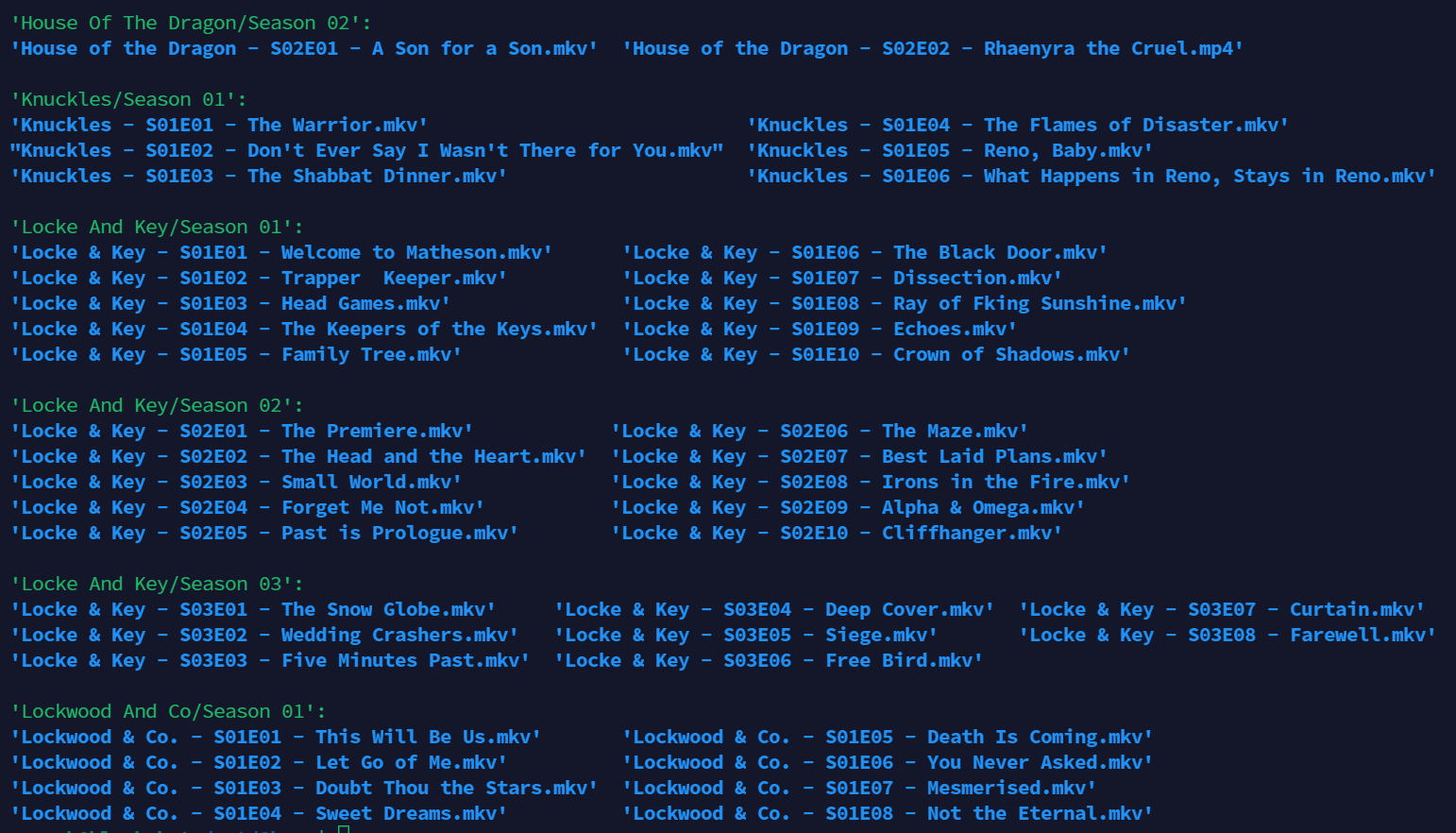
CineSync is a Python-based library management system designed to efficiently organize debrid libraries for TV shows, eliminating the need for Sonarr/Radarr. Users downloading from DMM Manager can seamlessly sort their library into seasons, whether it's a single file or a folder. CineSync streamlines the organization of your library and creates symbolic links, providing full control over your data locally. While highly optimized for debrid platforms, CineSync is also versatile and works effectively with non-debrid platforms.
