Orchestrate-Redshift-ETL-using-AWS-Glue-and-Step-Functions
Business Overview
Data Analytics and Machine Learning work-streams rely on ETL for their basis. ETL cleanses and organizes data using a set of business rules to meet particular business intelligence requirements, such as monthly reporting. Still, it may also handle complex analytics to enhance back-end operations or end-user experiences. An organization's ETL is frequently used to:
- Retrieve data from legacy systems.
- To improve data accuracy and reliability, clean the data.
- Update a target database with data.
It is prevalent to use Redshift as a data-warehousing tool in the AWS cloud. However, there are quite some ways to orchestrate the loading, unloading and querying Redshift. In this project, we use in-house AWS tools to orchestrate end-to-end loading and deriving business insights. Since it uses in-house tools, the availability and durability of the solution are guaranteed by AWS.
Tech Stack
- Language:
- Python3
- SQL
- Services:
Data Description
One of Amazon's most recognizable products is Amazon Customer Reviews. Millions of Amazon consumers have posted over a hundred million reviews to express their thoughts and explain their experiences with items on the Amazon.com website during the past two decades. This makes Amazon Customer Reviews a valuable resource for academics working in disciplines like Natural Language Processing, Information Retrieval, and Machine Learning. This dataset was created specifically to reflect a sample of customer evaluations and opinions, variance in product perception across geographic locations, and promotional purpose or bias in reviews.
The Parquet dataset, which is one of two accessible formats, including TSV, is partitioned (split into subfolders) on S3 by "product category" to increase further query speed. This enables queries that include a WHERE clause on "product category" only to read data from that category.
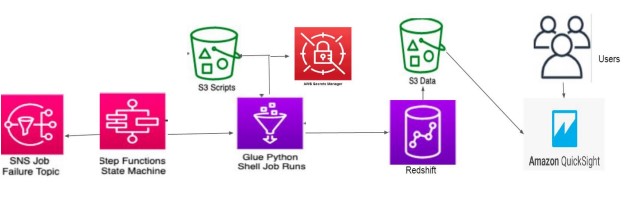
Approch
- The state machine starts a series of AWS Glue Python Shell jobs, each with parameters for obtaining database connection information from AWS Secrets Manager and a SQL file from S3.
- The database connection information is used by each execution of the AWS Glue Python Shell task to connect to the Amazon Redshift cluster and submit the queries in the SQL file.
- Task 1: The cluster utilizes Amazon Redshift Spectrum to read data from S3 and load it into an Amazon Redshift table
- Task 2: The cluster executes an aggregation query and exports the results to another Amazon S3 location via UNLOAD.
- The state machine may send a notification to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) topic in the case of pipeline failure. Users can query the data from the cluster or retrieve report output files directly from S3/Redshift using QuickSight.