C++ implementation of ChatGLM-6B and ChatGLM2-6B for real-time chatting on your MacBook.
- Pure C++ implementation based on ggml, working in the same way as llama.cpp.
- Accelerated memory-efficient CPU inference with int4/int8 quantization, optimized KV cache and parallel computing.
- Streaming generation with typewriter effect.
- Python binding, web demo, and more possibilities.
Preparation
Clone the ChatGLM.cpp repository into your local machine:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/li-plus/chatglm.cpp.git && cd chatglm.cppIf you forgot the --recursive flag when cloning the repository, run the following command in the chatglm.cpp folder:
git submodule update --init --recursiveQuantize Model
Use convert.py to transform ChatGLM-6B or ChatGLM2-6B into quantized GGML format. For example, to convert the fp16 base model to q4_0 (quantized int4) GGML model, run:
# For ChatGLM-6B
python3 convert.py -i THUDM/chatglm-6b -t q4_0 -o chatglm-ggml.bin
# For ChatGLM2-6B
python3 convert.py -i THUDM/chatglm2-6b -t q4_0 -o chatglm2-ggml.binFor LoRA model, specify -l <lora_model_name_or_path> flag to merge your LoRA weights into the base model.
Build & Run
Compile the project using CMake:
cmake -B build
cmake --build build -jNow you may chat with the quantized ChatGLM-6B model by running:
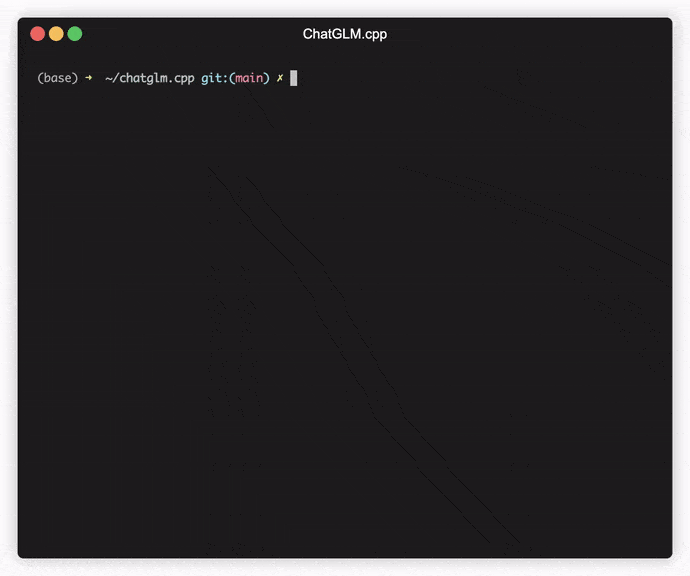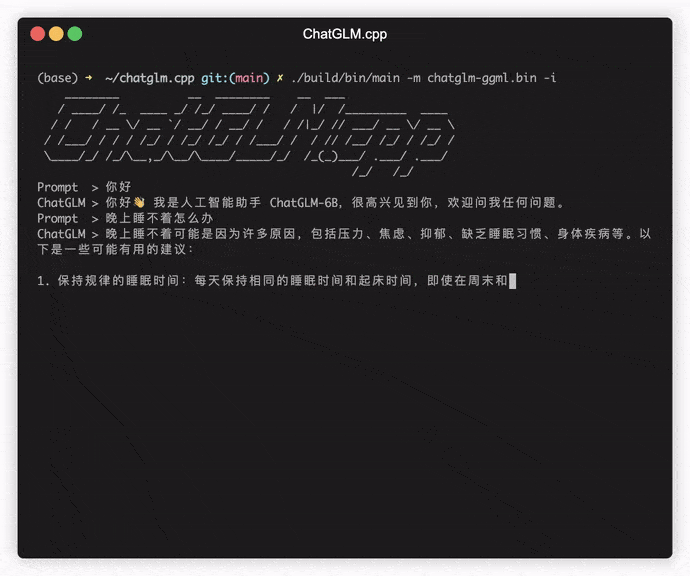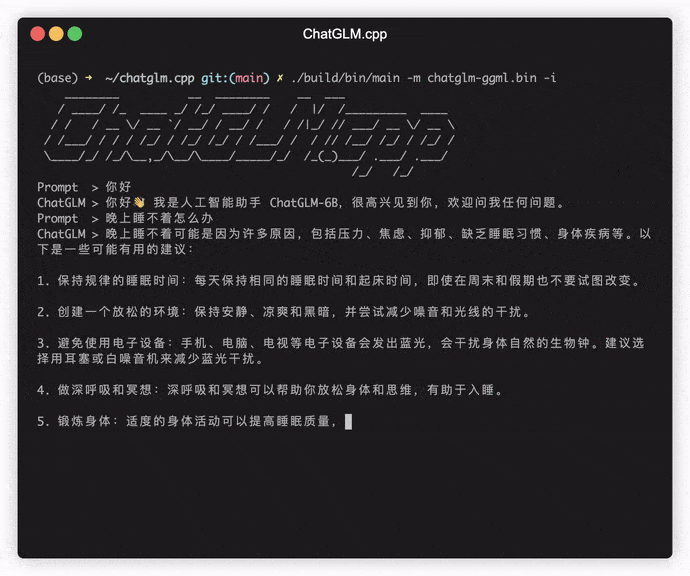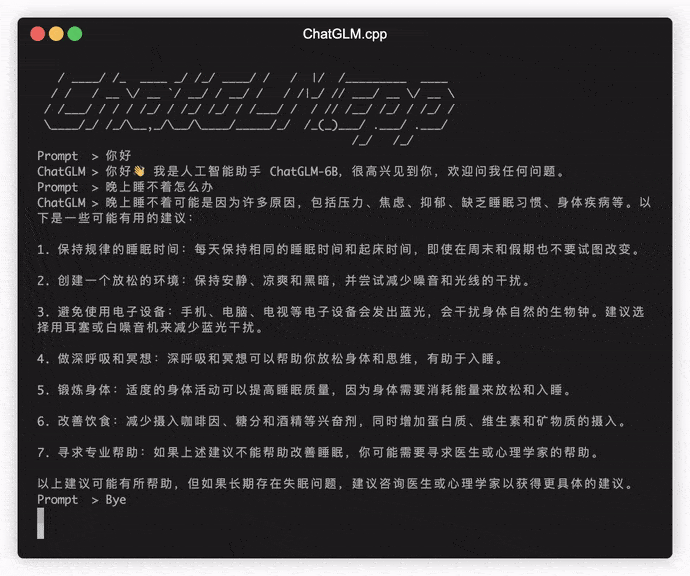
