- Table of Contents
- Overview
- Requirements
- Setup Instructions
- Starting all Processes
- Monitoring and Debugging
- Architecture Details
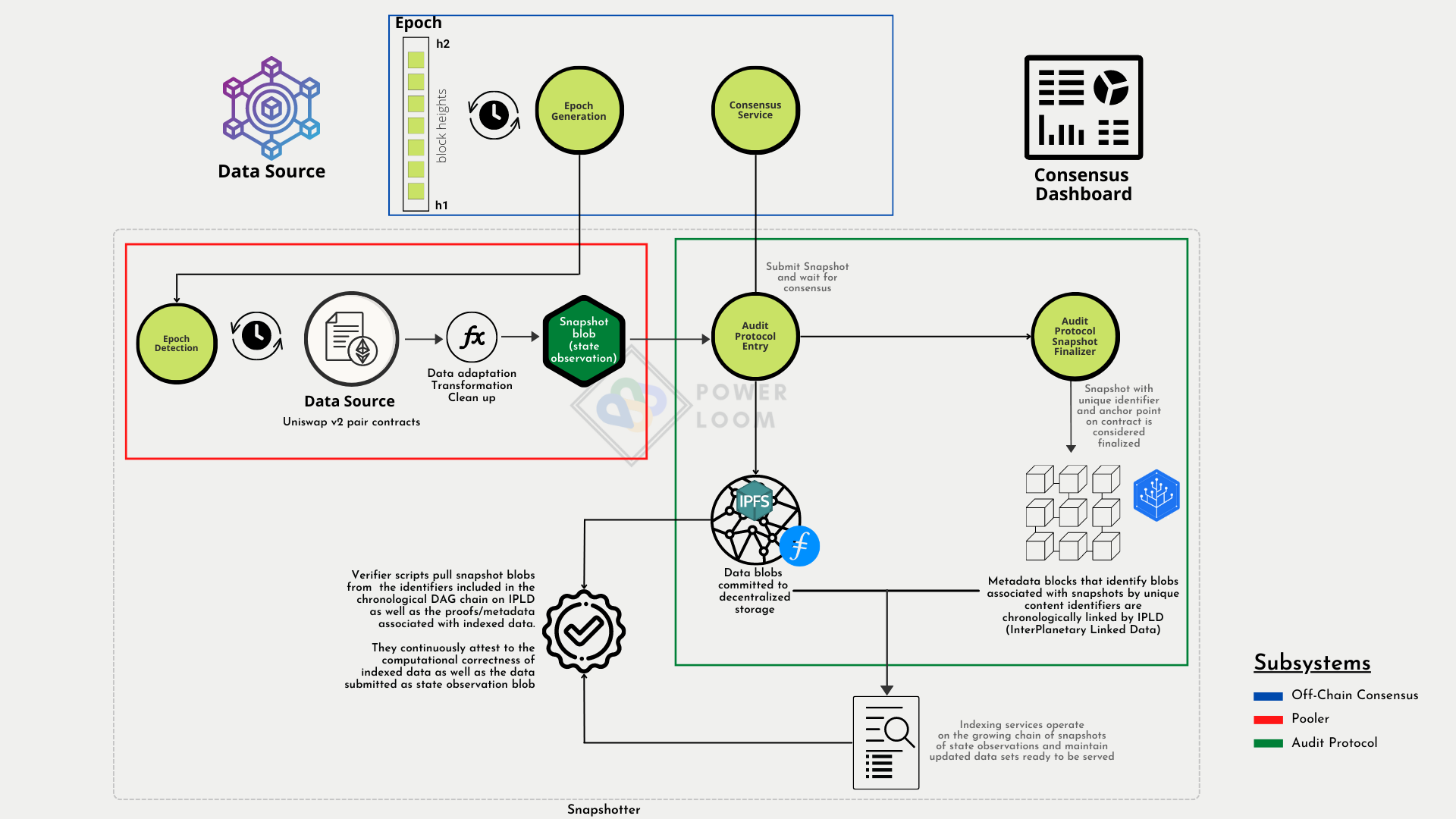 Audit-Protocol is the component of a fully functional, distributed system that works alongside Pooler, off-chain consensus and together they are responsible for
Audit-Protocol is the component of a fully functional, distributed system that works alongside Pooler, off-chain consensus and together they are responsible for
- generating a time series database of changes occurring over smart contract state data and event logs, that live on decentralized storage protocols
- higher order aggregated information calculated over decentralized indexes maintained atop the database mentioned above
Audit-protocol can also be used for storing stream of json encoded data from any on-chain source(like a smart contract on a blockchain). It has the following functions:
- Store snapshots on decentralized storage protocols like IPFS and Filecoin.
