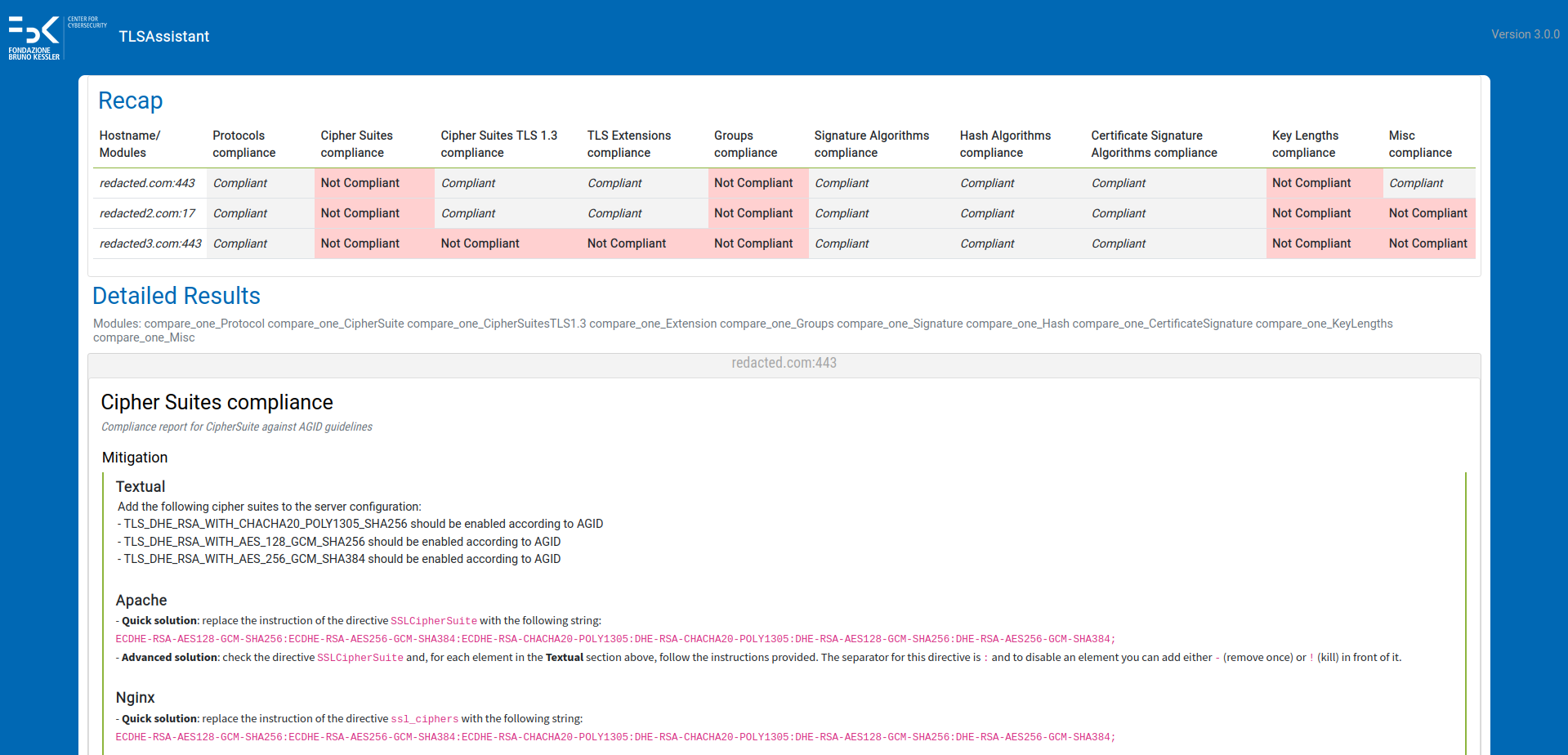
Compliance analysis
TLSAssistant is able to perform an automated compliance analysis against fivefive agency-issued technical guidelines:
- AgID ver.2020-01
- ANSSI v1.2
- BSI TR-02102-2 and TR-03116-4
- Mozilla v5.7
- NIST SP 800-52 Rev. 2 (and related)
It supports the following use-cases:
- compare-to-one - compare an already existing configuration against a single guideline. The output consists of a report that highlights the differences between the current and the target configuration and guides the system administrator towards closing the gap;
- compare-to-many - similar to the compare-to-one but considering multiple guidelines;
- generate-after-one - generate a working configuration compliant with a single guideline, taking into account any additional narrowing set by the user;
- generate-after-many - similar to the generate-after-one but considering multiple guidelines.