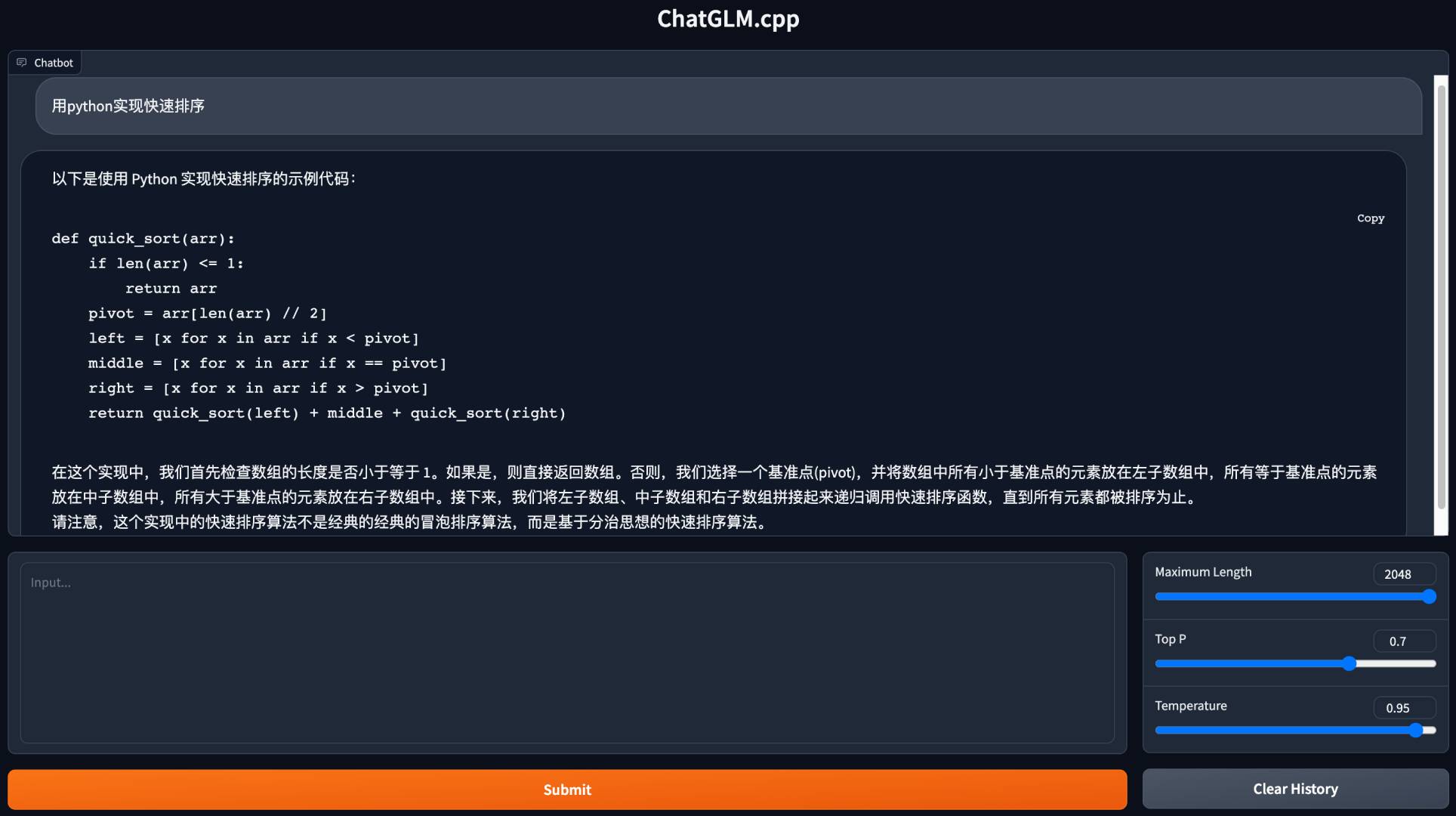
./build/bin/main -m chatglm-ggml.bin -p 你好 # ChatGLM-6B
# 你好👋!我是人工智能助手 ChatGLM-6B,很高兴见到你,欢迎问我任何问题。
./build/bin/main -m chatglm2-ggml.bin -p 你好 --top_p 0.8 --temp 0.8 # ChatGLM2-6B
# 你好👋!我是人工智能助手 ChatGLM2-6B,很高兴见到你,欢迎问我任何问题。To run the model in interactive mode, add the -i flag. For example:
./build/bin/main -m chatglm-ggml.bin -iIn interactive mode, your chat history will serve as the context for the next-round conversation.
Run ./build/bin/main -h to explore more options!
BLAS library can be integrated to further accelerate matrix multiplication. However, in some cases, using BLAS may cause performance degradation. Whether to turn on BLAS should depend on the benchmarking result.
Accelerate Framework
Accelerate Framework is automatically enabled on macOS. To disable it, add the CMake flag -DGGML_NO_ACCELERATE=ON.
OpenBLAS
OpenBLAS provides acceleration on CPU. Add the CMake flag -DGGML_OPENBLAS=ON to enable it.
cmake -B build -DGGML_OPENBLAS=ON
cmake --build build -jcuBLAS
cuBLAS uses NVIDIA GPU to accelerate BLAS. Add the CMake flag -DGGML_CUBLAS=ON to enable it.
cmake -B build -DGGML_CUBLAS=ON
cmake --build build -jNote that the current GGML CUDA implementation is really slow. The community is making efforts to optimize it.
To install the Python binding from source, run:
# install from the latest source hosted on GitHub
pip install git+https://github.com/li-plus/chatglm.cpp.git@main