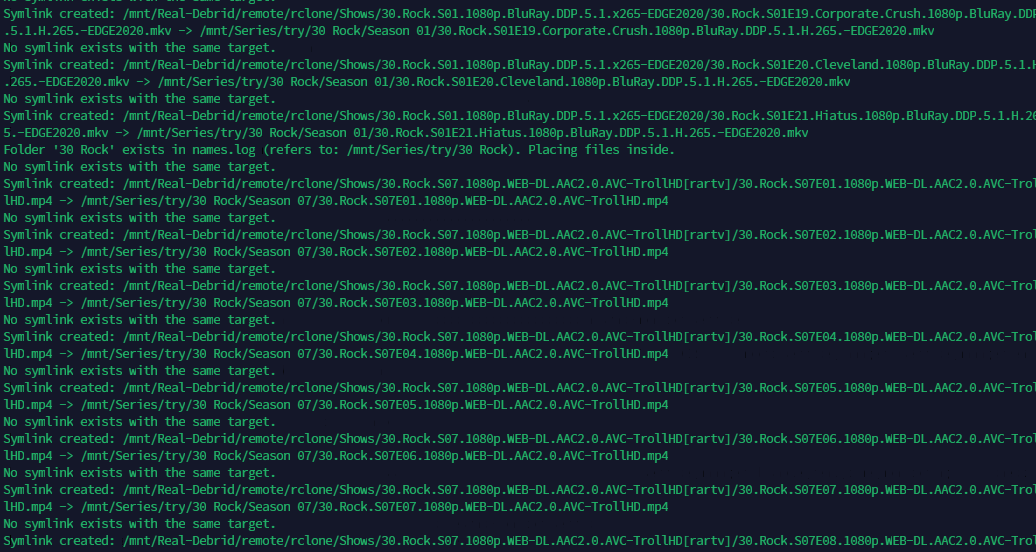
CineSync works by creating symbolic links from the source directory to the destination directory and organizing them according to the user's preferences. This allows users to maintain a well-structured library without physically moving or duplicating the original files.
The CineSync Docker image is available on Docker Hub:
amd64(x86_64)arm64(aarch64)
- Library Organization: Easily sort your library into seasons, regardless of file or folder structure.
- Symbolic Link Creation: Create symbolic links to organize your library without moving or duplicating files.
- Real-Time Monitoring for Files: Monitor the watch directory for any new files and automatically create symbolic links for them, ensuring your library stays updated in real-time.
- Support for Single Symlinks Creation: CineSync now supports creating symbolic links for single files or folders, providing flexibility in managing your library.
- Ability to Skip Already Present Symlinks: CineSync includes the ability to skip the creation of symbolic links for files or folders that are already present, even if the folder name is different. This feature ensures efficient management of your library by preventing duplicate symlinks.
- Rename Files: Properly rename your files based on TMDB data .
- Cross-Platform Support: Works on both Linux and Windows operating systems.
- Movie Collection-Based Separation: Organize movies into collections based on TMDb or IMDb data, ensuring that all movies from the same collection are grouped together.
- Docker Support: Easily deploy CineSync in a Docker container for consistent and isolated environments.
- TMDb ID Integration: Utilize TMDb IDs for more precise organization and naming of your media files.
- Automatic Separation of Extras and Resolutions: Automatically separate extras from main episodes and sort files based on resolution (e.g., 720p, 1080p, 4K), ensuring a well-organized library.
Note: Real-time monitoring is an optional feature. CineSync now includes the ability to monitor all files once the full scan is completed.
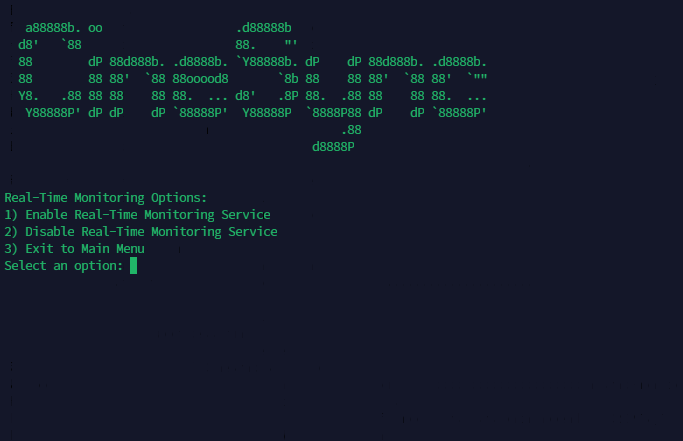
CineSync offers a powerful real-time monitoring feature that allows users to keep track of changes in their library automatically. This feature is particularly useful for handling daily series or shows that are regularly downloaded. Here's how it works:
-
Watch Directory: CineSync continuously monitors a designated watch directory where new files or folders are expected to be added.