Tip
We suggest to download the pre-built Docker provided by GitHub by fetching it with.
docker pull ghcr.io/stfbk/tlsassistant:v3.1and running it with
docker run --rm -v ${PWD}/results:/tlsassistant/results -t ghcr.io/stfbk/tlsassistant:v3.1 -s www.fbk.euHowever, if you want to install the dependencies on the system, you can use the following building methods:
To install the tool (in a virtual environment), execute the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install git python3-dev python3-pip python3-venv -y && git clone https://github.com/stfbk/tlsassistant.git && cd tlsassistant && python3 -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate && pip3 install -r requirements.txt && python3 install.py -vIf you want to download and install by executing every step:
Show single steps
- Install git
sudo apt update && sudo apt-get install git -y- Download the tool by running
git clone https://github.com/stfbk/tlsassistant.git && cd tlsassistant- Install python
sudo apt update && sudo apt-get install python3-dev python3-pip python3-venv -y- Optional but recommended: Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv venvand activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate- Install the requirements
pip3 install -r requirements.txt- Run the installer
python3 install.pyRecommended for non-Ubuntu users:
Since it does use APT and install dependencies, we can use the Dockerfile to build the image and contain the installation process.
Docker build and run tutorial
clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/stfbk/tlsassistant.git && cd tlsassistantBuild the docker image:
docker build -t tlsassistant .Run the docker image:
docker run --rm -v ${PWD}/results:/tlsassistant/results -t tlsassistant -s www.fbk.euadd all the args that we want to pass after the tlsassistant keyword.
We can use the -v flag to mount directories with the TLS configuration files.
docker run --rm -v ${PWD}/results:/tlsassistant/results -v ${PWD}/configurations_to_mount:/tlsassistant/config_mounted -t tlsassistant -f config_mounted/apache.confpython3 run.py -hShow raw output
usage: TLSAssistant [-h] [--version] [-v] [--openssl OPENSSL | --ignore-openssl] [-ot {pdf,html}] [-o OUTPUT] [--group-by {host,module}] (-s SERVER | -f FILE | -d DOMAIN_FILE | -l [LIST] | -a APK) [--apply-fix [APPLY_FIX]]
[-c CONFIGURATION | -m CONFIGURATION [CONFIGURATION ...]] [-e EXCLUDE [EXCLUDE ...]] [--stix] [--webhook [WEBHOOK]] [--prometheus [PROMETHEUS]] [--config_type {apache,nginx,auto}] [--guidelines COMPLIANCE_ARGS]
[--apache] [--security COMPLIANCE_ARGS] [--output_config COMPLIANCE_ARGS] [--certificate_index COMPLIANCE_ARGS] [--custom_guidelines COMPLIANCE_ARGS] [--use_cache] [--clean] [--no_psk]
TLSAssistant Help
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version show program's version number and exit
-v, --verbosity increase output verbosity
--openssl OPENSSL, --openssl-version OPENSSL
Add openSSL version to consider if configuration analysis is asked.
--ignore-openssl During configuration analysis, ignore openssl version completely.
-ot {pdf,html}, --output-type {pdf,html}
The type of the report output.
Output type can be omitted and can be obtained by --output extension.
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Set report path.
--group-by {host,module}
Choose how to group results by.
-s SERVER, --server SERVER
The hostname, target of the analysis.
-f FILE, --file FILE The configuration to analyze.
-d DOMAIN_FILE, --domain_file DOMAIN_FILE
The file path which has the hostname to analyze.
-l [LIST], --list [LIST]
List all modules or print an help of a module.
For Example
-l freak
-a APP, --app APP The apk/ipa path, target of the analysis.
--apply-fix [APPLY_FIX]
Apply fix in the current configuration.
Give a path if using -s.
i.e.
python3 run.py -s fbk.eu --apply-fix myconf.conf
-c CONFIGURATION, --conf CONFIGURATION, --configuration CONFIGURATION
Configuration path.
-m CONFIGURATION [CONFIGURATION ...], --modules CONFIGURATION [CONFIGURATION ...]
List of modules to run
For example
-m breach crime freak
-e EXCLUDE [EXCLUDE ...], --exclude EXCLUDE [EXCLUDE ...]
List of modules to exclude
For example
-e breach crime
--stix Generate STIX2 compliant output.
--webhook [WEBHOOK] Add a webhook url to send the results.
--prometheus [PROMETHEUS]
Generate the prometheus output in a default path or in the specified path.
--config_type {apache,nginx,auto}
Define the type of configuration to analyze.
--guidelines COMPLIANCE_ARGS
A string containing the names of the guidelines that should be checked in the form: guideline_version1_version2 in the case of multiple guidelines they should be comma separated. Use "list" for a list of valid strings and "aliases" for a list of aliases.
--apache Default to False. If True the output configuration will have apache syntax, if false nginx will be used.
--security COMPLIANCE_ARGS
Default to True. If False the legacy level priority will be used
--output_config COMPLIANCE_ARGS
Where to save the output configuration file, only needed for generate one/many
--certificate_index COMPLIANCE_ARGS
The index of the certificate to use for the analysis, only needed if the website has multiple certificates.Default to 1 (first certificate).
--custom_guidelines COMPLIANCE_ARGS
A path to a custom guideline file, only needed if the user wants to use a custom guideline.
