👉🏻 Please check out my improved version of this project at https://superruzafa.github.io/visual-scala-reference
Drops longest prefix of elements that satisfy a predicate.
def dropWhile(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): Seq[A]
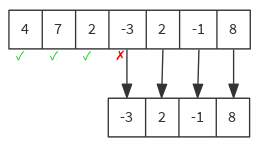
val list = List(4, 7, 2, -3, 2, -1, 8)
list dropWhile { n => n >= 0 } // List(-3, 2, -1, 8)
Selects all elements of this traversable collection which satisfy a predicate.
def filter(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): Seq[A]
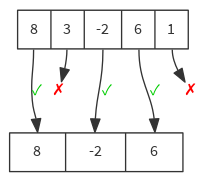
val list = List(8, 3, -2, 6, 1)
list filter { n => n % 2 == 0 } // List(8, -2, 6)
Selects all elements of this traversable collection which do not satisfy a predicate.
def filterNot(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): Seq[A]
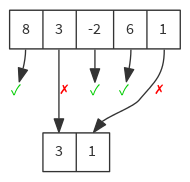
val list = List(8, 3, -2, 6, 1)
list filterNot { n => n % 2 == 0 } // List(3, 1)
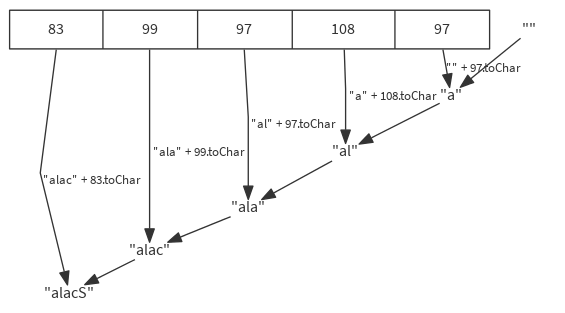
Applies a binary operator to a start value and all elements of this traversable or iterator, going left to right.
def foldLeft[B](z: B)(op: (B, A) ⇒ B): B
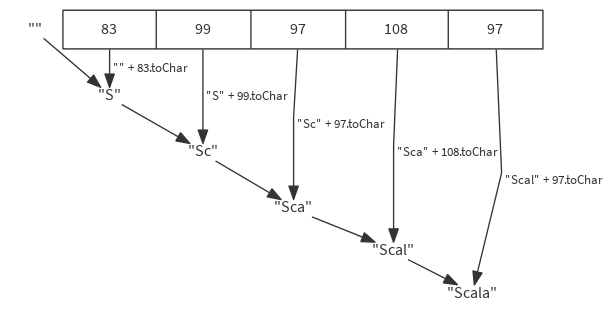
val list = List(83, 99, 97, 108, 97)
(list foldLeft "") { (acc, item) => acc + item.toChar } // "Scala"
Applies a binary operator to all elements of this iterable collection and a start value, going right to left.
def foldRight[B](z: B)(op: (A, B) ⇒ B): B
val list = List(83, 99, 97, 108, 97)
(list foldRight "") { (item, acc) => acc + item.toChar } // "Scala"
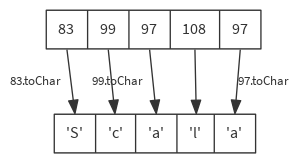
Builds a new collection by applying a function to all elements of this sequence.
def map[B](f: A ⇒ B): Seq[B]
val list = List(83, 99, 97, 108, 97)
list map { code => code.toChar } // List('S', 'c', 'a', 'l', 'a')
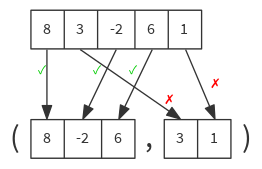
Partitions this traversable collection in two traversable collections according to a predicate.
