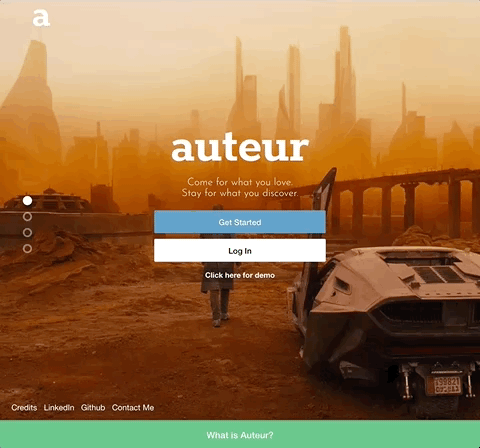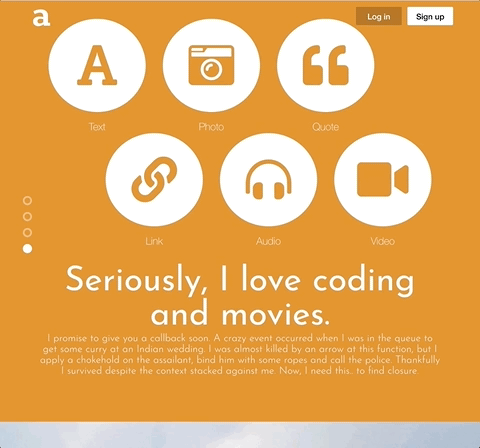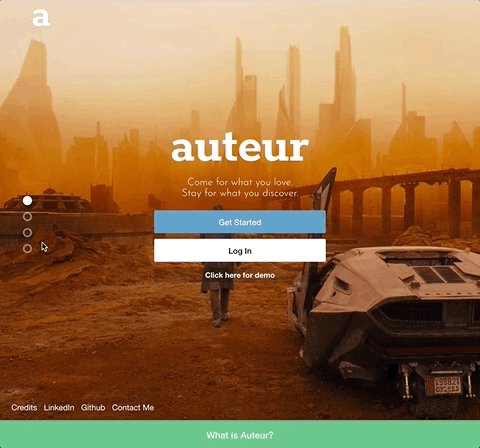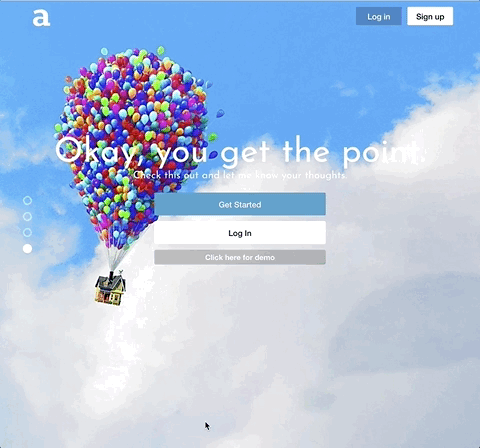
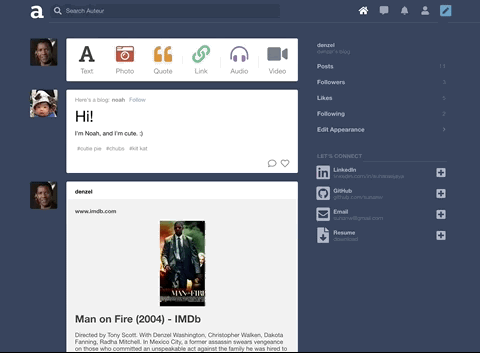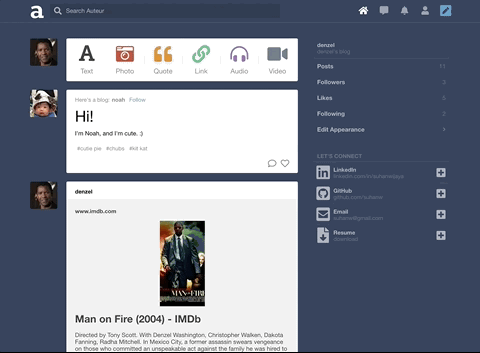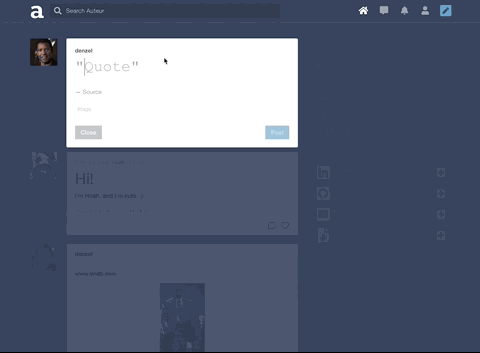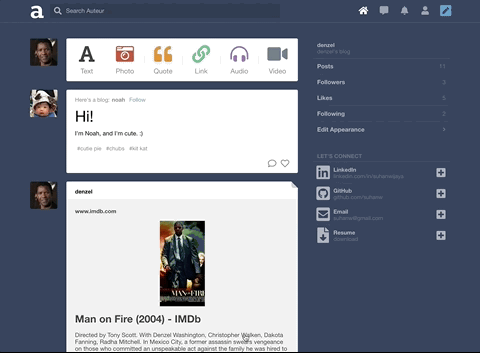
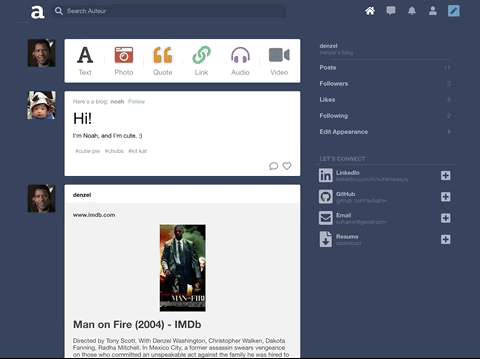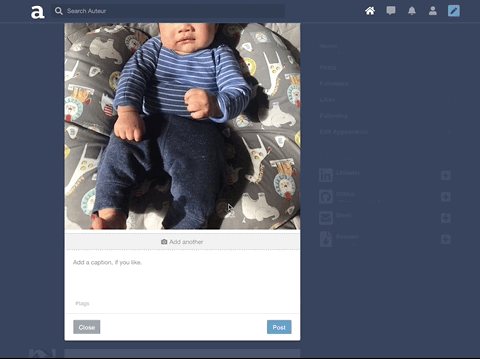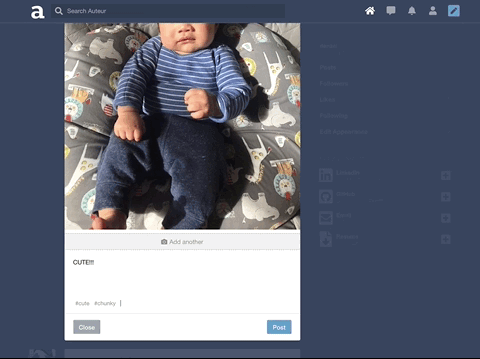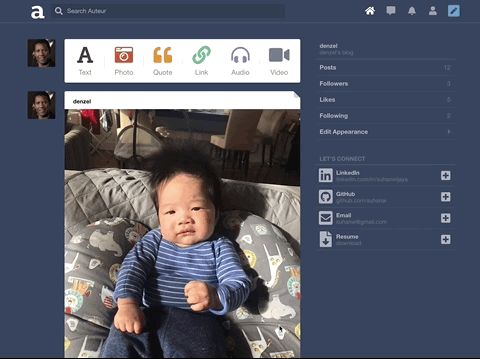