--use_cache Default to False. If True the program will use the cached testssl analysis, if False the cache will be ignored.
--clean Default to False. If True the program will remove the cached testssl analysis for this host.
--no_psk Default to False. If True the program will not consider PSK ciphersuites during analysis.
Show advanced examples
- Perform a server analysis
python3 run.py -s fbk.euIf no configuration or module list provided, default_server.json is loaded.
- Perform a configuration file analysis
Here we specify the openssl version of the system which runs the web server.
python3 run.py -f my_apache_conf.conf --openssl 1.1.1We can also ignore the openssl version, assuming the weakest version:
python3 run.py -f my_apache_conf.conf --ignore-openssl- Perform a TLS configuration file analysis and apply fixes
By default, the configuration analyzed is changed in place.
python3 run.py -f my_apache_conf.conf --apply-fixWe can specify an output path of the fixed configuration:
python3 run.py -f my_apache_conf.conf --apply-fix my_output_conf.conf- Perform an analysis by selecting modules
python3 run.py -s fbk.eu -m breach crime freak poodle hsts_preloadingOr by selecting a TLSAssistant configuration file:
python3 run.py -s fbk.eu -c default_server.json We can also exclude some modules without editing the configuration file:
python3 run.py -s fbk.eu -c default_server.json -e hsts_preloadingget the full module list with:
python3 run.py -l- Perform an analysis with subdomain enumeration
python3 run.py -s *.fbk.eu- Perform an analysis on a .apk/.ipa file
python3 run.py -a my_app[.apk/.ipa]If no configuration or module list provided, default_android.json is loaded.
- Analyze all domains in a file (one per line, including subdomains enumeration)
Assuming the file domains_list.log looks like this:
music.amazon.it
facebook.com
*.fbk.eu
we execute:
python3 run.py -d domains_list.log- Check the compliance of an existing deployment against AgID TLS guidelines
python3 run.py -m compare_one --guidelines agid -s www.example.com --ignore-openssl- Generate a new configuration, already compliant with NIST guidelines
python3 run.py -m generate_one --guidelines nist --output_conf compliant_config.conf --openssl-version 3.0.2 -s placeholderShow modules list
python3 run.py -lResults:
Here's a list of all the modules available:
Android:
accepting_all_certificates
allow_all_hostname
certificate_keystore_disclosure
crypto_ecb_cipher
debuggable_application
default_scheme_http
insecure_connection
insecure_hostname_verifier
insecure_socket_factory
insecure_socket
invalid_server_certificate
obfuscated_code
ssl_getinsecure_method
weak_algorithms
webview_ssl_errors
Compliance:
compare_one
compare_many
generate_one
generate_many
iOS:
allow_http_plist
allow_connection_plist
allow_tls_version_plist
no_forward_secrecy_plist
weak_crypto
Server:
3shake
alpaca
beast
breach
ccs_injection
certificate_transparency
crime
drown
freak
heartbleed
hsts_preloading
hsts_set
https_enforced
logjam
lucky13
mitzvah
nomore
padding_oracle
pfs
sslpoodle
tlspoodle
raccoon
renegotiation
robot
sloth
sweet32
ticketbleed
Use
-l module_name
to read the details.
The various types of analysis that can (currently) be performed are:
Since most of the vulnerabilities analyzed by the tool are covered by testssl.sh tool, we decided to make the analysis more efficient by performing a pre-analysis to populate a cache with its result. These will be used by the corresponding testssl.sh modules such as POODLE (an attack that exploits the availability of SSLv3 to downgrade the strength of the connection), during current and future analysis. Thus, in Step 3a the arguments of each individual module related to testssl.sh are obtained. These arguments will be provided to the method in order to perform the testssl.sh pre-analysis and populate the cache with the results. Once this is done, the individual modules are executed (Step 3b) and mitigations added if vulnerable.
Each Android-related module, such as Unsecure TrustManager (which evaluates if a custom implementation may be exploited to break certificate validation), runs the analysis (Step 3b) on the provided APK.
We perform a Single Host analysis on each one of the domains specified in an input list. Each result is concatenated and provided to the Output module as a single output.
If a configuration file is provided, a WhiteBox analysis is performed by loading the TLS configuration into memory and performing a complete check of all available modules (Step 3b). Otherwise, if a configuration file is provided along with a valid hostname, a singlehost analysis is performed and then the fixes are integrated in the provided TLS configuration. We refer to this analysis as Hybrid: we perform a BlackBox analysis on the hostname and then we apply the fixes on the configuration file.
Please refer to the related Wiki page.
-
Employed in the context of the industrial collaboration with IPZS/F&C
-
Integrated in the Horizon 2020 FINSEC project
-
Listed as software of interest for the Italian Public Administrations
Copyright 2019, Fondazione Bruno Kessler
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Developed within the Security & Trust research unit, part of the Center for Cybersecurity at Fondazione Bruno Kessler (Italy)