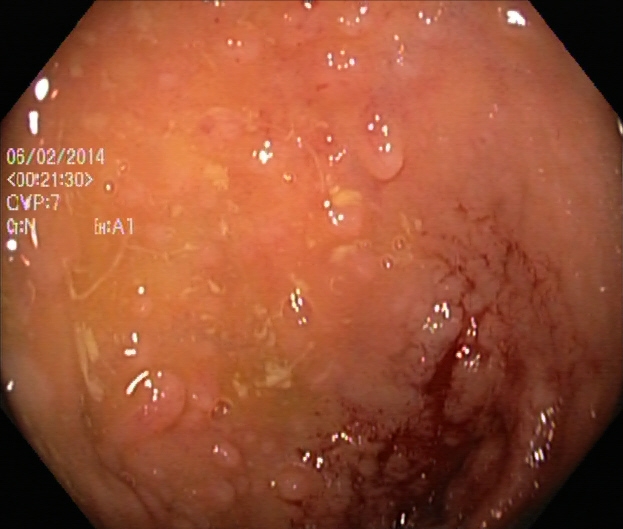
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract and is divided into Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis. It occurs in genetically susceptible individuals after an exaggerated immune response to a normal stimulus, such as food and intestinal flora. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of inflammatory bowel disease and explains the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition
