In recent years, one of the biggest applications of machine learning has been in image classification — the ability for a computer to intelligently recognize an object. Such work is being done at the greatest technology companies, and it’s since spawned this unwarranted notion of exclusivity. We’ve crafted a narrative that in order to get your hands dirty with machine learning and artificial intelligence, you have to be some sort of certifiable genius, or at least an engineering graduate just to break in. So I’m going to to show you how in less than 45 minutes, you can build a fully-functioning image classifier that can recognize any (yes, any) object with insanely high probabilities.
After completing this how-to, the reader will be able to:
- Learn Watson Studio to build a image classification model using image data from any source.
- Build an android application which classify images using the model.
-
IBM Cloud account - sign up if you don't have an account yet.
-
Enough space on IBM Cloud for 3 services. If not, delete some services to make room.
-
You will require Android Studio, download the latest version Android Studio 3.1.3
-
Install JAVA JDK SE 8
-
A dataset that you want to model.
If you don't have your own dataset, then you can download this Sample Dataset
To complete this how-to it should take around 45 minutes.
Watson Studio is a cloud based development and deployment environment for Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Data Governance and Data Expolaration. A platform build for business analyst, data engineer, data scientist and developer to simply there task with an intuitive UI and provide massive computing power. A platform where insights can be traced back to models, projects, notebooks and data sources and where model can evolve and automatically update themselves.
- Navigate to datascience.ibm.com
- Sign in on the IBM Cloud
-
Click on Get Started and you will be redirected to the Watson Studio dashboard.
-
An interactive menu will be shown Get started with key tasks.
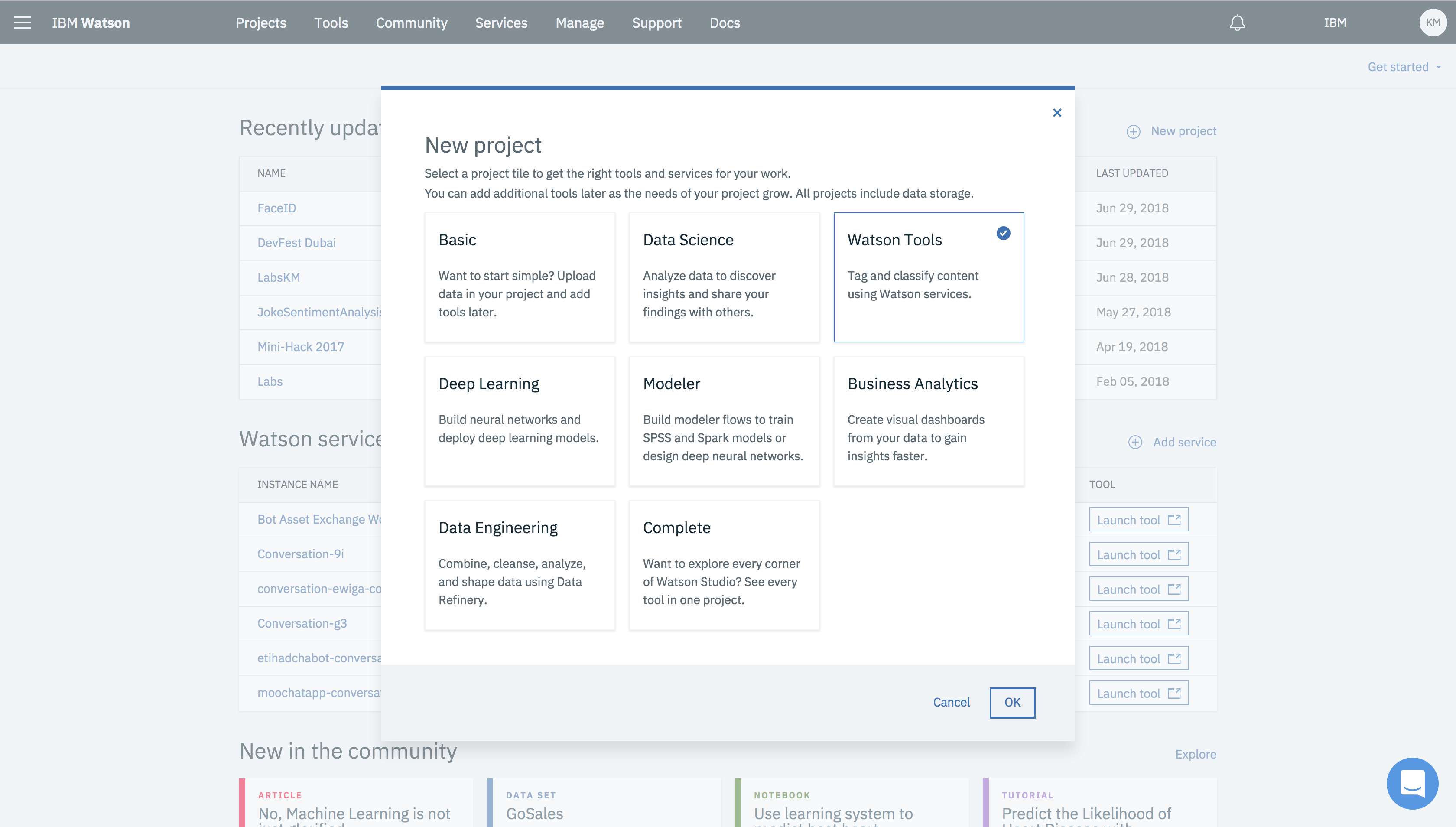
- Click on New Project and select Watson Tools.