- Commit anchor-proof of snapshot on-chain
- Submit snapshots for consensus
- Track the snapshot finalization and build a continuous DAG chain of snapshots
- Provide API to access the DAG chain. of snapshots
- Perform various high order operations such as time based indexing and aggregations on top of generated DAG chains
For a more detailed overview of the audit-protocol, please refer to the protocol overview
- macOS or Linux (We're still working on windows support)
- Python 3.8 or above and pip
- Redis
- RabbitMQ
- Pm2
- IPFS
There are 2 ways to run audit-protocol, using docker or running processes directly in your environment. For simplicity it is recommended to run using docker.
- Install Docker Desktop
- Follow the instructions below to setup virtual env and configure settings.
- Run services via docker as mentioned here
Note that these steps will only run audit-protocol. If you want to run the complete system, follow the steps mentioned in Docker Setup
- Install required software as mentioned in requirements section
- Follow instructions to setup virtual env and configure settings
- Start all processes by running the command
pm2 start pm2.config.js- Setup a python virtual environment Ref
# pyenv install 3.8.13
# pyenv virtualenv 3.8.13 {venv-name}
# cd audit-protocol-private/
# pyenv local {venv-name}- Install the required python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt- There is a settings.example.json file in the project folder. Navigate to the project and the type the following command:
cp settings.example.json settings.json- Create
settings.jsonfromsettings.example.jsontemplate provided and populate it according to the following steps- Configure the provided
uuidinsettings.instance_id - Add your
rpcdetails insettings.rpc_url - Configure the
pooler-namespace - Configure consensus URL at
consensus_config.service_url.
- Configure the provided
- Optional Steps
- Increase rate-limit config
consensus_config.rate_limittowards consensus based on number of pairs being snapshotted. - Configure
settings.dag_verifier.slack_notify_URLif you want to receive alerts on slack channel. In order to setup slack workflow, refer steps here.
- Increase rate-limit config
- Copy over
static/cached_pair_addresses.jsonfrompooler/static/cached_pair_addresses.json.
- Note that by default many of these services uses default ports which are set to 9000, 9002, 9030 and 8000 but if you already have some services running at that ports, you can change them to any other ports that are free in your system.
To launch all the required processes, you can run
pm2 start pm2.config.js
- To monitor the status of running processes, you simply need to run
pm2 status. - To see all logs you can run
pm2 logs - To see logs for a specific process you can run
pm2 logs <Process Identifier> - To see only error logs you can run
pm2 logs --err - You can monitor the last indexed status of all the projects with the following cli command. This command shall output the startEpoch and last finalized epoch for each project along with any issues with DAG chains and epochs pending finalization. Sample output is shown below.
python cli_cmd.py projectstatus
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ ┃ First Epoch ┃ Current Epoch ┃ Dag chain ┃ Epochs pending ┃
┃ ProjectId ┃ Start Height ┃ End Height ┃ issues ┃ finalization ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │
│ uniswap_pairC… │ 16619241 │ 16633420 │ 0 │ 0 │Audit protocol provides various endpoints which helps in users utilizing the basic functionality of :
- Registering projects to be tracked
- Committing sequence of Snapshots pertaining to the project
- Query DAG blocks and payloads stored for the project
A high level user-interaction workflow is depicted in the diagram ap-usage
You can get more details about these endpoints in the postman collection.
Details about working of various components is present in Introduction if you're interested to know more about audit-protocol.