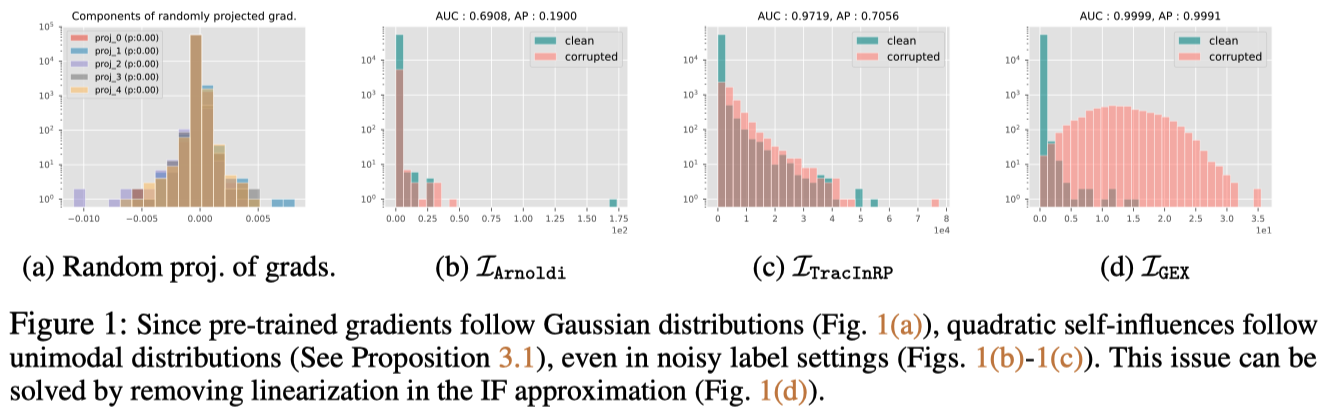
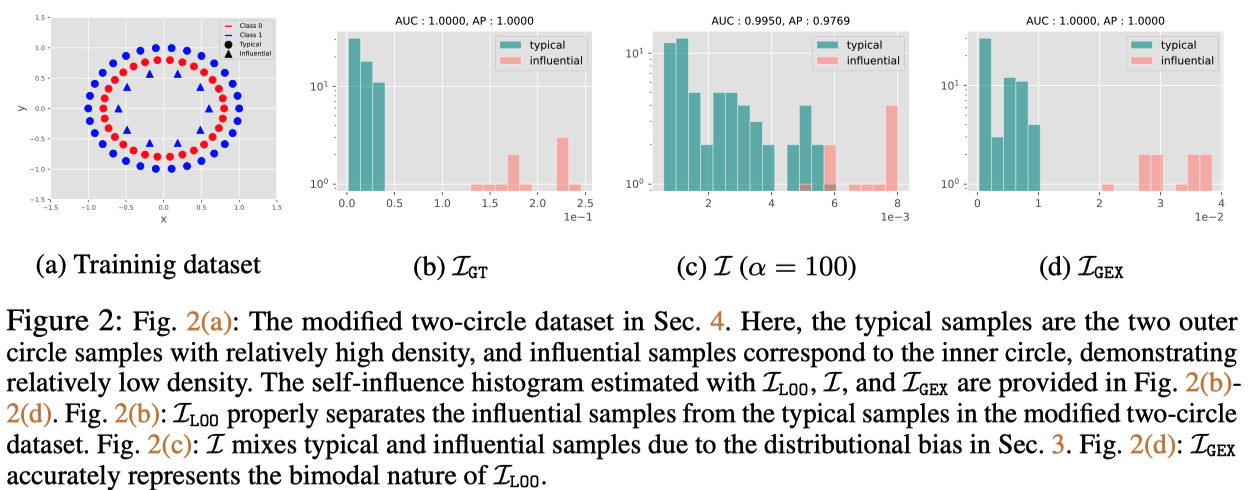
Official code implementation of "GEX: A flexible method for approximating influence via Geometric Ensemble" (NeurIPS 2023)
docker pull sungyubkim/jax:ntk-0.4.2docker run -p 8080:8080/tcp -it --rm --gpus all \
--ipc=host -v $PWD:/root -w /root \
sungyubkim/jax:ntk-0.4.2# to pre-train NN
python3 -m gex.pretrain.main \
--dataset=mnist \
--model=vgg \
--corruption_ratio=0.1# to estimate influence of pre-trained NN
python3 -m gex.noisy.main \
--dataset=mnist \
--model=vgg \
--corruption_ratio=0.1 \
--num_ens=8 \
--ft_lr=0.05 \
--ft_step=800 \
--ft_lr_sched=cosine \
--if_method=la_fgebash gex/mnist/total.sh./gex/{task}/result/{pretrain_hyperparameter_settings}/{posthoc_hyperparameter_settings}As sample-wise gradient (
Influence Function can be interpreted as linearized sample-loss deivation (or more simply covariance) given parameters are sampled from Laplace Approximation.
(1) Remove linearizations in sample-loss deviation and (2) Replace Laplace Approximation with Geometric Ensemble to mitigate the singularity of Hessian.
from gex.influence.estimate import compute_influence
# to compute influence kernel (N_tr, N_te) between train-test
influence_kernel = compute_influence(trainer, dataset_tr, dataset_te, dataset_opt , self_influence=False)
# to compute self-influence (N_tr) for train dataset
influence_kernel = compute_influence(trainer, dataset_tr, dataset_te, dataset_opt , self_influence=True)- Random Projection (
--if_method=randproj) - TracIn Random Projection (
--if_method=tracinrp) - Arnoldi (
--if_method=arnoldi) - Laplace approximation with K-FAC (
--if_method=la_kfac) - Geometric Ensemble (
--if_method=la_fge)
This work was supported by Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No.2019-0-00075, Artificial Intelligence Graduate School Program(KAIST))