-
On selecting Watson Tools project tile, two services i.e Object Storage and Watson Visual Recognition will be created in your IBM cloud dashboard.
-
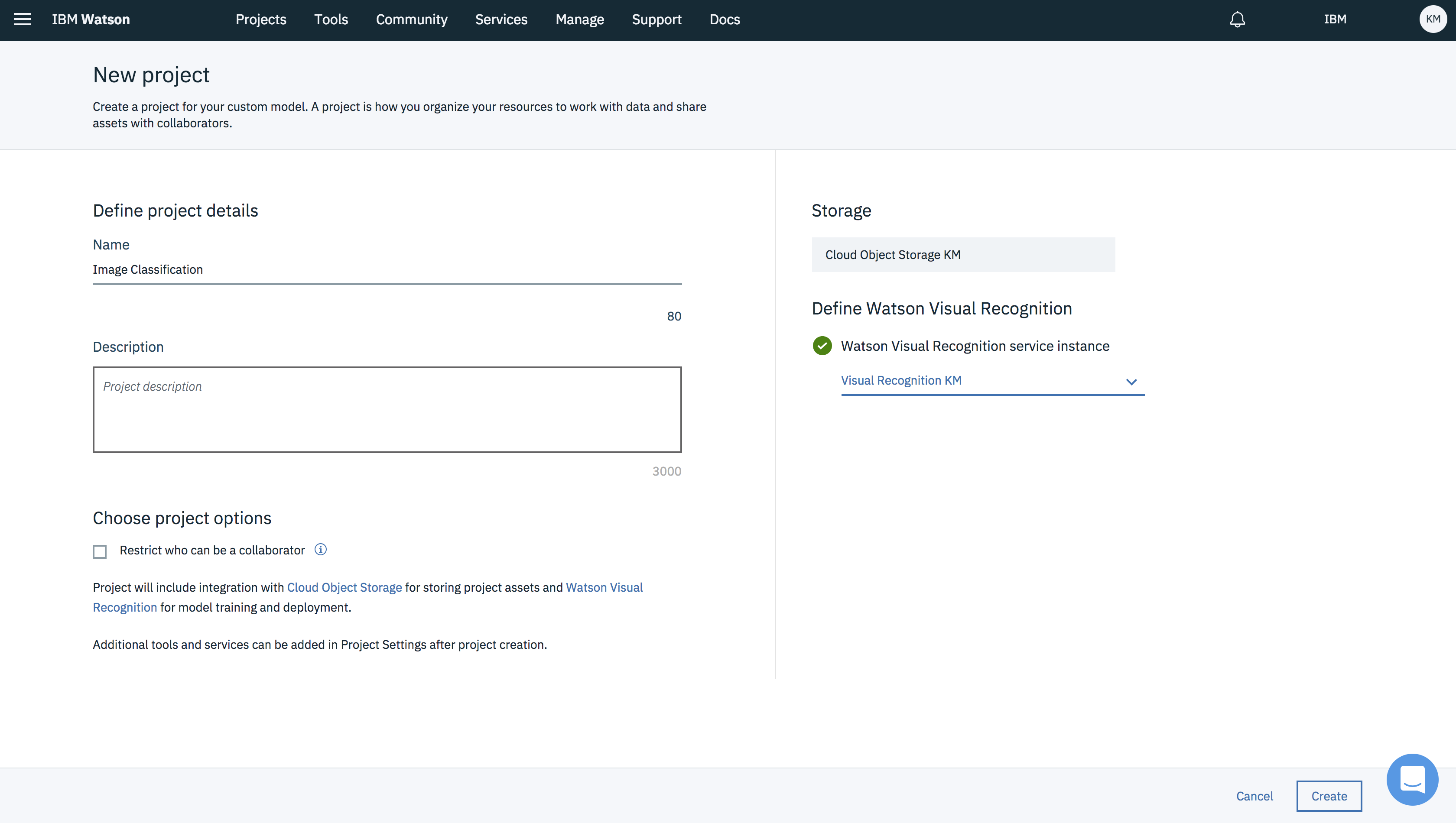
Enter Project Name, details (optional), choosing Restrict who can be a collaborator (optional). Notice on the side that Object Storage and Watson Visual Recognition services are selected.
- If by some error in the server they are not created, they can be added from the drop-down list too via Watson Studio.
- Project dashboard will be shown. That will have tabs like Overview, Assets, Bookmarks, Access Control, Settings.
- Select the Assets tab.
- Click on New data asset.
- A side navigation drawer will open with Load tab selected.
- Click on browse or simply drag and drop the data assets of your project. (Note:- In case of Watson Visual Recognition project, have your data assets in a zip file).
- Click on New Visual Recognition model.