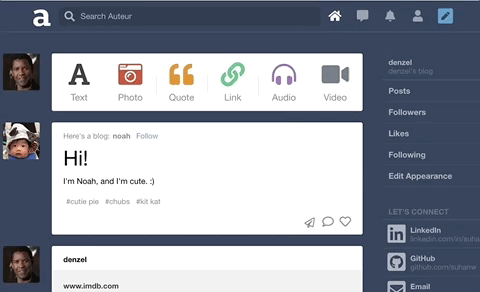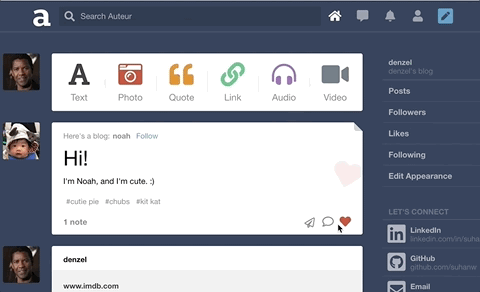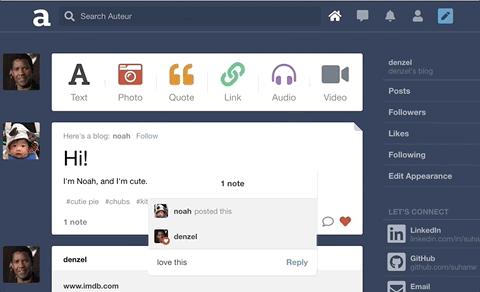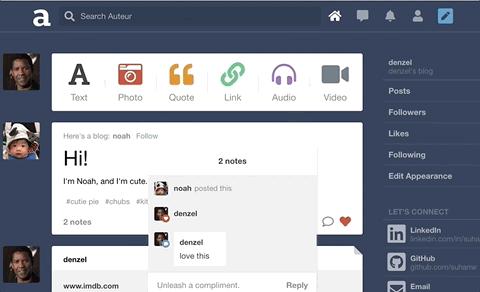
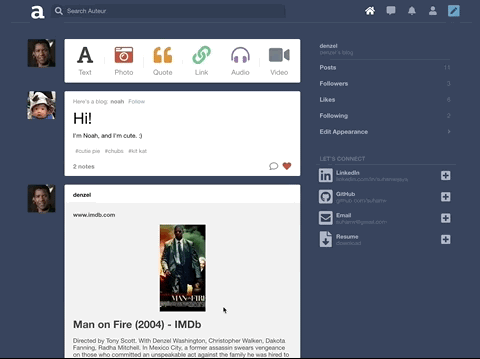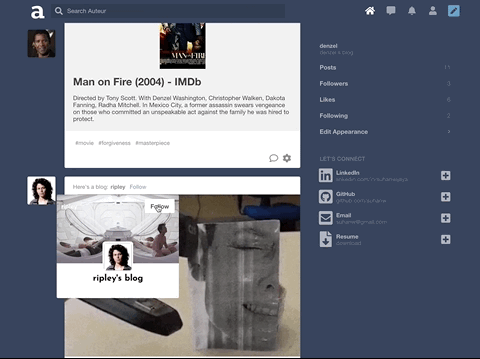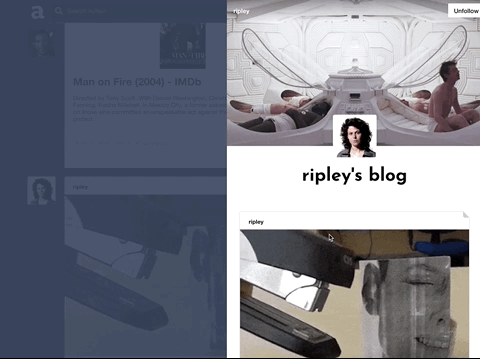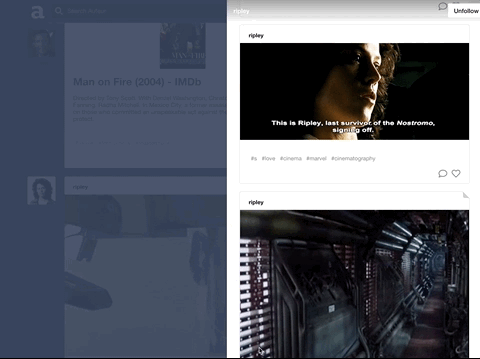
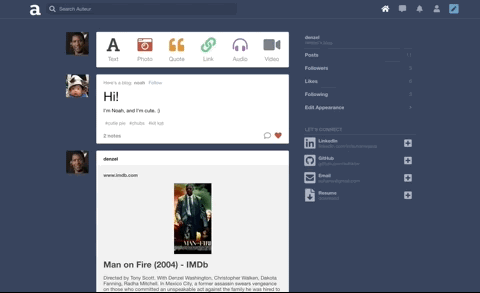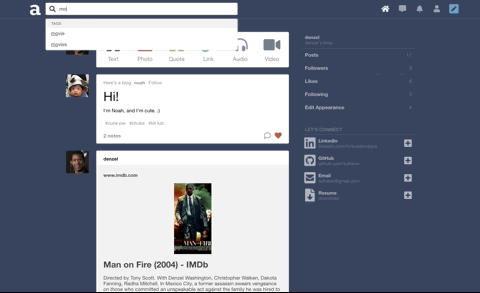