A fully configurable proxy in NodeJS, which can handle HTTPS requests perfectly.
Home page : AnyProxy.io
(Chinese in this doc is nothing but translation of some key points. Be relax if you dont understand.)
- 支持https明文代理
- 支持低网速模拟
- 支持二次开发,可以用javascript控制代理的全部流程,搭建前端个性化调试环境
- 提供web版界面,观测请求情况
- 中文文档:
- 中文主页:http://anyproxy.io
- work as http or https proxy
- fully configurable, you could modify a request at any stage with your customized javascript code
- when working as https proxy, AnyProxy could intercept https requests for any domain without complaint by browser (after you trust its root CA)
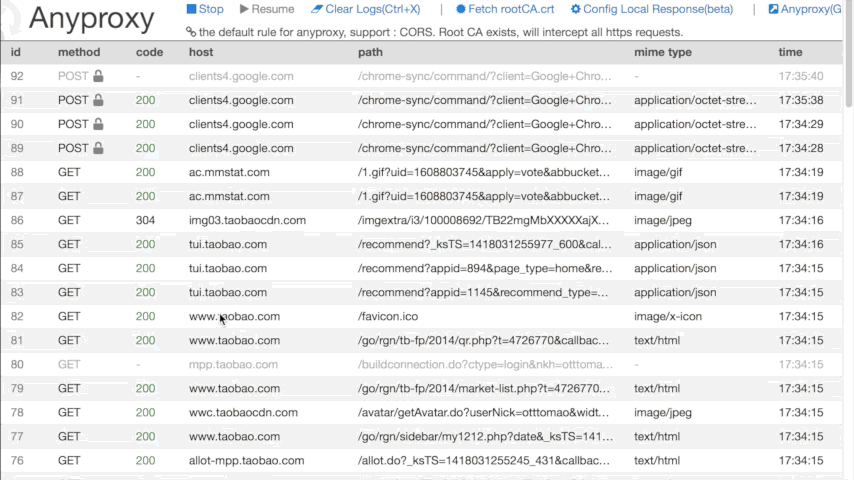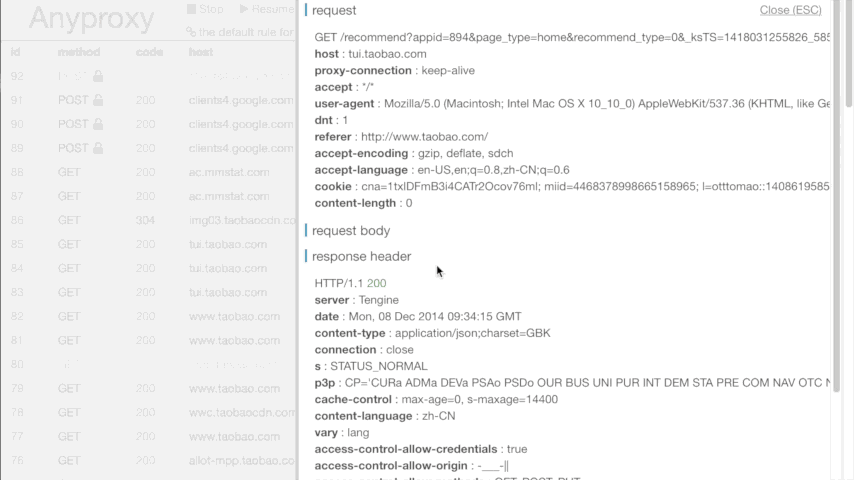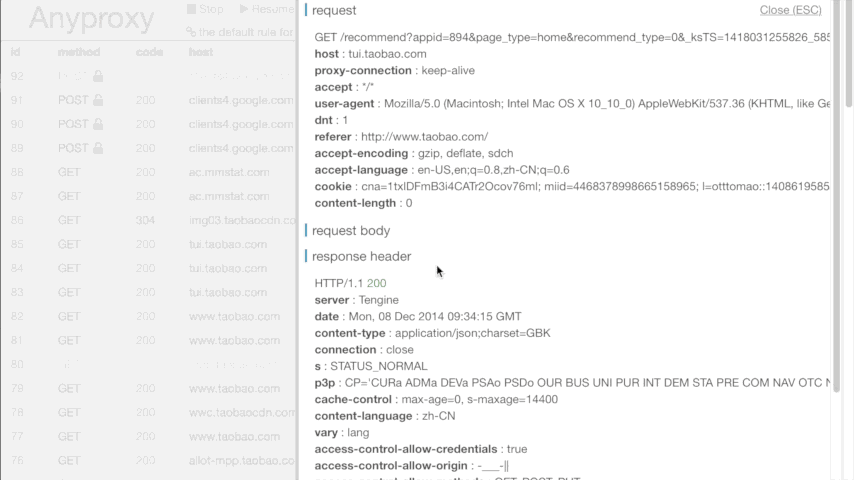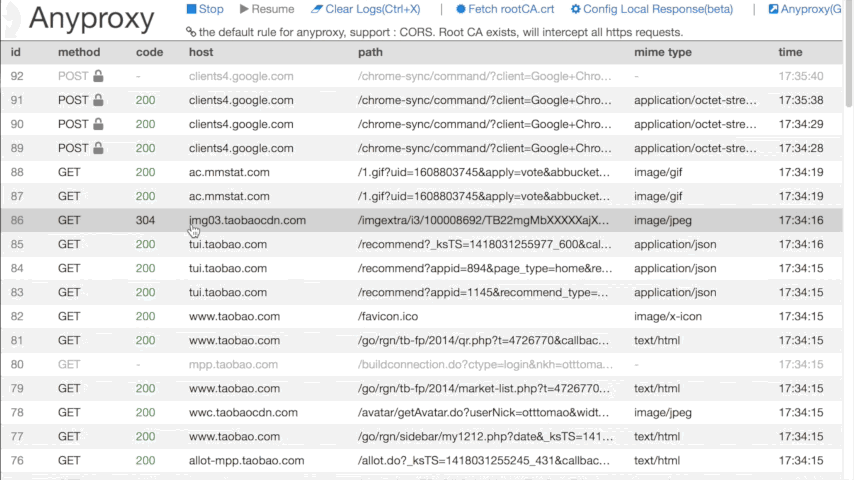
- a web interface for you to watch realtime request details, where html with (almost) any charset could be shown correctly
- install NodeJS
npm install -g anyproxy, may requiresudo- python is optional, it will be OK if you get some error about it during installing.
- start with default settings :
anyproxy - ...or start with a specific port:
anyproxy --port 8001 - ...start with a rule file:
anyproxy --rule ./rule_sample/rule_allow_CORS.js
- default proxy should be 127.0.0.1:8001 , or you_ip_address:8001 on remote devices
- visit http://127.0.0.1:8002 ,you will see realtime requests in your browser
- be sure to use web interface with modern browsers
-
Rule module is the specialty for AnyProxy. Think it as a middleware, you could write your own code to hack requests at any stage, no matter it is about to response or the proxy just gets the request. In this way, AnyProxy would be flexible to meet your own demands.
-
It's highly recommended to read this guide before using: What is rule file and how to write one ?
-
An entire scheme of rule file could be found at ./rule_sample/rule__blank.js. Besides, there are some samples at ./rule_sample. That may help you a lot when writing your own rule files.
After configuring rootCA, AnyProxy could help to decrypt https requests, whose approach is also called Man-In-The-Middle(MITM).