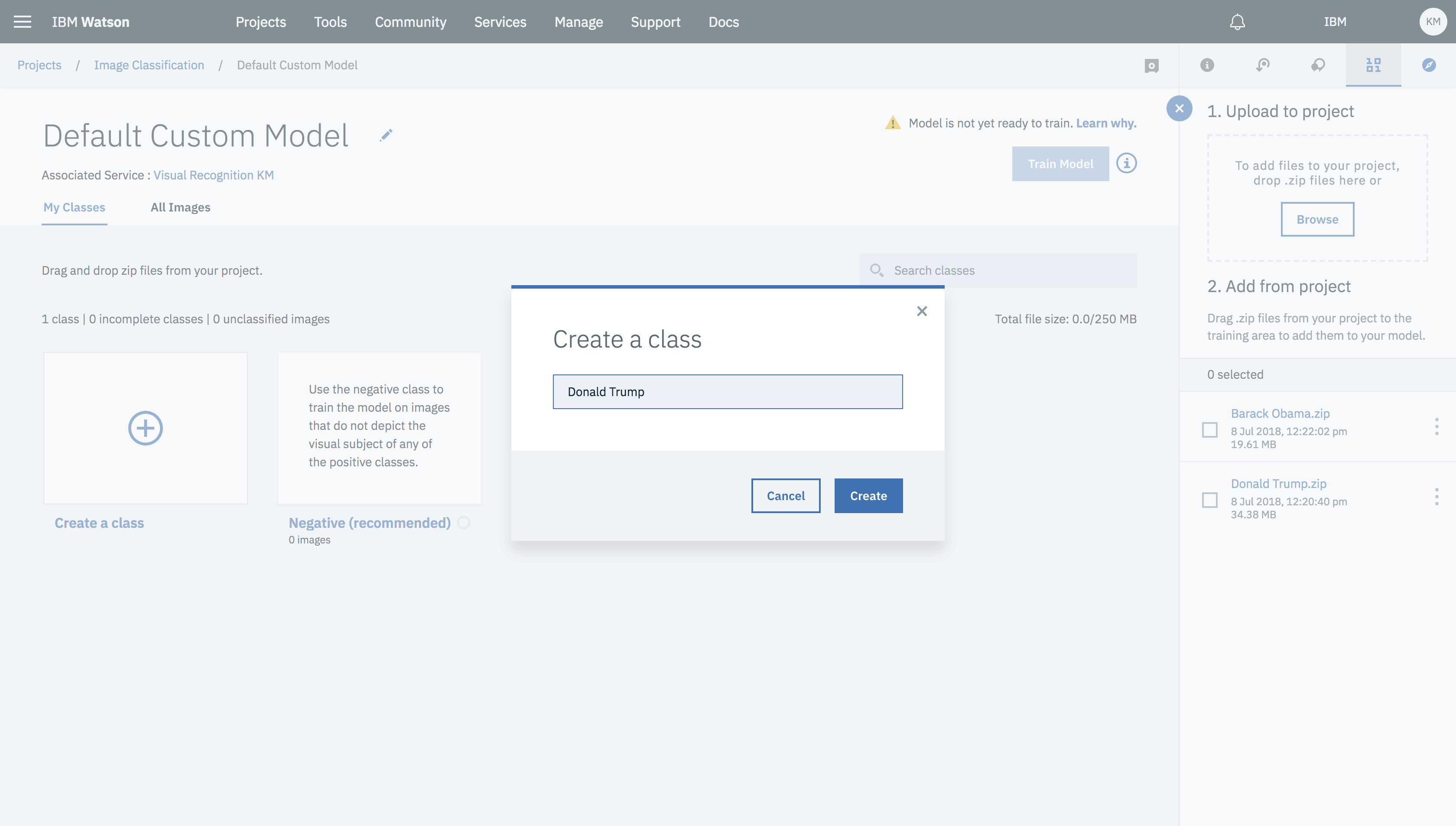
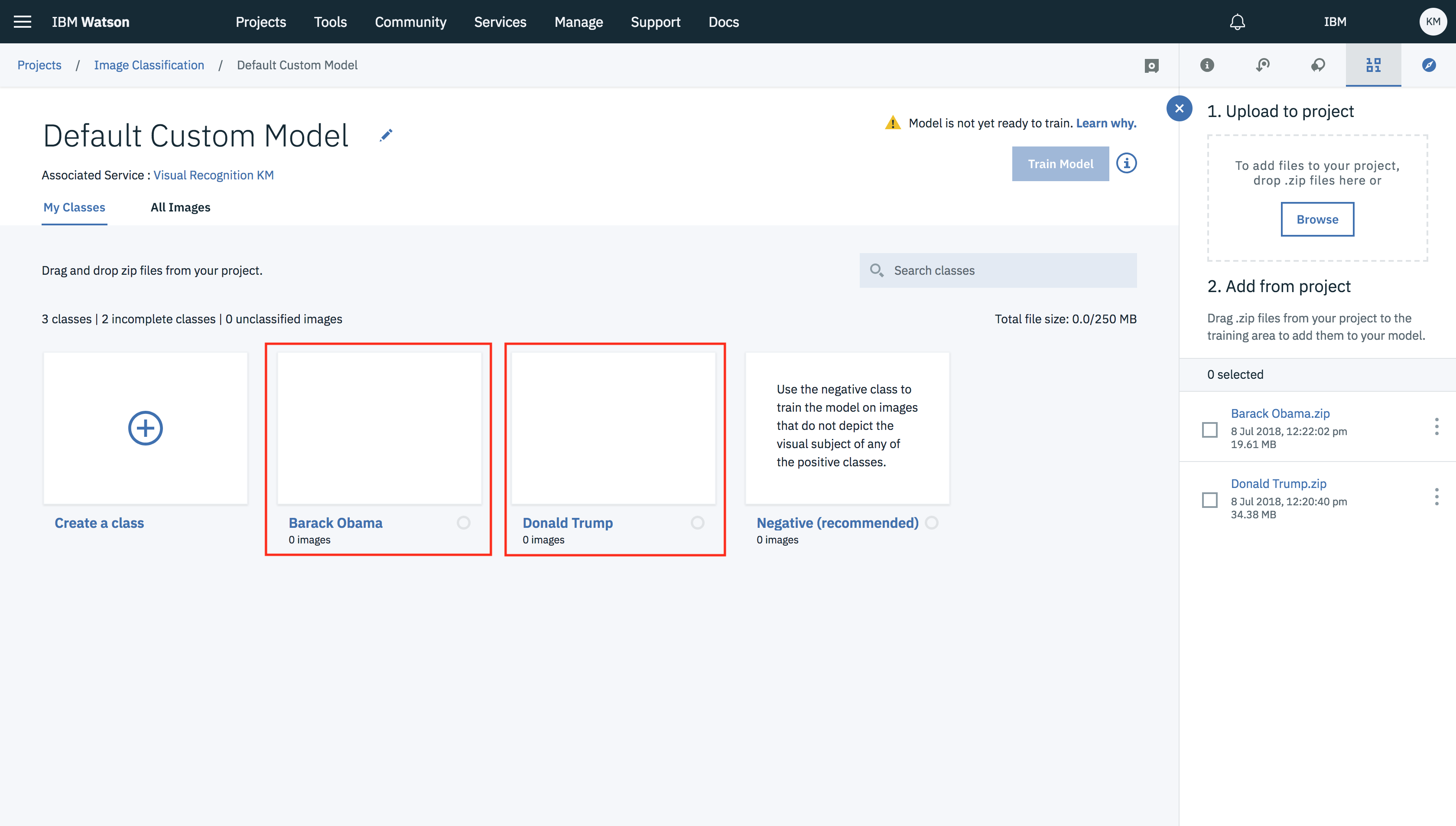
- New dashboard will open with model names as Default Custom Model. Dashboard will show two tabs My Classes and All Images.