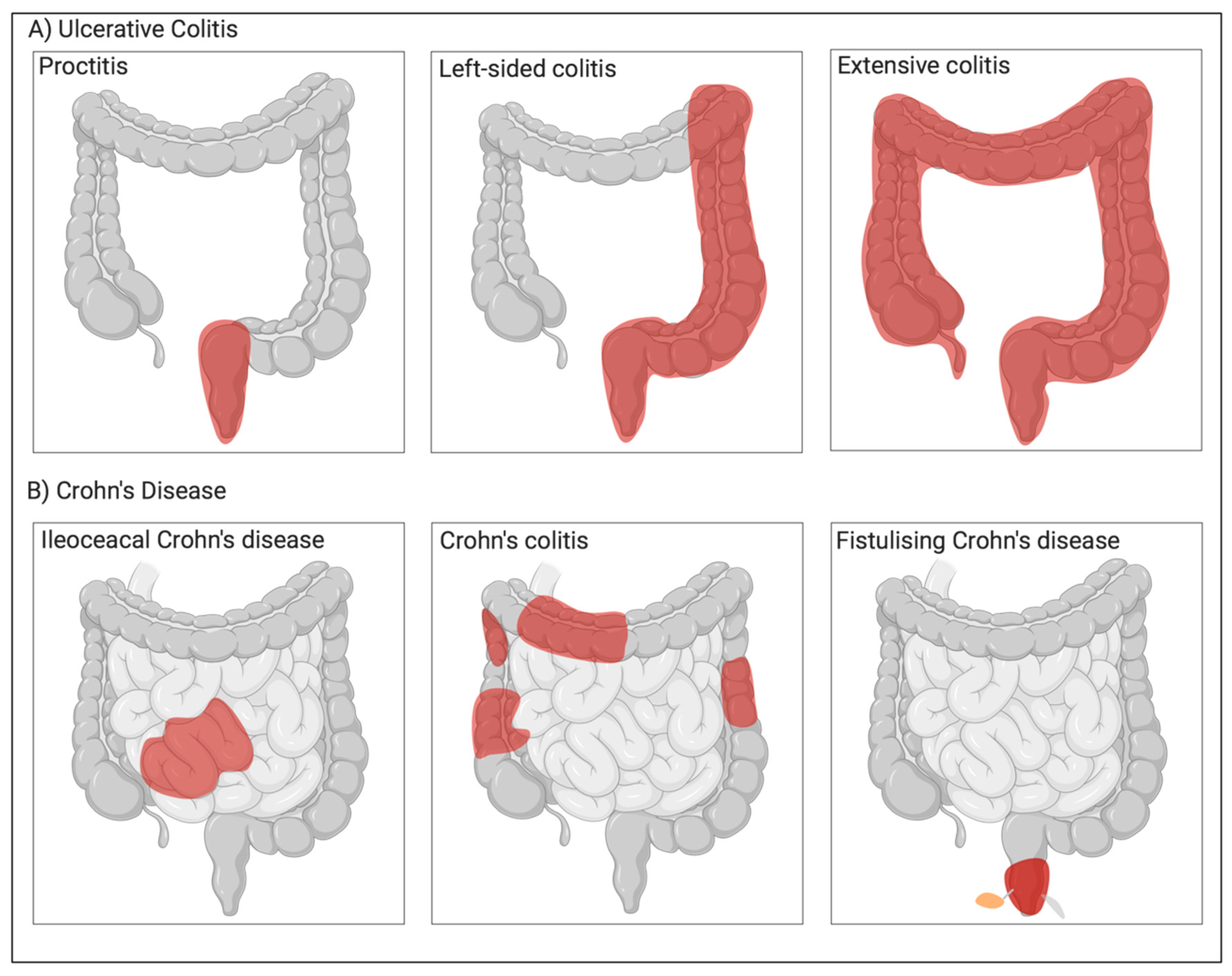
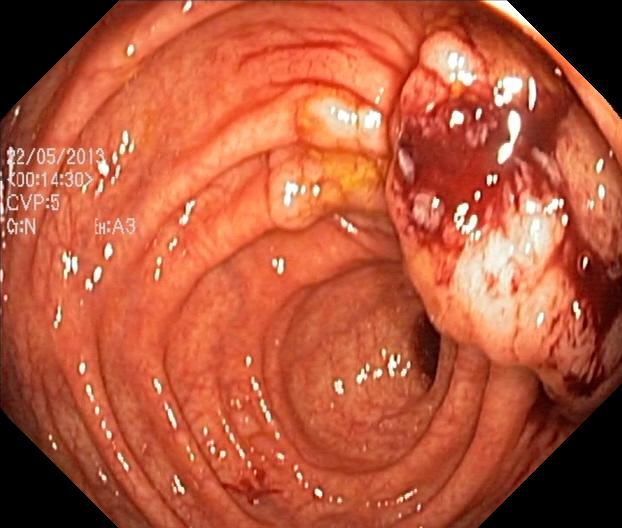
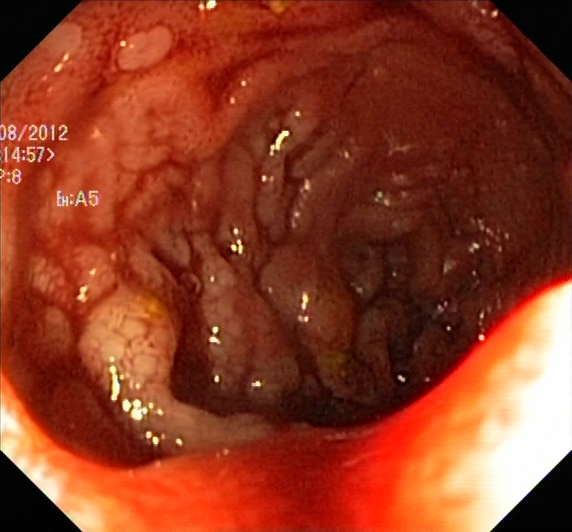
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can cause inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus. Inflammation can cause redness, swelling and pain, and is the body’s response to injury or irritation. There may be times when someone with Crohn’s has little to no symptoms (remission) and times when symptoms are more active (flare-ups).