A guide about configuring https features is here : https://github.com/alibaba/anyproxy/wiki/How-to-config-https-proxy
HTTPS配置中文教程 : https://github.com/alibaba/anyproxy/wiki/HTTPS%E7%9B%B8%E5%85%B3%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B
- to save request data to local file, use
anyproxy --file /path/to/file - anyproxy uses nedb to save request data. Since NeDB's persistence uses an append-only format, you may get some redundant record in local file. For those dupplicated ones with the same id, just use the lastest line of record.
- TrafficeRecorder is another tool based on anyproxy to help recording all request data, including header and body. You may have a try.
- for instance,
anyproxy --throttle 10sets the speed limit to 10kb/s (kbyte/sec) - this is just a rough throttling for downstream, not for network simulation
- use it as a module and develop your own proxy.
npm install anyproxy --save
var proxy = require("anyproxy");
//create cert when you want to use https features
//please manually trust this rootCA when it is the first time you run it
!proxy.isRootCAFileExists() && proxy.generateRootCA();
var options = {
type : "http",
port : 8001,
hostname : "localhost",
rule : require("path/to/my/ruleModule.js"),
dbFile : null, // optional, save request data to a specified file, will use in-memory db if not specified
webPort : 8002, // optional, port for web interface
socketPort : 8003, // optional, internal port for web socket, replace this when it is conflict with your own service
throttle : 10, // optional, speed limit in kb/s
disableWebInterface : false, //optional, set it when you don't want to use the web interface
silent : false //optional, do not print anything into terminal. do not set it when you are still debugging.
rootCaDir : __dirname + "/anyproxy/rootCa" //optional, your CA file dir.
};
new proxy.proxyServer(options);- Please feel free to raise issue, or give us some advice. :)
- AnyProxy用户旺旺群:1203077233
- Apache License, Version 2.0