- In the My Classes tab click on Create a class and create a class you want to classify. (Note:- class of an image, it relates to the object classification task).
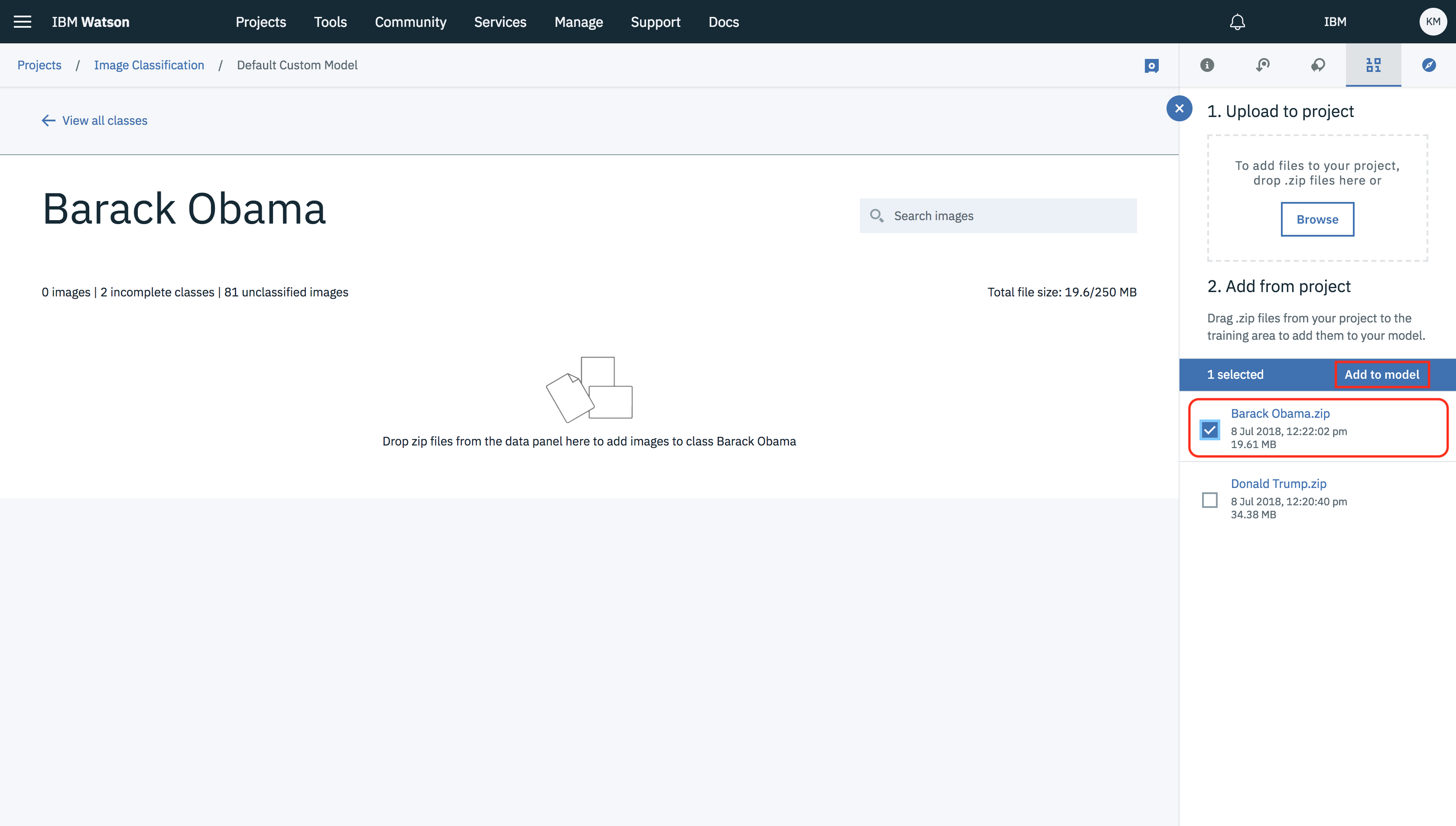
- Click on the created class and add the data asset to it by selected the data asset and clicking on Add to model.