# or install from your local source
pip install .Run the Python example to chat with the quantized model:
python3 cli_chat.py -m chatglm-ggml.bin -iYou may also launch a web demo to chat in your browser:
python3 web_demo.py -m chatglm-ggml.binFor ChatGLM2, change the model path to chatglm2-ggml.bin and everything works fine.
Measured on a Linux server with Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8260 CPU @ 2.40GHz using 16 threads.
ChatGLM-6B:
| Q4_0 | Q8_0 | F16 | F32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ms/token | 74 | 114 | 189 | 357 |
| file size | 3.3GB | 6.2GB | 12GB | 23GB |
| mem usage | 4.0GB | 6.9GB | 13GB | 24GB |
ChatGLM2-6B:
| Q4_0 | Q8_0 | F16 | F32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ms/token | 64 | 106 | 189 | 372 |
| file size | 3.3GB | 6.2GB | 12GB | 24GB |
| mem usage | 3.4GB | 6.2GB | 12GB | 23GB |
- To perform unit tests, add the CMake flag
-DCHATGLM_ENABLE_TESTING=ON, recompile, and run./build/bin/chatglm_test. For benchmark only, run./build/bin/chatglm_test --gtest_filter=ChatGLM.benchmark. - To format the code, run
cmake --build build --target lint. You should haveclang-format,blackandisortpre-installed. - To check performance issue, add the CMake flag
-DGGML_PERF=ON. It will show timing for each graph operation when running the model.
- This project is greatly inspired by @ggerganov's llama.cpp and is based on his NN library ggml.
- Thank @THUDM for the amazing ChatGLM-6B and ChatGLM2-6B and for releasing the model sources and checkpoints.