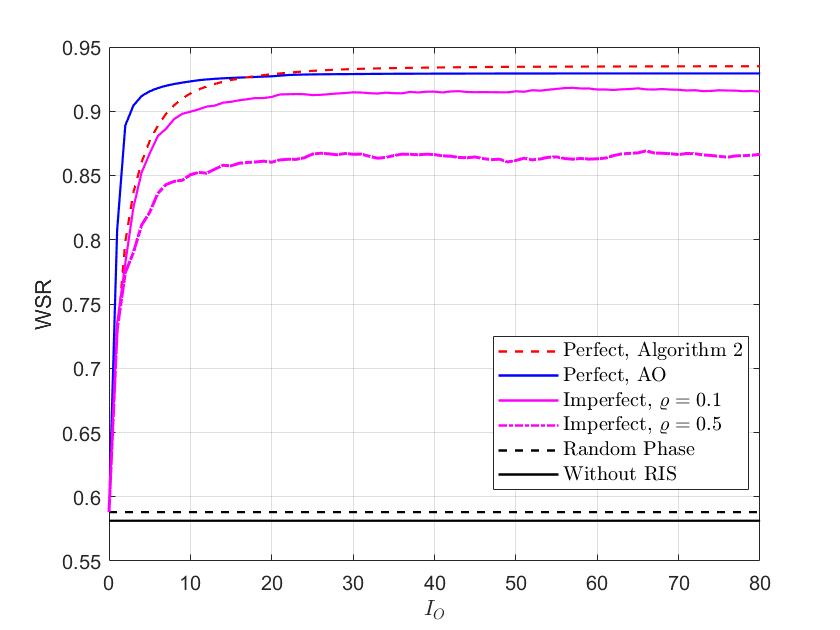
This repository contains the source codes of the Fig.4(b) in the paper ``Weighted Sum-Rate Maximization for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Wireless Networks'' published in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications.
You may cite us by
@ARTICLE{8982186,
author={H. Guo and Y.-C. Liang and J. Chen and E. G. Larsson},
journal={IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun.},
title={Weighted Sum-Rate Maximization for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Wireless Networks},
year={Early Access, DOI:10.1109/TWC.2020.2970061},
ISSN={1558-2248},}
The recent version of this paper can also be found in ArXiv (see https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11999)
One previous version of this paper is named ``Weighted Sum-Rate Optimization for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Enhanced Wireless Networks'', which can be found in ArXiv as well (see https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.07920). The short version has been presented in IEEE GLOBECOM 2019.
Run the file ``converge_plot.m''. You may get the following figure
To generate one snapshot for simulation, one may run following three files in sequence:
- ``generate_location.m'': Random the users' locations
- ``generate_pathloss.m'': Calucate the pathloss according to the locations
- ``generate_channel.m''" Randomly generate the channel realizations
The following are the main code files for the 5 algorihtms shown in the figure.
- ``without_RIS.m'': There's no RIS in the system.
- ``RIS_phaserand.m'': The RIS adopts random phase.
- ``converge_AO_perfect.m'': Alternating optimization approach illustrated in Section III. Note that, to support the Riemannian conjugate gradient (RCG) algorithm, one should download the Manopt toolbox from https://www.manopt.org/ at first.
- ``converge_A2_perfect.m'': Proposed algorithm under the perfect CSI setup.
- ``converge_A2_imperfect.m'': Proposed algorithm under the imperfect CSI setup.
If you are intersted in the passive radio communications, there are several interesting works on ambient backscatter communications, which you can discuss with me as well:
[1] H. Guo, Q. Zhang, S. Xiao and Y.-C. Liang, "Exploiting multiple antennas for cognitive ambient backscatter communication," in IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 765-775, Feb. 2019.
[2] Q. Zhang, H. Guo, Y.-C. Liang and X. Yuan, "Constellation learning-based signal detection for ambient backscatter communication systems," in IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 452-463, Feb. 2019.
[3] S. Xiao, H. Guo, and Y.-C. Liang, “Resource allocation for full-duplex-enabled cognitive backscatter networks,” in IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 3222-3235, 2019.
[4] R. Long, Y.-C. Liang, H. Guo, G. Yang, and R. Zhang, “Symbiotic radio: A new communication paradigm for passive Internet-of-Things,” in IEEE Internet Things J., Early Access.