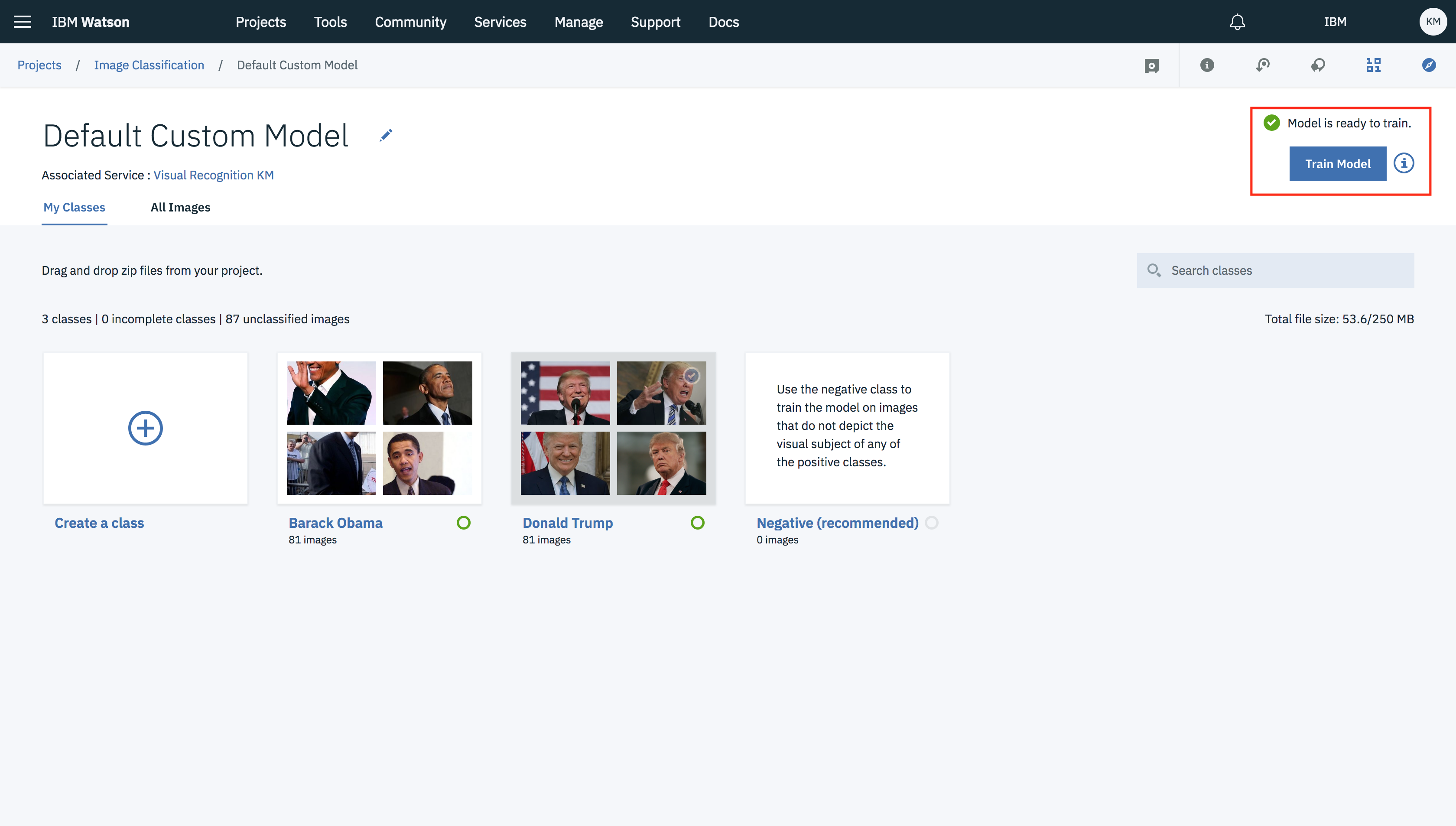
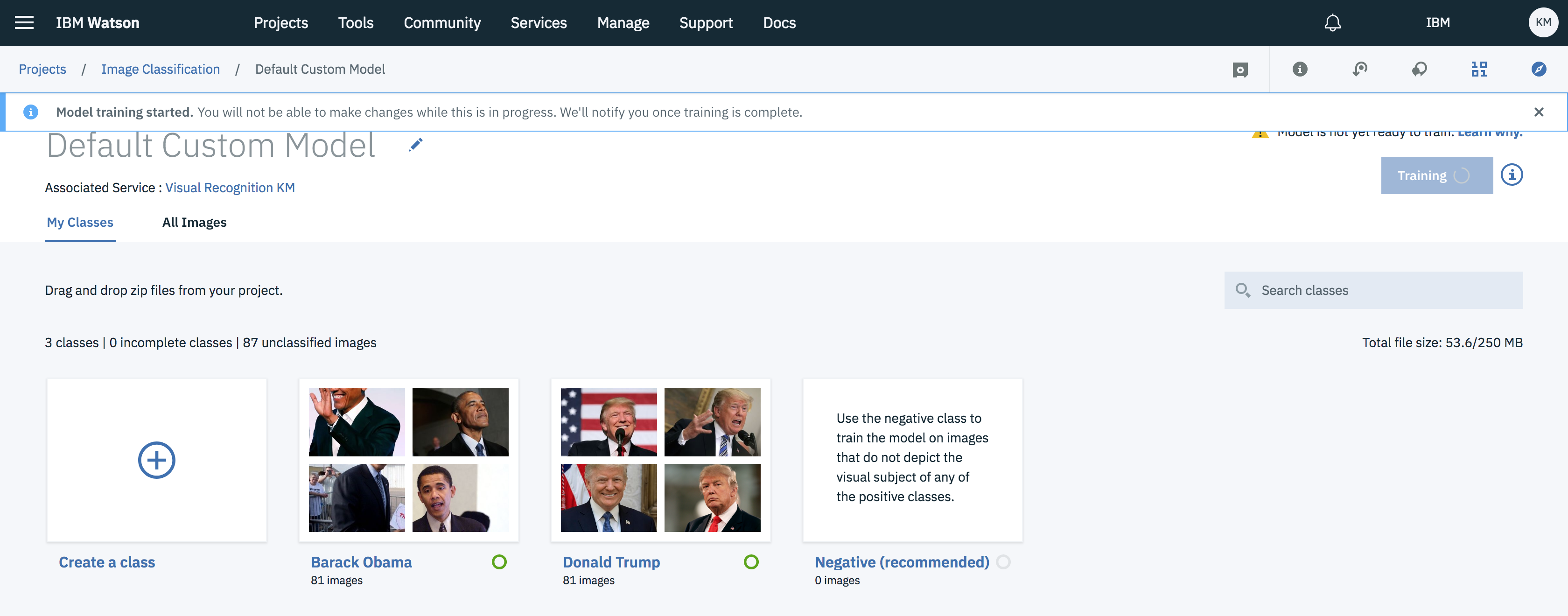
- Once data assets have been added to the respective classes click on Train Model button.
- Process will take around 10-15 min to train the model for respective classes.