-
Default Monitoring Interval: By default, CineSync checks the watch directory every 60 seconds for any changes. You can Increase/Decrease the time limit inside RealTime-Monitoring.py
-
Automatic Identification: When a new file or folder is detected in the watch directory, CineSync automatically identifies it.
-
Symbolic Link Creation: After identification, CineSync creates symbolic links for the newly added file or folder. These symbolic links ensure that the organization of the library remains intact without physically moving or duplicating the files.
-
Efficiency: Real-time monitoring ensures that users stay up-to-date with their library changes without manual intervention. It streamlines the process of handling daily series or shows by automatically organizing new additions.
-
Customization: Users have the flexibility to customize the monitoring interval according to their preferences or specific requirements.
By leveraging real-time monitoring in CineSync, users can effortlessly manage their library and maintain a well-organized collection of media files.
- Python 3.x
- For Windows: Git Bash with symbolic links enabled
- NSSM for Windows (if you want to enable real-time monitoring).
- Zurg (optional)
Make sure to edit the .env value before running the script. Below are the configurable variables used in the script, along with their descriptions and default values:
| Variable | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
SOURCE_DIR |
The directory path where the source files are located. Multiple directories can be specified, separated by commas. | /path/to/files |
DESTINATION_DIR |
The path to the destination directory where the symlinks or files will be placed. | /path/to/destination |
LOG_LEVEL |
Defines the level of logging. Available options: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL. |
INFO |
RENAME_ENABLED |
Enable or disable file renaming functionality based on TMDb data. | false |
TMDB_API_KEY |
Your API read access token for TMDb. | your-api-read-access-token |
MOVIE_COLLECTION_ENABLED |
Enable or disable separating movie files based on collections. When true, movies will be organized into folders according to their collections (e.g., Harry Potter series). | false |
RELATIVE_SYMLINK |
Create relative symlinks instead of absolute symlinks. When true, symlinks will use relative paths. | false |
MAX_PROCESSES |
Set the maximum number of parallel processes for creating symlinks. Increase this number to speed up processing if you have a multi-core CPU. Set to 1 for single-threaded processing to minimize system load. | 1 |
SKIP_EXTRAS_FOLDER |
Enable or disable the creation and processing of extras folder files. When true, files meant for the 'Extras' folder will be skipped and not processed. This can be useful if you want to temporarily exclude extras files from being processed. | true |
SLEEP_TIME |
Sleep time (in seconds) for real-time monitoring script. This determines how frequently the script will check for changes in the watch directories. Adjust this value based on your needs and system performance. | 60 |
Here's an enhanced version of the instructions:
-
Clone the Repository: Clone the CineSync repository from GitHub and navigate to the cloned directory:
git clone https://github.com/sureshfizzy/CineSync.git && cd CineSync -
Update Paths in
.env: Open the.envfile located inside theCineSyncfolder. Update the following paths:SOURCE_DIR: Specify the path for the Source directory.DESTINATION_DIR: Set the ultimate destination directory where you want to save the symbolic links.TMDB_API_KEY: Enter your TMDb API key to access TMDb services.
Note: Ensure that the paths are correctly updated to reflect your system's configuration.
-
Execute CineSync: After updating the paths, execute the main script:
python3 CineSync.pyThis will launch the CineSync interface, allowing you to perform various library management tasks, including full library scans, real-time monitoring, and more.
By following these steps and updating the necessary paths, you'll be able to successfully use CineSync to manage your debrid library.
-
Install Python: Install Python from the official website: Python.org. Make sure to add Python to your system PATH during installation.
-
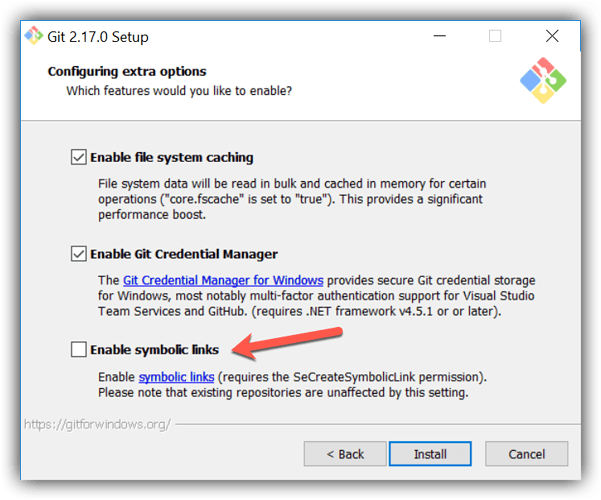
Install Git Bash: Install Git Bash from Git for Windows. During installation, enable the symbolic links checkbox.
