- It builds a Docker container from Google Cloud Source Repositories or GitHub with eg. Google Cloud Build.
- It publishes the image to the Container Registry as
eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/android-builder. - It's based upon
amazoncorretto:17-al2-jdk, Androidsdkmanager, Gradle, as well as a simple Android application for testing purposes. - It supports publishing to Bucket & Firebase App Distribution with Cloud KMS decryption for credentials.
- Android NDK and Firebase Crashlytics NDK crash reporting can be enabled by uncommenting a few lines.
- The image first needs to be built itself (!), in order to build Android applications with it.
- Hosting the built image would be a) less customizable and b) the traffic would be charged.
- In order to get started, import to Cloud Source Repositories and set up a build trigger there.
- After having built the image, a new container should show up below
eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/android-builder. - This container can then be used in another Android project's (or another Git branch's)
cloudbuild.yaml, in order not to build it every time.
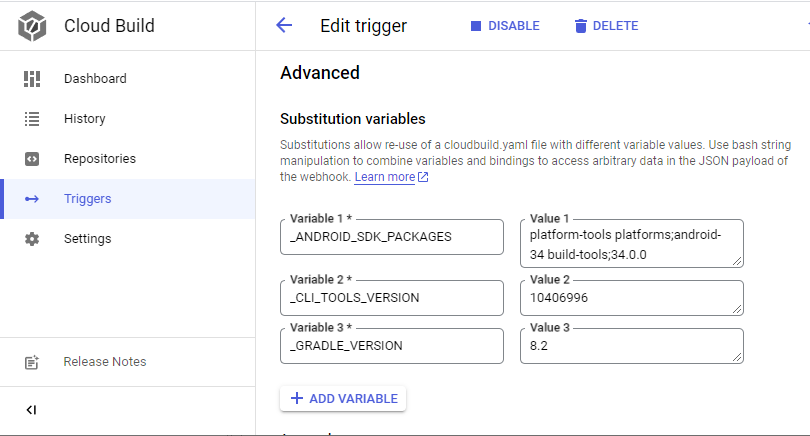
One can pre-install SDK packages with the sdkmanager, when passing _ANDROID_SDK_PACKAGES.
And one can pre-install Gradle by passing _GRADLE_VERSION.
At the moment these are both statically set in cloudbuild.yaml, but the code is there.
_CLI_TOOLS_VERSION~10406996_ANDROID_SDK_PACKAGES~platform-tools platforms;android-34 build-tools;34.0.0_GRADLE_VERSION~8.8
These examples assume that you already have the image in your project's private container registry.
Hostname eu.gcr.io (also bucket name eu.artifacts) can be replaced with us.gcr.io or gcr.io.
a) This uploads debug APK files with gsutil to gs://eu.artifacts.$PROJECT_ID.appspot.com/android/:
# cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
- name: eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/cloudbuild-android
id: 'docker-pull'
args: ['cp', '-a', '.', '/persistent_volume']
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
id: 'gradle-build'
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
args: ['run', '-v', 'data:/workspace', '--rm', 'eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/cloudbuild', '/bin/sh', '-c', 'cd /workspace && ./gradlew mobile:assembleDebug && mv mobile/build/outputs/apk/debug/mobile-debug.apk mobile/build/outputs/apk/debug/$REPO_NAME-$SHORT_SHA-debug.apk && ls -la mobile/build/outputs/apk/debug/$REPO_NAME-$SHORT_SHA-debug.apk']
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/gsutil
id: 'publish-gsutil'
args: ['cp', '/persistent_volume/mobile/build/outputs/apk/debug/$REPO_NAME-$SHORT_SHA-debug.apk', 'gs://eu.artifacts.$PROJECT_ID.appspot.com/android/']
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
timeout: 1200s
b) Cloud KMS can be used to decrypt credentials; this requires IAM role roles/cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter for the service account:
The first step mounts volume data. The second step runs gcloud kms decrypt (there are scripts in the /scripts directory, for encrypting the *.enc files). The Gradle task in the third step runs mobile:assembleRelease mobile:appDistributionUploadRelease, which uploads a signed release APK to Firebase App Distribution. This requires a separate service account with a google-service-account.json, because it is not possible to access the Cloud Build service account credentials.
# cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
- name: eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/cloudbuild-android
id: 'docker-pull'
args: ['cp', '-a', '.', '/persistent_volume']
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud
id: 'kms-decode'
entrypoint: 'bash'
waitFor: ['docker-pull']
args:
- '-c'
- |
mkdir -p /persistent_volume/.android
gcloud kms decrypt --ciphertext-file=credentials/keystore.properties.enc --plaintext-file=/persistent_volume/keystore.properties --location=global --keyring=android-gradle --key=default
gcloud kms decrypt --ciphertext-file=credentials/google-service-account.json.enc --plaintext-file=/persistent_volume/credentials/google-service-account.json --location=global --keyring=android-gradle --key=default
gcloud kms decrypt --ciphertext-file=credentials/google-services.json.enc --plaintext-file=/persistent_volume/mobile/google-services.json --location=global --keyring=android-gradle --key=default
gcloud kms decrypt --ciphertext-file=credentials/debug.keystore.enc --plaintext-file=/persistent_volume/.android/debug.keystore --location=global --keyring=android-gradle --key=default
gcloud kms decrypt --ciphertext-file=credentials/release.keystore.enc --plaintext-file=/persistent_volume/.android/release.keystore --location=global --keyring=android-gradle --key=default
rm -v ./credentials/*.enc
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
id: 'firebase-distribution'
waitFor: ['kms-decode']
env:
- 'BUILD_NUMBER=$BUILD_ID'
volumes:
- name: data
path: /persistent_volume
args: [
'run',
'--rm', 'eu.gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/cloudbuild',
'-v', 'data:/workspace',
'/bin/sh', '-c', 'cd /workspace && gradle mobile:assembleRelease mobile:appDistributionUploadRelease'
]
timeout: 1200s
The example app uses Google Cloud KMS Gradle Plugin, which depends on environmental variable _CLOUD_KMS_KEY_PATH. It does about the same as the above step kms-decode does, but at build time:
./gradlew mobile:cloudKmsDecrypt mobile:assembleRelease mobile:appDistributionUploadReleaseThe variable substitutions look pretty much the same, being called "Parameters".
While these substitutions use no underscore (being mapped at build-time: .space.kts).
CLI_TOOLS_VERSION~11076708ANDROID_SDK_PACKAGES~platform-tools platforms;android-34 build-tools;34.0.0GRADLE_VERSION~8.5DOCKER_IMAGE~ the location of the Docker image previously built.
The following example .space.kts uses xxd (instead of gcloud kms) to revert hex-dumps of binary files.
/**
* JetBrains Space Automation
* This Kotlin script file lets you automate build activities
* For more info, see https://www.jetbrains.com/help/space/automation.html
*/
job("Bundle application") {
startOn {
gitPush { enabled = false }
}
parameters {
text("GRADLE_TASKS", value = "mobile:bundleDebug", description = "Gradle tasks") {
options("mobile:bundleDebug", "mobile:bundleRelease") {
allowMultiple = false
}
}
}
container(displayName = "Gradle build", image = "{{ project:DOCKER_IMAGE }}:lts") {
env["KEYSTORE_PROPERTIES"] = "{{ project:KEYSTORE_PROPERTIES }}"
env["RELEASE_KEYSTORE"] = "{{ project:RELEASE_KEYSTORE }}"
env["DEBUG_KEYSTORE"] = "{{ project:DEBUG_KEYSTORE }}"
env["GRADLE_USER_HOME"] = "{{ project:GRADLE_USER_HOME }}"
env["GRADLE_TASKS"] = "{{ GRADLE_TASKS }}"
cache {
location = CacheLocation.FileRepository(name = CacheLocation.DefaultRepositoryName, remoteBasePath = "android")
storeKey = "gradle-{{ hashFiles('build.gradle') }}"
localPath = "{{ project:GRADLE_USER_HOME }}/caches"
}
shellScript {
location = "{{ project:BUILD_SCRIPT }}"
interpreter = "/bin/bash"
}
}
}
- for Firebase AppDistribution, the service account needs IAM role "Firebase App Distribution Admin".
- for Google Play Store, the "Google Play Android Developer API" needs to be enabled for the project.
- Creating a Serverless Mobile Delivery Pipeline
- Simplify your CI processes with GitHub and Google Cloud Build
- Marketplace Google Cloud Build for GitHub integration.
- GitHub: Google Cloud Build (official).
- Jetbrains Space: Automation (CI/CD).
- Jetbrains Space IDE plugin