Detection and localization of abnormalities in Computed Tomography (CT) scans is a critical routine task for radiologists. Accurate, automated detection of suspicious regions could greatly support screening, diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression. Most previous work focuses on a specific type of lesion within a relatively constrained (anatomical) context, such as lymph nodes, lung nodules and brain microbleeds.
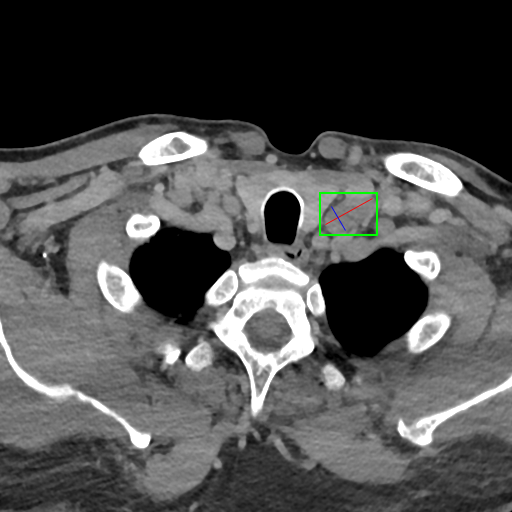
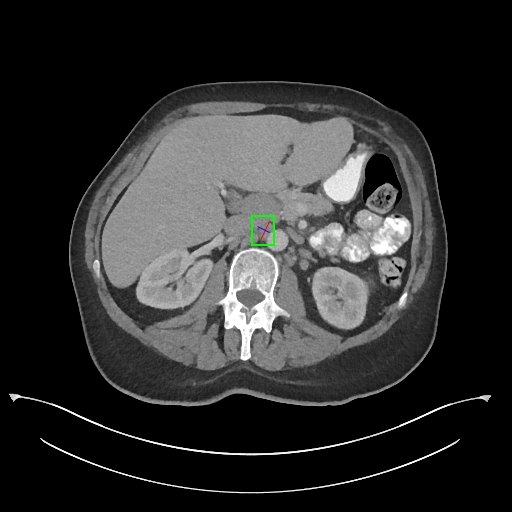
DeepLesion dataset consists of 32,120 axial CT slices from 10,594 studies of 4,427 patients There are 1~2 lesions in each slice, adding up to 32,735 lesions altogether.
The backbone of our approach is a RetinaNet, a recent one-stage method for object detection. The use of a focal loss addresses the common problem of class imbalance in detection tasks. The feature pyramids and lateral connections with a top-down architecture are adopted for detecting objects at different scales. This is an important difference with methods such as 3DCE, since the feature pyramids can effectively capture information about lesions of varying sizes including very small ones.