- Once the traning is complete click on here in the snakbar.
- A new dashboard will open having three tabs
- Overview
- Test
- Implementation
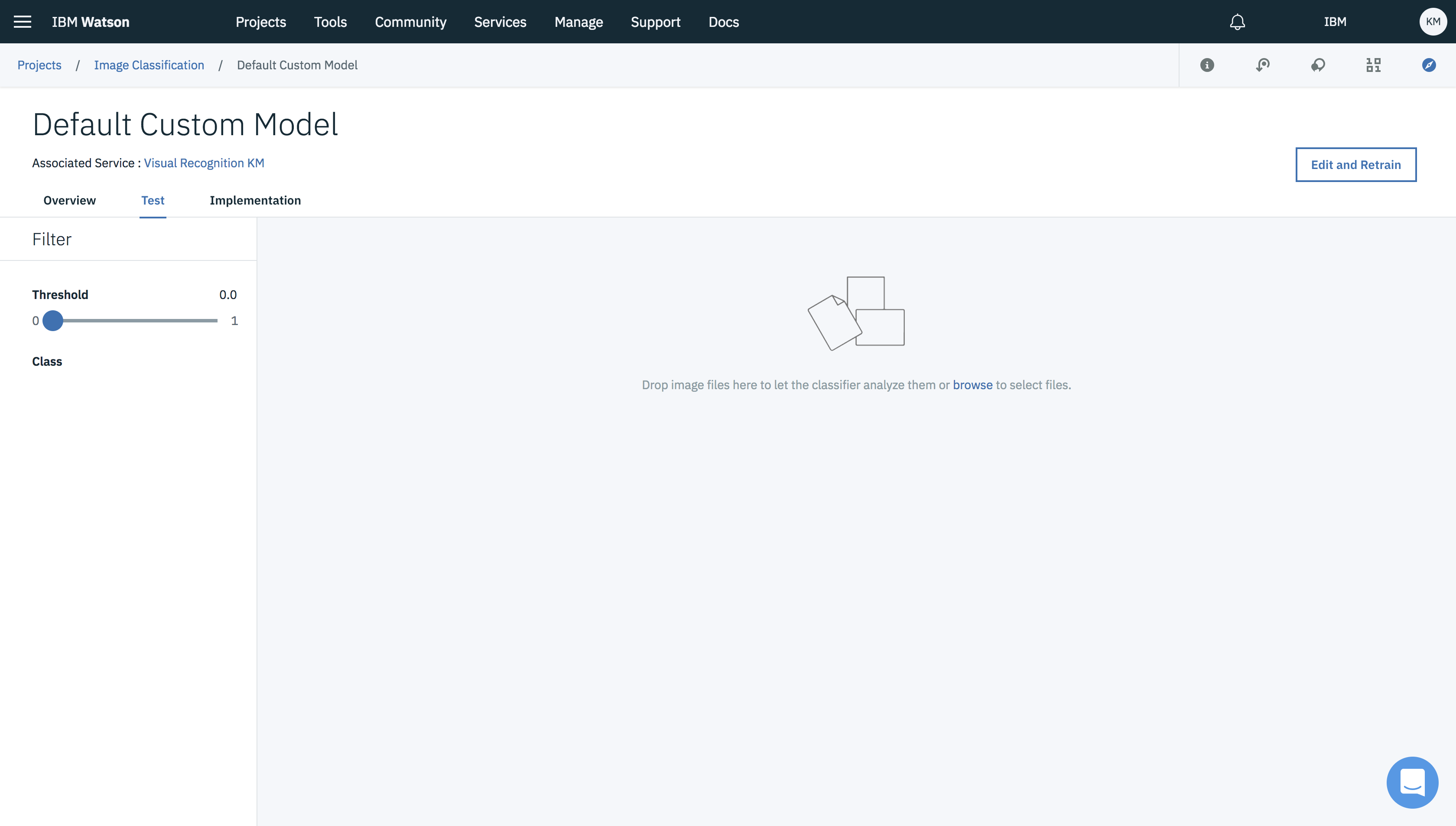
- Click on the Test tab.
