Generative Modeling
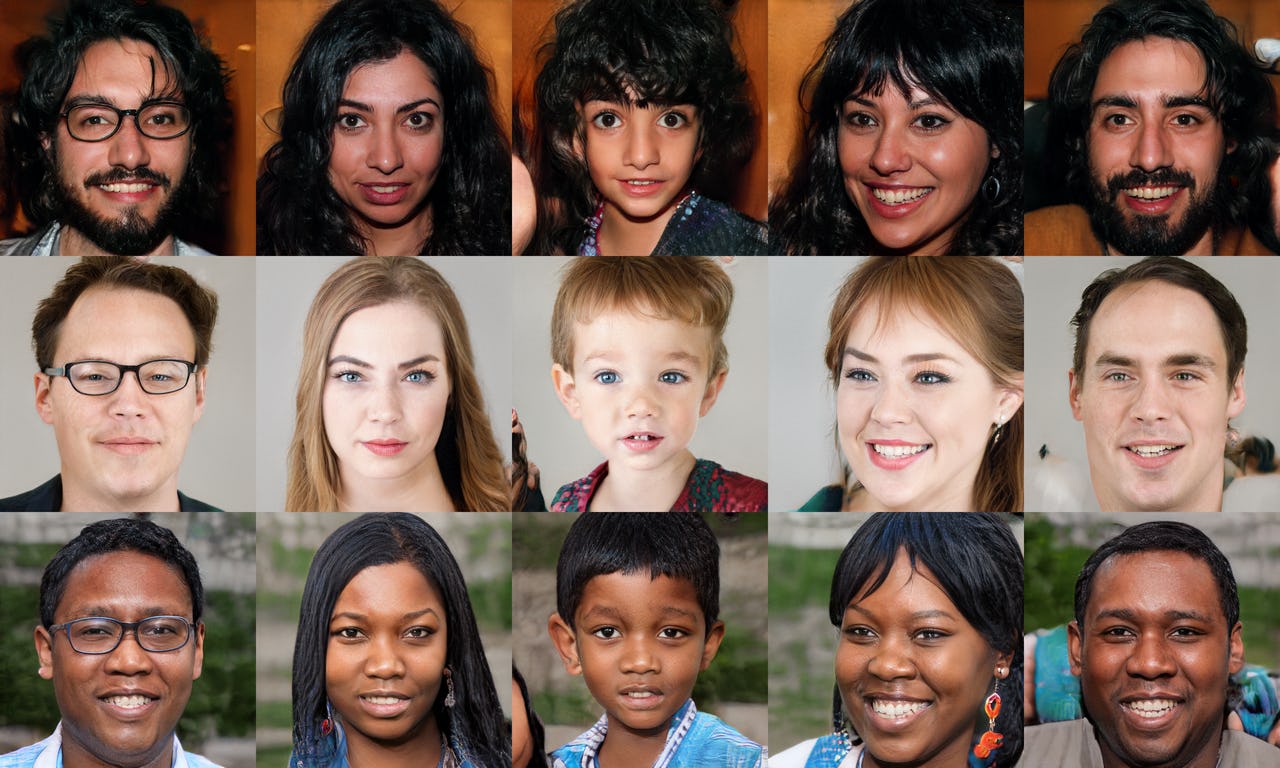
Here, I have used a General Adversarial Network to generate human celeb faces from random noises.
You can find the dataset here : Celeba
Deep neural networks are used mainly for supervised learning: classification or regression. Generative Adversarial Networks or GANs, however, use neural networks for a very different purpose: Generative modeling
Generative modeling is an unsupervised learning task in machine learning that involves automatically discovering and learning the regularities or patterns in input data in such a way that the model can be used to generate or output new examples that plausibly could have been drawn from the original dataset. - Source
To get a sense of the power of generative models, just visit thispersondoesnotexist.com. Every time you reload the page, a new image of a person's face is generated on the fly. The results are pretty fascinating:
While there are many approaches used for generative modeling, a Generative Adversarial Network takes the following approach:
There are two neural networks: a Generator and a Discriminator. The generator generates a "fake" sample given a random vector/matrix, and the discriminator attempts to detect whether a given sample is "real" (picked from the training data) or "fake" (generated by the generator). Training happens in tandem: we train the discriminator for a few epochs, then train the generator for a few epochs, and repeat. This way both the generator and the discriminator get better at doing their jobs.
GANs however, can be notoriously difficult to train, and are extremely sensitive to hyperparameters, activation functions and regularization. In this tutorial, we'll train a GAN to generate images of anime characters' faces.
Using a GPU
- To seamlessly use a GPU, if one is available, we define a couple of helper functions (
get_default_device&to_device) and a helper classDeviceDataLoaderto move our model & data to the GPU, if one is available.
Discriminator Network
The discriminator takes an image as input, and tries to classify it as "real" or "generated". In this sense, it's like any other neural network. We'll use a convolutional neural networks (CNN) which outputs a single number output for every image. We'll use stride of 2 to progressively reduce the size of the output feature map.
Generator Network
The input to the generator is typically a vector or a matrix of random numbers (referred to as a latent tensor) which is used as a seed for generating an image. The generator will convert a latent tensor of shape (128, 1, 1) into an image tensor of shape 3 x 28 x 28. To achive this, we'll use the ConvTranspose2d layer from PyTorch, which is performs to as a transposed convolution (also referred to as a deconvolution). Learn more
Discriminator Training
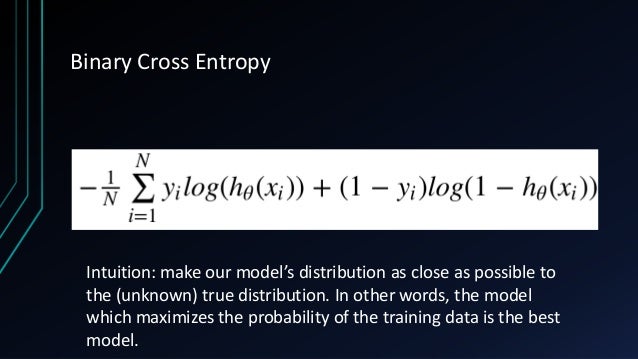
Since the discriminator is a binary classification model, we can use the binary cross entropy loss function to quantify how well it is able to differentiate between real and generated images.
Generator Training
Since the outputs of the generator are images, it's not obvious how we can train the generator. This is where we employ a rather elegant trick, which is to use the discriminator as a part of the loss function. Here's how it works:
-
We generate a batch of images using the generator, pass the into the discriminator.
-
We calculate the loss by setting the target labels to 1 i.e. real. We do this because the generator's objective is to "fool" the discriminator.
-
We use the loss to perform gradient descent i.e. change the weights of the generator, so it gets better at generating real-like images to "fool" the discriminator.
Full Training Loop
Let's define a fit function to train the discriminator and generator in tandem for each batch of training data. We'll use the Adam optimizer with some custom parameters (betas) that are known to work well for GANs. We will also save some sample generated images at regular intervals for inspection.
Training Time
I trained the model for around 3-4 hours which is pretty less considering the complexity of the project.Hence, few areas, the model needs few improvements.
GANs Score and Loss
Future Scope
I am planning on improving the architecture and using a deep neural network for discriminator and generator and few techniques to eleminate noises. The fact that discriminator networks are very unstable remains unchanged. So, future work will be on designing a more stable network.