Enabling symbolic links is important for certain operations, so ensure that the checkbox for symbolic links is checked during installation.
-
Edit
.bashrc(Windows): Open Git Bash as an administrator and edit the.bashrcfile. You can use thenanoeditor to open the file by running the following command:nano /etc/bash.bashrcAdd the following line at the bottom of the file:
export MSYS=winsymlinks:nativestrictSave the changes by pressing
Ctrl + O, then pressEnterto confirm. Exit the editor by pressingCtrl + X.Important: Ensure that the
export MSYS=winsymlinks:nativestrictline is added to the.bashrcfile. This configuration is essential to ensure that symbolic links are handled correctly on Windows when using Git Bash. Without this setting, CineSync may copy files instead of creating symbolic links, leading to undesired behavior. -
Enable Windows Developer Mode:
Enabling Developer Mode grants your system additional privileges necessary for certain operations, helping to prevent permission-related errors during development.
To avoid "Operation not permitted" errors during symlink process, it's essential to enable Windows Developer Mode. Follow these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Go to Update & Security.
- Click on For developers.
- Enable the Developer mode option.
- Restart the PC
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone https://github.com/sureshfizzy/CineSync.git -
Update Paths in
.env: Open the.envfile located inside theCineSyncfolder. Update the following paths:SOURCE_DIR: Specify the path for the Source directory.DESTINATION_DIR: Set the ultimate destination directory where you want to save the symbolic links.TMDB_API_KEY: Enter your TMDb API key to access TMDb services.
Note: Ensure that the paths are correctly updated to reflect your system's configuration.
-
Run the Script:
python3 CineSync.py
This guide will walk you through the process of setting up real-time monitoring for CineSync Monitor on Windows using NSSM (Non-Sucking Service Manager). Real-time monitoring ensures that CineSync Monitor runs continuously in the background as a system service.
- NSSM: Download and install NSSM from the official website: NSSM Releases
- Download the latest version of NSSM from the official website.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP file to a location on your computer.
- Open the extracted folder and locate the
nssm.exeexecutable.
-
Place NSSM Executable Inside the Scripts Folder: Move the
nssm.exeexecutable into the Scripts folder. -
Run NSSM Install Command: Open a Command Prompt with administrative privileges, navigate to the Scripts folder, and run the following command:
nssm install CineSync-Monitor
-
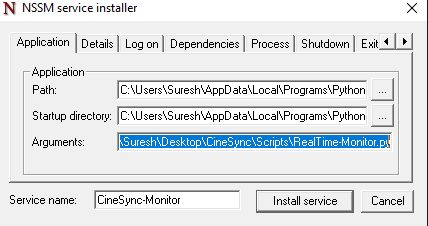
Configure NSSM: In the NSSM GUI that appears:
- Application Path: Choose the
python.exeexecutable. You can find it by opening Git Bash and runningwhich python. - Arguments: Pass the folder path where
realtime-monitor.pyis located, for example:C:\Users\YourUserName\Desktop\CineSync\Scripts\RealTime-Monitor.py. - Click "Install Service".
- Application Path: Choose the
-
Set Source and Destination Paths: Before running
realtime-monitor.pyas a system service, ensure that source and destination paths are correctly set insidelibrary.sh. -
Run Real-Time Monitoring: After installation, the files will be watched in real-time, and symlinks will be created if any changes are detected.
-
Removing the System Service: To remove the system service, simply type:
nssm remove CineSync-Monitor
Additionally, you can also directly run the Python script on Git Bash if needed.