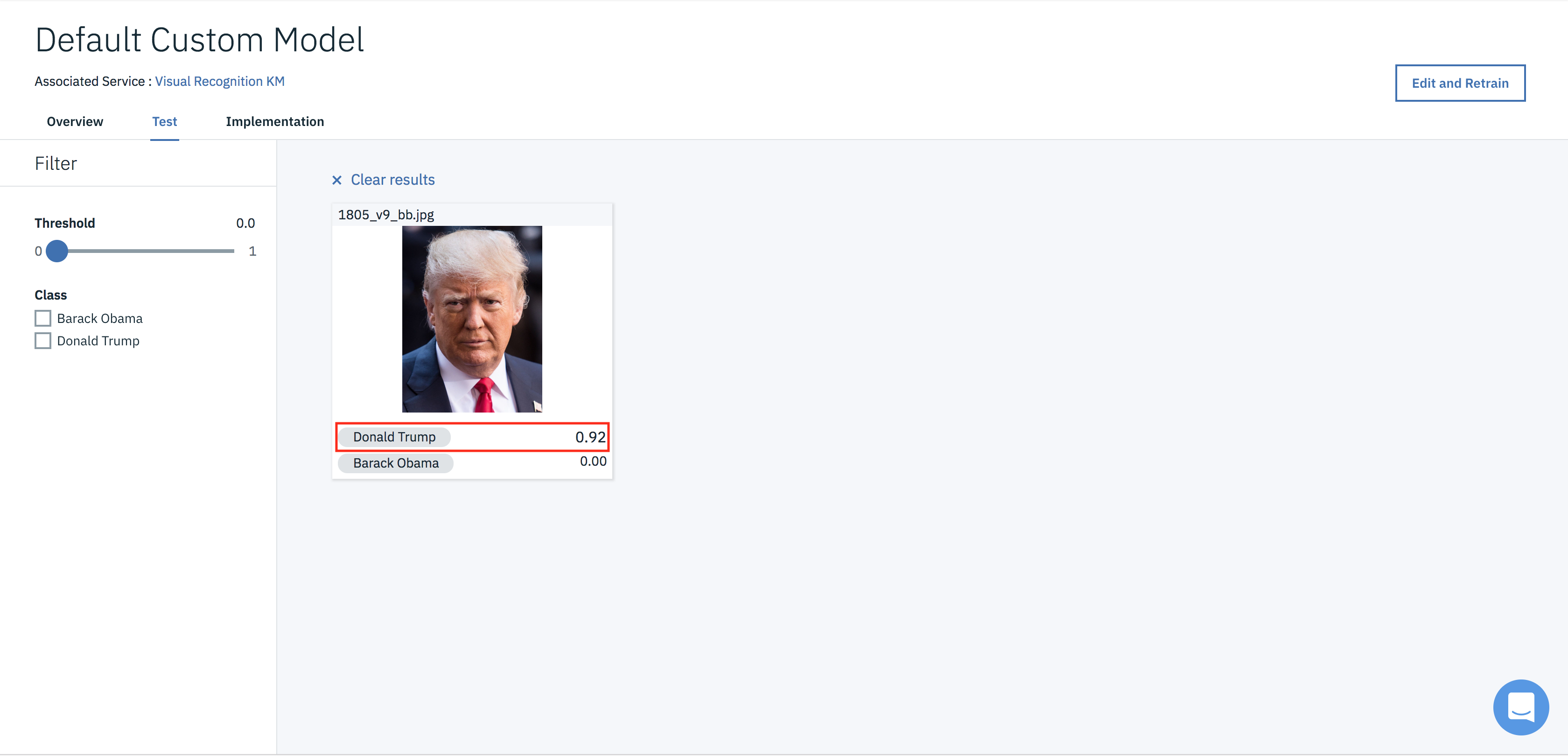
- Take a test image from any source and click on browse or simply drag and drop the image on to the dashboard.
- After loading the image into image classifier, it run the image classification algorithm which returns the accuracy within the range from 0 to 1 that identifies your class or object.
- Start Android Studio and create a new project.