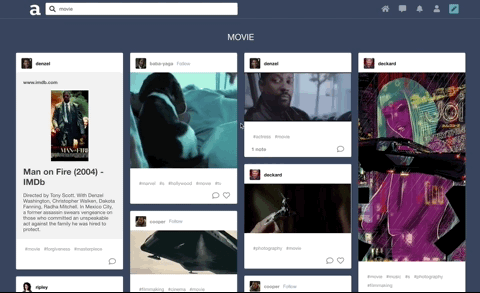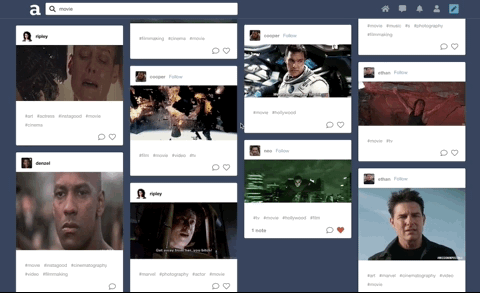
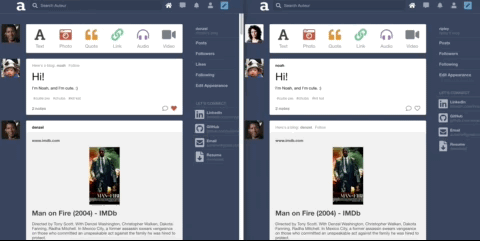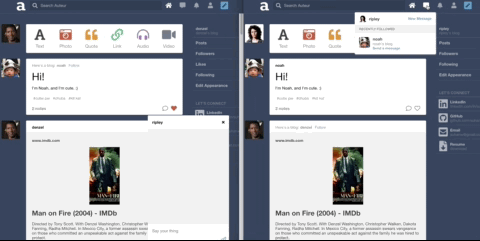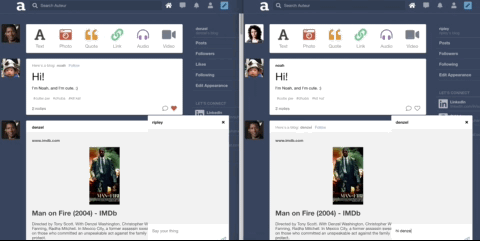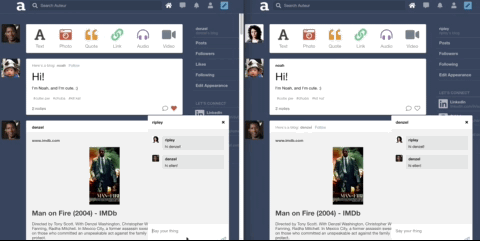
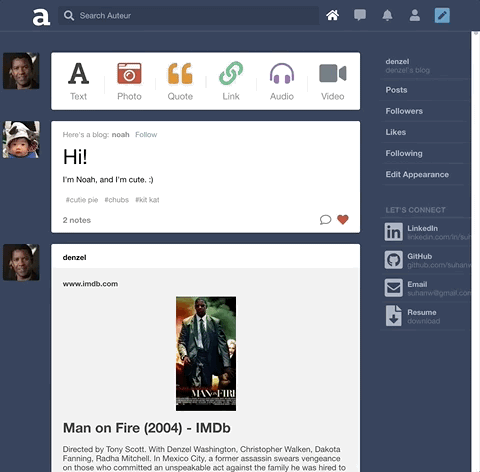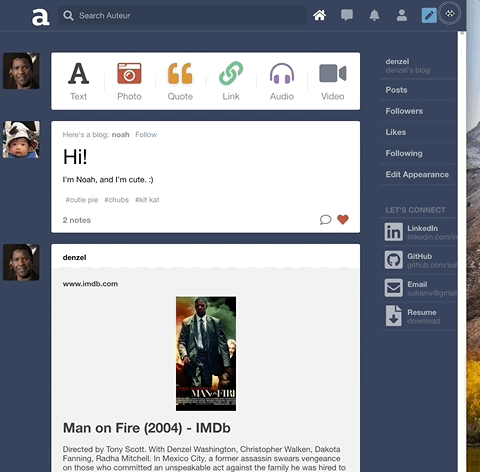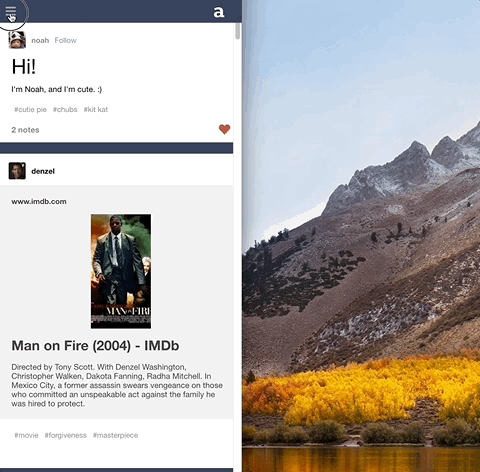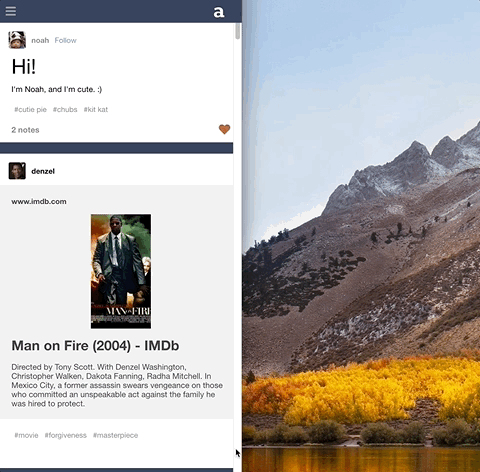
Auteur is a full-stack web application inspired by Tumblr. It utilizes Node.js on the backend, a MongoDB database, and React.js with a Redux architectural framework on the frontend.
Auteur is a single page app that allows for quick navigation between its various components. As data is fetched from NodeJS, components are only updated when necessary.
Integrated React stateful components, CSS keyframe animations, and DOM events to create a carousel that responds to arrow keys, strokes on the touchpad, and mouse clicks.
To keep code DRY, leveraged Higher Order Components and component composition to render different types of posts and new/edit forms.
Incorporated AWS SDK to upload images to AWS S3 and persist image data to MongoDB
On the backend, designed a polymorphic and extensible MongoDB schema for different note types such as likes and comments.
Integrated React and CSS3 keyframes to animate page elements and improve user experience.