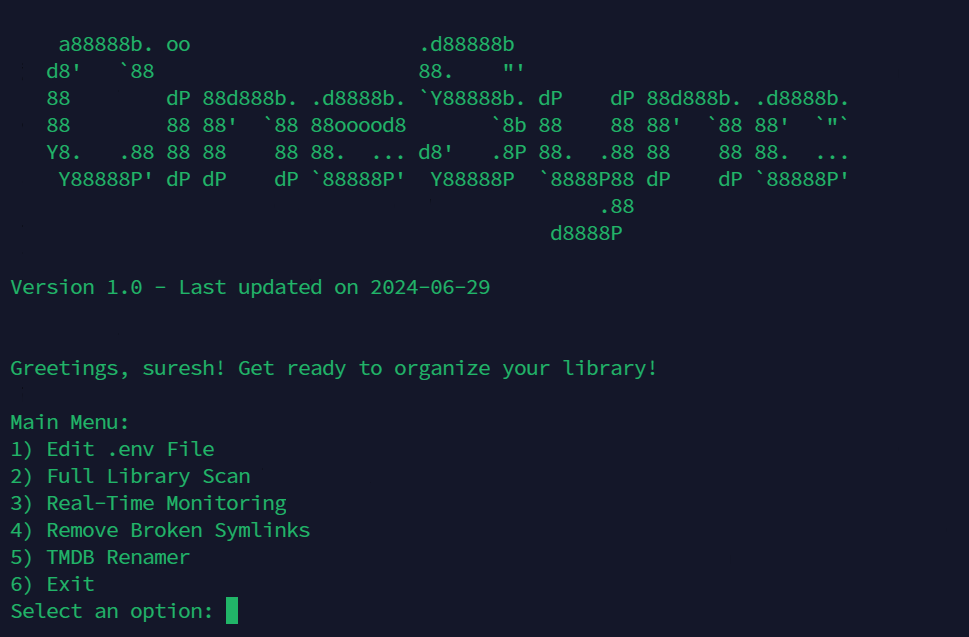
CineSync provides a user-friendly interface for managing your debrid library. Upon running the script, you'll be presented with a main menu where you can choose from various options:
-
1) Edit .env file: Update Basic Configurations in this file.
-
2) Full Library Scan: Perform a comprehensive scan of your entire library.
- 3) Real-Time Monitoring (Linux Only): Enable real-time monitoring to stay updated on library changes. System services are automatically created, and the scan is triggered every 60 seconds. You can adjust the frequency inside
RealTime-Monitor.py. - 4) Remove Broken Symlinks : Identify and remove broken symbolic links within your library.
- 5) TMDB Renamer: Ability to perform renaming for all the files present in destination directory.
- 6) Exit: Quit the CineSync application.
Note: Real-Time Monitoring is currently supported only on Linux due to system service limitations on Windows. However, you can still manually trigger real-time monitoring using the provided instructions in the README.
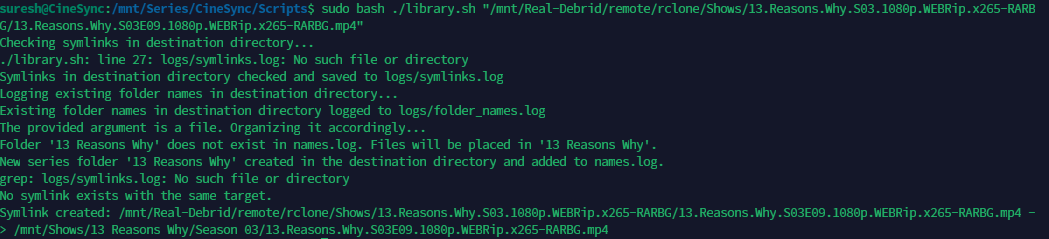
CineSync also supports the creation of single file or folder symlinks. Follow these steps to create a symlink for a single file or folder:
-
Navigate to Scripts Folder:
- Open your terminal or command prompt and navigate to the Scripts folder of the CineSync repository.
-
Enter Series Name and Full Path:
- Inside the Scripts folder, run the following command:
Replace
bash ./library.sh "/mnt/Real-Debrid/remote/rclone/Shows/13.Reasons.Why.S03.1080p.WEBRip.x265-RARBG/13.Reasons.Why.S03E09.1080p.WEBRip.x265-RARBG.mp4""/mnt/Real-Debrid/remote/rclone/Shows/13.Reasons.Why.S03.1080p.WEBRip.x265-RARBG/13.Reasons.Why.S03E09.1080p.WEBRip.x265-RARBG.mp4"with the full path to the file or folder you want to create a symlink for.
- Inside the Scripts folder, run the following command:
-
Execute Command:
- Press Enter to execute the command.
By following these steps, you can easily create a symlink for a single file or folder using CineSync.
- Suresh S❤️
- Special thanks to Paolo for testing the application.!
- Buy Me a Coffee☕