The solution is based on the paper [1] published in 2021 by Dawid Rymarczyk, Adriana Borowa, Jacek Tabor, and Bartosz Zieliński.
The authors considered an identical problem and derived a new approach called Self-Attention Attention-based Multiple Instance learning. Together with the paper, a framework is distributed with an MIT license, so I could build the solution around their work.
To meet the criteria stated in the task, the method of MistBags was modified with the following code:
while True:
bag_length = int(self.r.normal(self.mean_bag_length, self.var_bag_length, 1))
if bag_length >= 5 and bag_length <= 250000000:
break
else:
continueWhile loop assures that bag_length < 5 and bag_length > 2500000000 will be rejected and another attempt to pick up the value from the desired range will be made.
The objective is to verify if 7 exists in the bag, so the parameter xor_number was set to 7.
I trained and tested the model for several sets of parameters. The first observation is that the additional constraint mentioned above does not affect the loss function. This fact is not surprising because rejected bags of instances are anyway unlikely to appear, so the data set is not much modified.
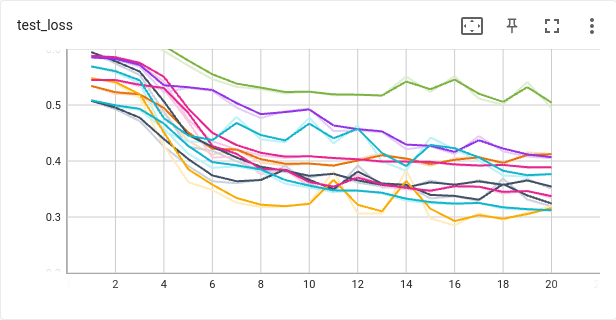
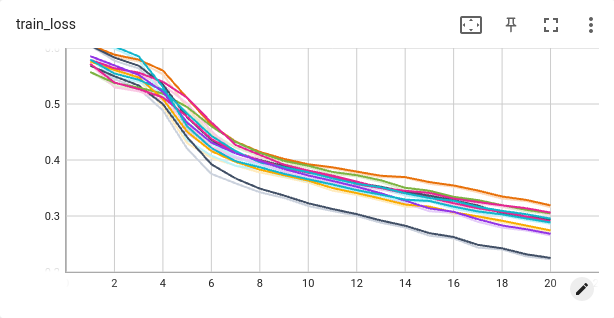
Below are presented train and test losses over 20 epochs for 10 different seeds. Undoubtedly, results are improving for all 10 random configurations of bags however, the variance cannot be neglected. Especially for test loss function. This suggests that the training of the model is sensitive to the specific configuration of the data set.
Self-Attention Attention-based Multiple Instance learning is a definitely powerful method and the authors illustrated in the paper[1] that it set new standards. As a new method, it can deal with a new range of problems with bigger complexity, which is already demonstrated by the authors[2].
[2] ProtoMIL: Multiple Instance Learning with Prototypical Parts for Whole-Slide Image Classification