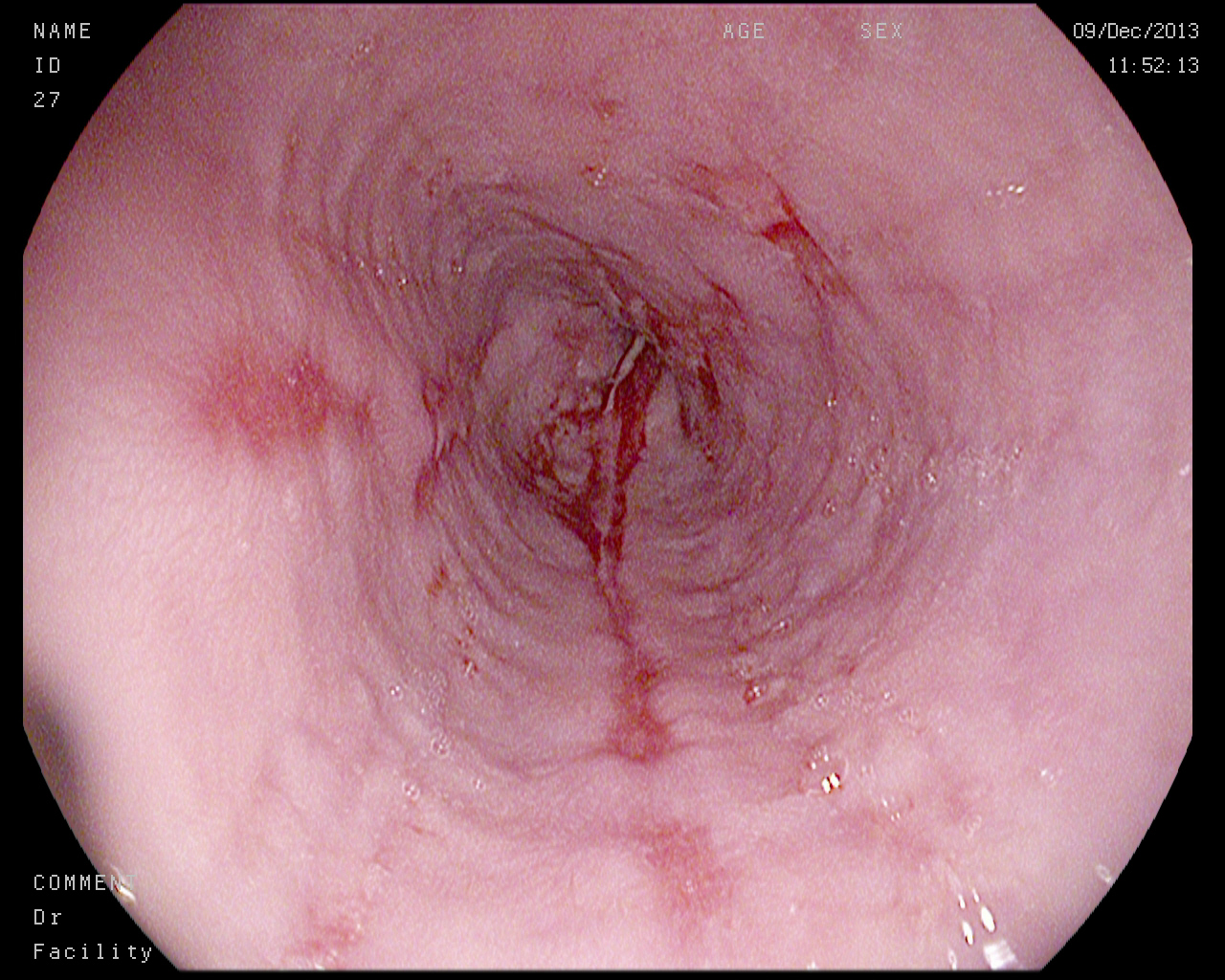
Ulcerative colitis is a type of IBD that can cause inflammation and ulceration in the large intestine (colon and rectum).Inflammation can cause redness, swelling and pain, and is the body’s response to injury or irritation. Ulcers (sores) also develop on the surface of the intestines inner lining which may bleed and produce mucus.
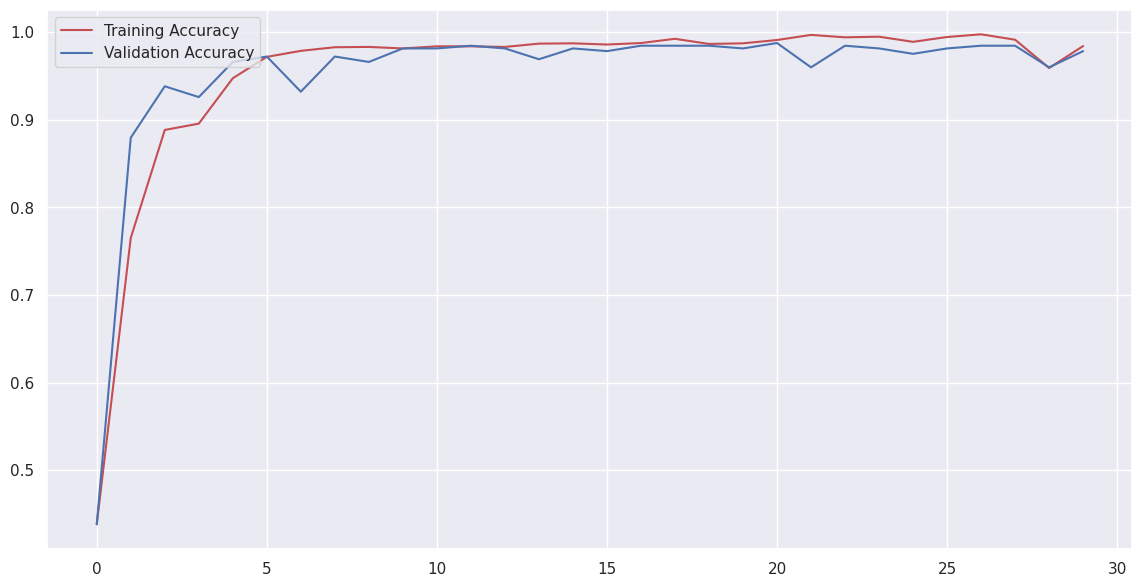
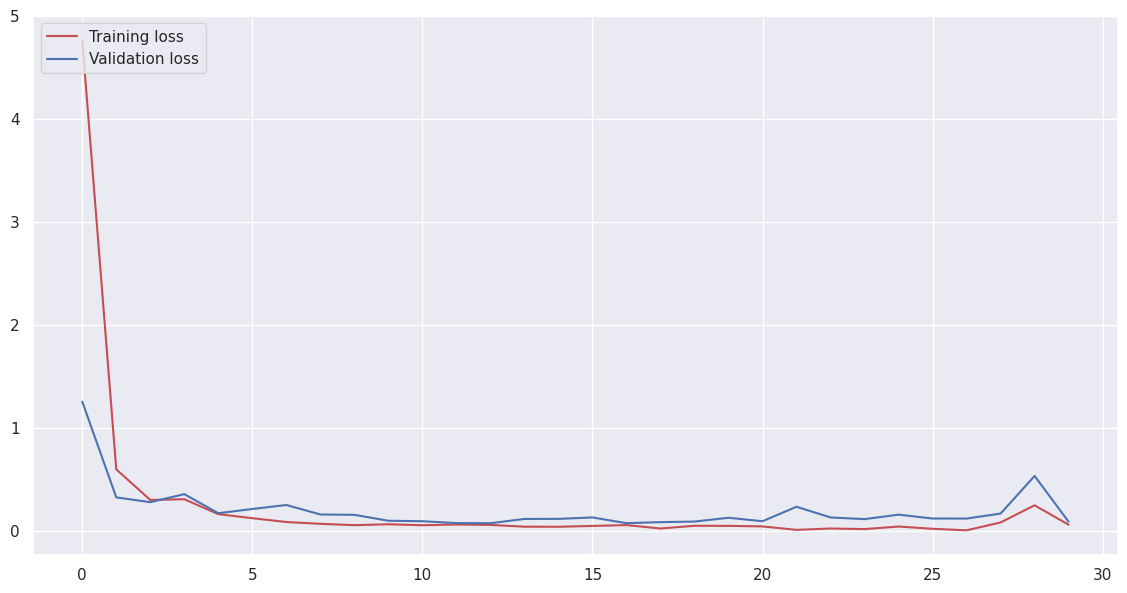
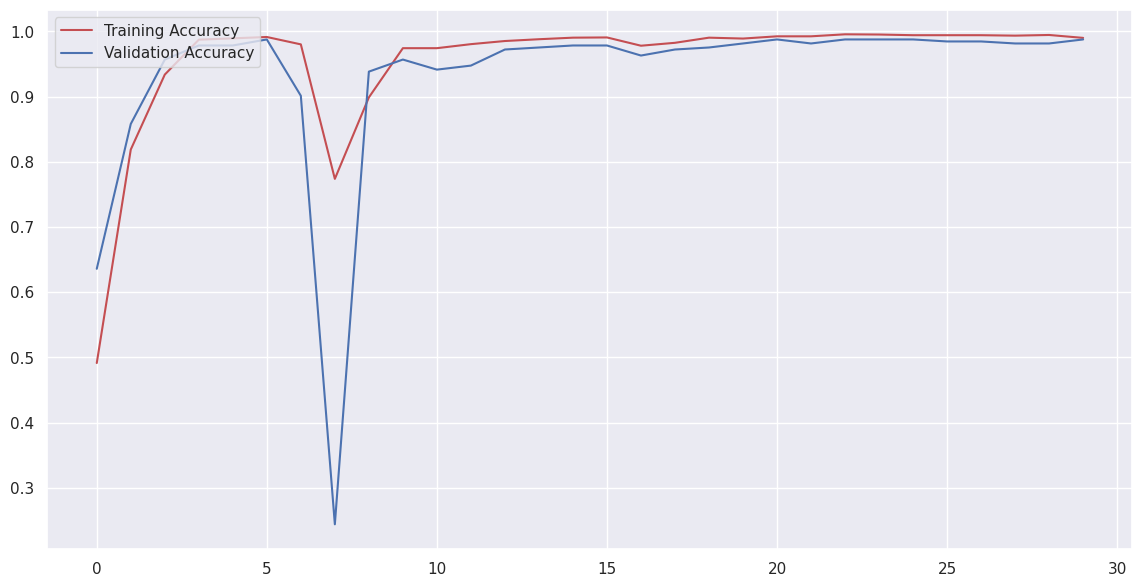
A deep convolutional neural network (CNN) was developed and trained on Kvasir capsule endoscopy images with a resolution of 256x256 pixels to detect inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The network achieved an impressive accuracy of 98%. This high accuracy demonstrates the potential of deep learning techniques in improving the diagnosis of IBD from capsule endoscopy images, offering a powerful tool for medical professionals to more accurately and efficiently identify the disease.