def partition(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): (Seq[A], Seq[A])
val list = List(8, 3, -2, 6, 1)
list partition { n => n % 2 == 0 } // ( List(8, -2, 6), List(3, 1) )
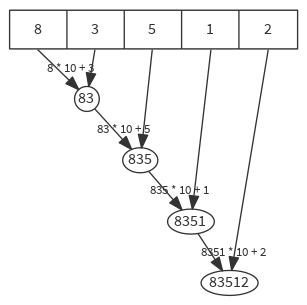
Applies a binary operator to all elements of this traversable or iterator, going left to right.
def reduceLeft[B >: A](op: (B, A) ⇒ B): B
val list = List(8, 3, 5, 1, 2)
list reduceLeft { (left, right) => left * 10 + right } // 83512
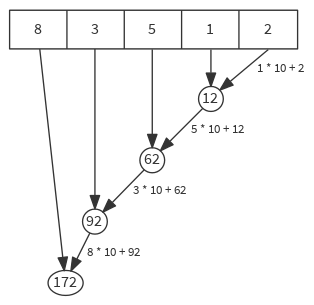
Applies a binary operator to all elements of this iterable collection, going right to left.
def reduceRight[B >: A](op: (A, B) ⇒ B): B
val list = List(8, 3, 5, 1, 2)
list reduceRight { (left, right) => left * 10 + right } // 172
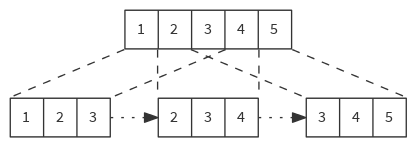
Groups elements in fixed size blocks by passing a "sliding window" over them (as opposed to partitioning them, as is done in grouped.) "Sliding window" step is 1 by default.
def sliding(size: Int): Iterator[Seq[A]]
def sliding(size: Int, step: Int): Iterator[Seq[A]]
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
list sliding 3 // Iterator( List(1, 2, 3), List(2, 3, 4), List(3, 4, 5) )
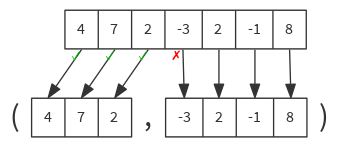
Splits this traversable collection into a prefix/suffix pair according to a predicate.
def span(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): (Seq[A], Seq[A])
val list = List(4, 7, 2, -3, 2, -1, 8)
list span { n => n >= 0 } // ( List(4, 7, 2), List(-3, 2, -1, 8) )
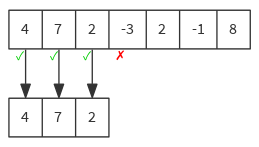
Takes longest prefix of elements that satisfy a predicate.
def takeWhile(p: (A) ⇒ Boolean): Seq[A]
val list = List(4, 7, 2, -3, 2, -1, 8)
list takeWhile { n => n >= 0 } // List(4, 7, 2)
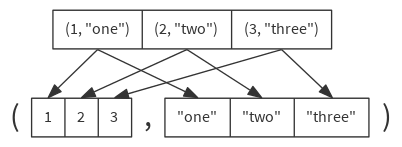
Converts this collection of pairs into two collections of the first and second half of each pair.
def unzip[A1, A2](implicit asPair: (A) ⇒ (A1, A2)): (Seq[A1], Seq[A2])
val pairlist = List((1, "one"), (2, "two"), (3, "three"))
pairlist.unzip // ( List(1, 2, 3), List("one", "two", "three") )
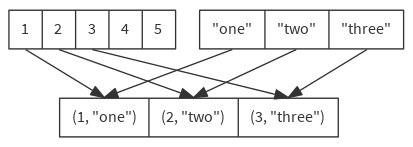
Returns a sequence formed from this sequence and another iterable collection by combining corresponding elements in pairs.
def zip[B](that: GenIterable[B]): Seq[(A, B)]
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val names = List("one", "two", "three")
numbers zip names // List( (1, "one"), (2, "two"), (3, "three") )