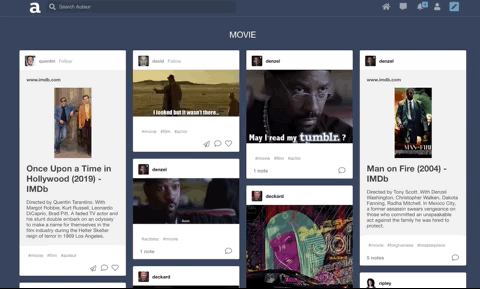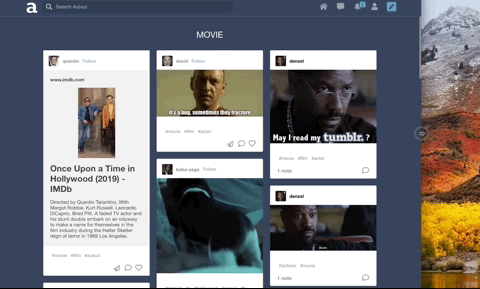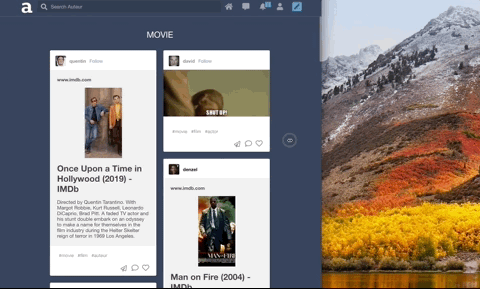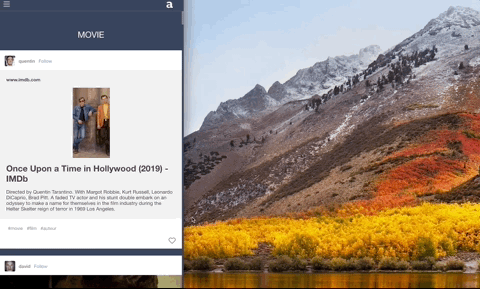
Built a search feature with autocomplete that suggests hashtags ranked by popularity. Integrated React and CSS3 Flexbox to accomplish a ‘masonry’ layout for search results.
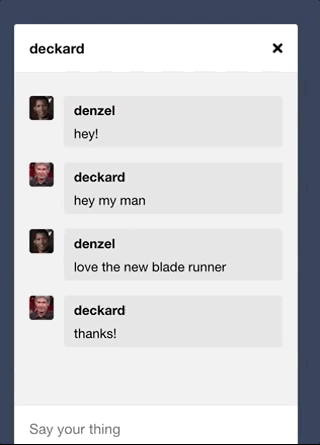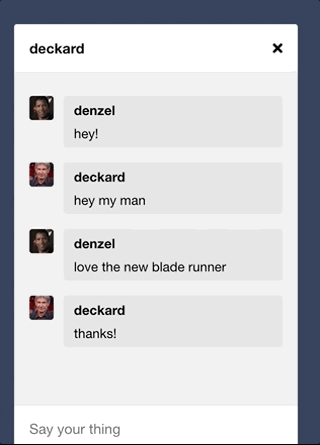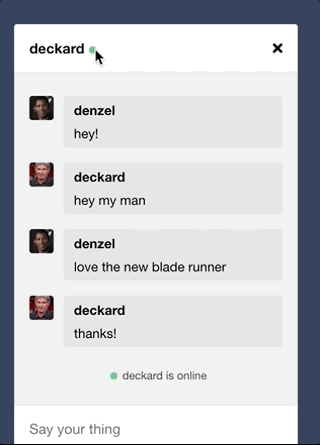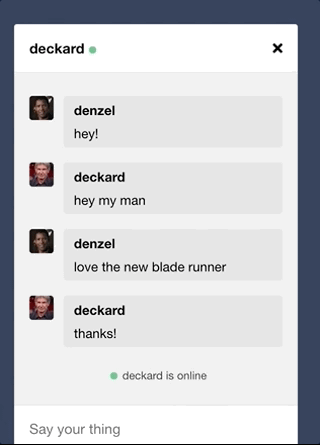
Leveraged WebSockets to implement the chat feature.
Implemented online indicator.