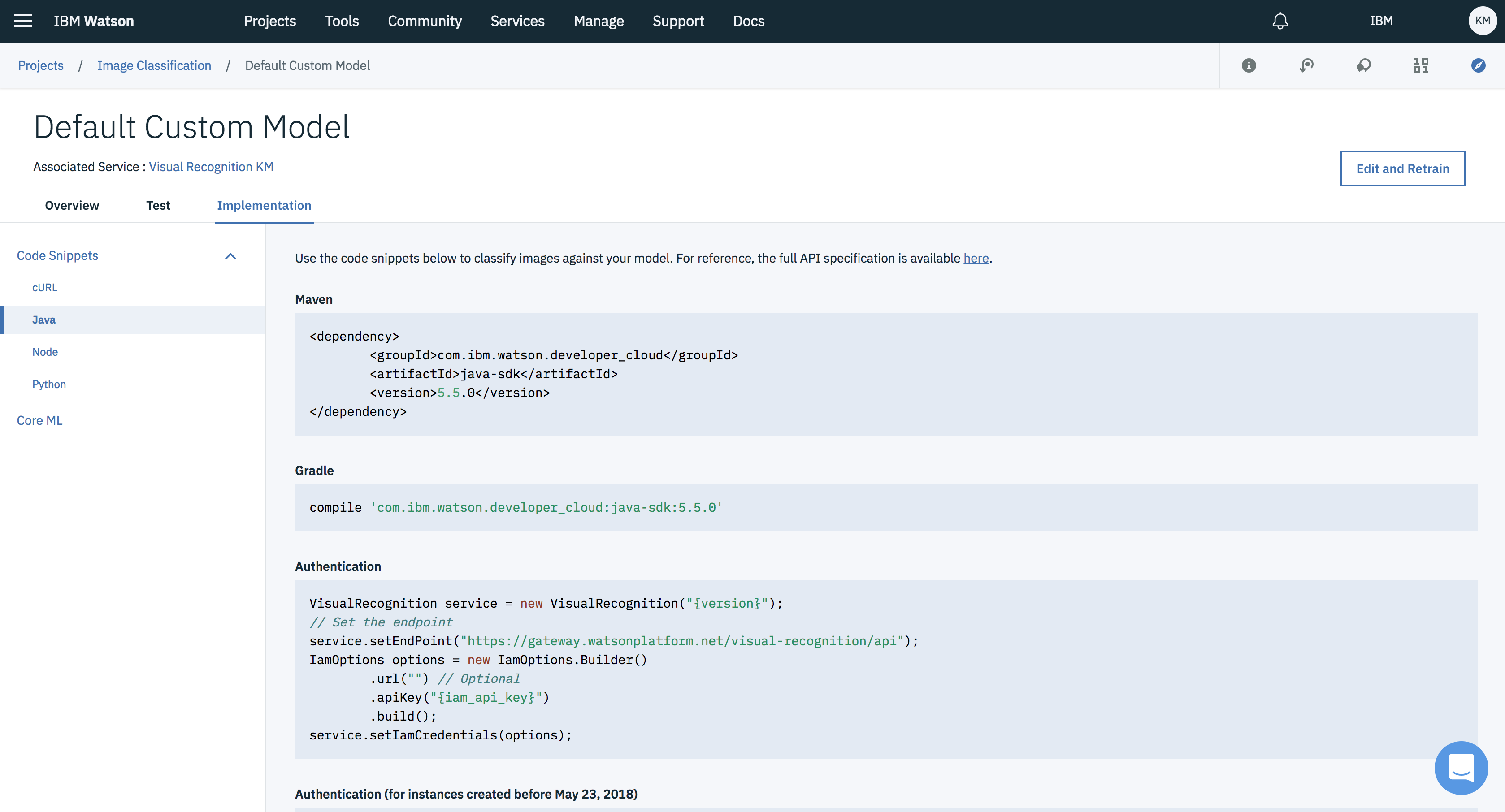
- Go back to your model in watson studio and click on Implementation tab.
- Under the Implementation tab look for Java on the left hand side navigation drawer and select it. You will find the code required to communicate with the model.
-
In Android Studio under Gradle Scripts/build.gradle (Module:app). Add
implementation 'com.ibm.watson.developer_cloud:java-sdk:5.5.0'in the dependencies block and click on Sync Now. -
After the sync process is complete, go to MainActivity under the java/package_name.project_name/ and add two global object
- VisualRecognition
- CameraHelper
VisualRecognition mVisualRecognition;
CameraHelper mCameraHelper;
- Under the onCreate method in Main Activity, initialize the objects.
mVisualRecognition = new VisualRecognition("{version}");
mVisualRecognition.setApiKey(api_key);
mCameraHelper = new CameraHelper(this);
- Once the above parts are done, under onActivityResult method create a background thread for making the network call, parsing the result and displaying the result to the UI.
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode == CameraHelper.REQUEST_IMAGE_CAPTURE) {
final Bitmap photo = mCameraHelper.getBitmap(resultCode);
final File photoFile = mCameraHelper.getFile(resultCode);
ImageView preview = findViewById(R.id.img_view_main);
preview.setImageBitmap(photo);
AsyncTask.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream imagesStream = null;
try {
imagesStream = new FileInputStream(photoFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ClassifyOptions classifyOptions = new ClassifyOptions.Builder()
.imagesFile(imagesStream)
.imagesFilename(photoFile.getName())
.threshold((float) 0.6)
.owners(Arrays.asList("me"))
.build();
ClassifiedImages result = mVisualRecognition.classify(classifyOptions).execute();
Gson gson = new Gson();
String json = gson.toJson(result);
String name = null;
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(json);
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObject.getJSONArray("images");
JSONObject jsonObject1 = jsonArray.getJSONObject(0);
JSONArray jsonArray1 = jsonObject1.getJSONArray("classifiers");
JSONObject jsonObject2 = jsonArray1.getJSONObject(0);
JSONArray jsonArray2 = jsonObject2.getJSONArray("classes");
JSONObject jsonObject3 = jsonArray2.getJSONObject(0);
name = jsonObject3.getString("class");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
final String finalName = name;
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
TextView detectedObjects = findViewById(R.id.text_view_main);
detectedObjects.setText(finalName);
detectedObjects.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this, RecommendationActivity.class));
}
});
}
});
}
});
}
}
Congratulations! Now you have an android application communicating with the model built and deployed on Watson Studio.
Link to the Github Repo contining the android code.
In this how-to we learned how to build a image classification model using Watson Tool project on Watson Studio and then use the model to build and android application.