Re-implementation of our paper Voice Conversion from Non-parallel Corpora Using Variational Auto-encoder.
(for VAWGAN, please switch to vawgan branch)
Linux Ubuntu 16.04
Python 3.5
- Tensorflow-gpu 1.2.1
- Numpy
- Soundfile
- PyWorld
- Cython
For example,
conda create -n py35tf121 -y python=3.5
source activate py35tf121
pip install -U pip
pip install -r requirements.txtsoundfilemight requiresudo apt-get install.- You can use any virtual environment packages (e.g.
virtualenv) - If your Tensorflow is the CPU version, you might have to replace all the
NCHWops in my code because Tensorflow-CPU only supportsNHWCop and will report an error:InvalidArgumentError (see above for traceback): Conv2DCustomBackpropInputOp only supports NHWC. - I recommend installing Tensorflow from the link on their Github repo.
pip install -U [*.whl link on the Github page]
- Run
bash download.shto prepare the VCC2016 dataset. - Run
analyzer.pyto extract features and write features into binary files. (This takes a few minutes.) - Run
build.pyto record some stats, such as spectral extrema and pitch. - To train a VAE, for example, run
python main.py \
--model ConvVAE \
--trainer VAETrainer \
--architecture architecture-vae-vcc2016.json- You can find your models in
./logdir/train/[timestamp] - To convert the voice, run
python convert.py \
--src SF1 \
--trg TM3 \
--model ConvVAE \
--checkpoint logdir/train/[timestamp]/[model.ckpt-[id]] \
--file_pattern "./dataset/vcc2016/bin/Testing Set/{}/*.bin"*Please fill in timestampe and model id.
7. You can find the converted wav files in ./logdir/output/[timestamp]
Voice Conversion Challenge 2016 (VCC2016): download page
- Conditional VAE
dataset
vcc2016
bin
wav
Training Set
Testing Set
SF1
SF2
...
TM3
etc
speakers.tsv (one speaker per line)
(xmax.npf)
(xmin.npf)
util (submodule)
model
logdir
architecture*.json
analyzer.py (feature extraction)
build.py (stats collecting)
trainer*.py
main.py (main script)
(validate.py) (output converted spectrogram)
convert.py (conversion)
The WORLD vocdoer features and the speaker label are stored in binary format.
Format:
[[s1, s2, ..., s513, a1, ..., a513, f0, en, spk],
[s1, s2, ..., s513, a1, ..., a513, f0, en, spk],
...,
[s1, s2, ..., s513, a1, ..., a513, f0, en, spk]]
where
s_i is spectral envelop magnitude (in log10) of the ith frequency bin,
a_i is the corresponding "aperiodicity" feature,
f0 is the pitch (0 for unvoice frames),
en is the energy,
spk is the speaker index (0 - 9) and s is the sp.
Note:
- The speaker identity
spkwas stored innp.float32but will be converted intotf.int64by thereaderinanalysizer.py. - I shouldn't have stored the speaker identity per frame; it was just for implementation simplicity.
- Define a new model (and an accompanying trainer) and then specify the
--modeland--trainerofmain.py. - Tip: when creating a new trainer, override
_optimize()and the main loop intrain(). - Code orgainzation
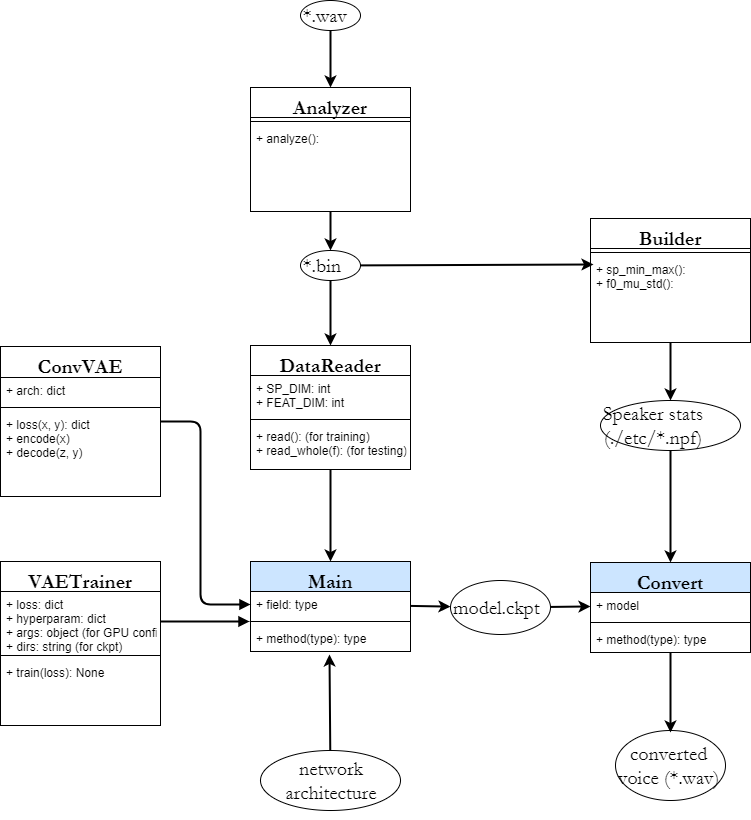 This isn't a UML; rather, the arrows indicates input-output relations only.
This isn't a UML; rather, the arrows indicates input-output relations only.
- WORLD vocoder is chosen in this repo instead of STRAIGHT because the former is open-sourced whereas the latter isn't.
I use pyworld, Python wrapper of the WORLD, in this repo. - Global variance post-filtering was not included in this repo.
- In our VAE-NPVC paper, we didn't apply the [-1, 1] normalization; we did in our VAWGAN-NPVC paper.
The original code base was originally built in March, 2016.
Tensorflow was in version 0.10 or earlier, so I decided to refactor my code and put it in this repo.
-
utilsubmodule (add to README) - GV
-
build.pyshould accept subsets of speakers