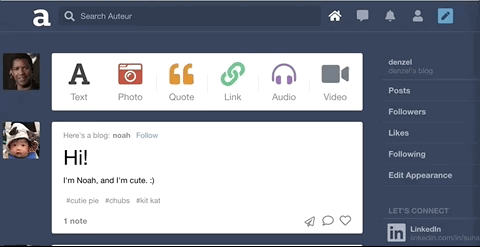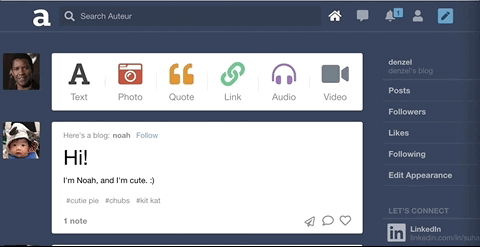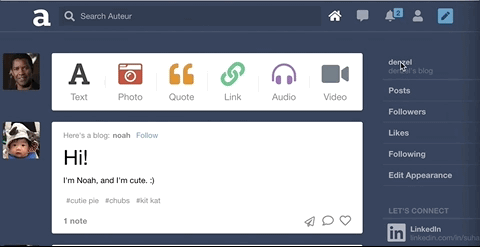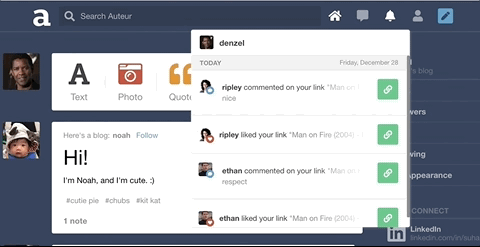
Leveraged WebSockets to implement the notifications feature. Likes and comments will create real-time in-app notifications for the relevant user.
Enabled selective rendering and responsive layout for mobile devices via CSS media query.
- Designed modular React components & normalized Redux state for a seamless single page experience.
- Used React Context to pass global data to nested components without manually threading props.
// global_context_provider.jsx
export const GlobalContext = React.createContext(null);
class GlobalContextProvider extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
const { children, currentUser } = this.props;
return (
<GlobalContext.Provider
value={{
currentUser,
}} >
{children}
</GlobalContext.Provider>
);
}
}// deeply nested component
import { GlobalContext } from '../../global_ context_provider';
class PostShowItem extends React.Component {
renderPostContent() {
const { currentUser } = this.context;
if (!currentUser.following.includes(blog._id)) {
// suggest user to follow blog
}
}
}
PostShowItem.contextType = GlobalContext;- Utilized Promises to simplify async code and minimize 'callback hell' on the NodeJS back-end.
// posts.js - API endpoint to create new post
router.post('/posts',
middleware.isLoggedIn,
upload.array('newFiles'),
function (req, res) {
// STEP 1 - find blog
modelQuery.findOneBlog(req.params.id)
.then((foundBlog) => {
let postBody = lodash.merge({}, req.body);
// ...
// STEP 2 - add tags to post
return modelQuery.addTagsToPost(postBody, foundBlog);
})
.then(({ post, blog }) => {
let newPost = new Post(post);
// STEP 3a - if a media post, upload files to AWS
if (['photo', 'video', 'audio'].includes(newPost.type)) {
// ...
return mediaUtil.uploadFiles(req.files, newPost, blog);
}
// STEP 3b - if not a media post, pass on to the next 'then' block
return { post: newPost, blog: blog };
})
.then(({ post, blog }) => {
// ...
// STEP 4 - save the new post
return post.save()
})
.then((post) => {
// STEP 5 - include post's tags
return post.populate({ path: 'tags', select: 'label' })
.execPopulate();
})
.then((post) => {
// STEP 6 - send http reponse json
return res.json(post);
})
// STEP 7 - handle error(s)
.catch((err) => res.status(422).json([err.message]));
});To run locally:
- Use Node v8
- Start local MongoDB
mongod --config /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf - Start app
npm run dev