- Load the data graph from disk (gzipped, n-triple files)
- Parse the RDF graph into a spark labeled property graph
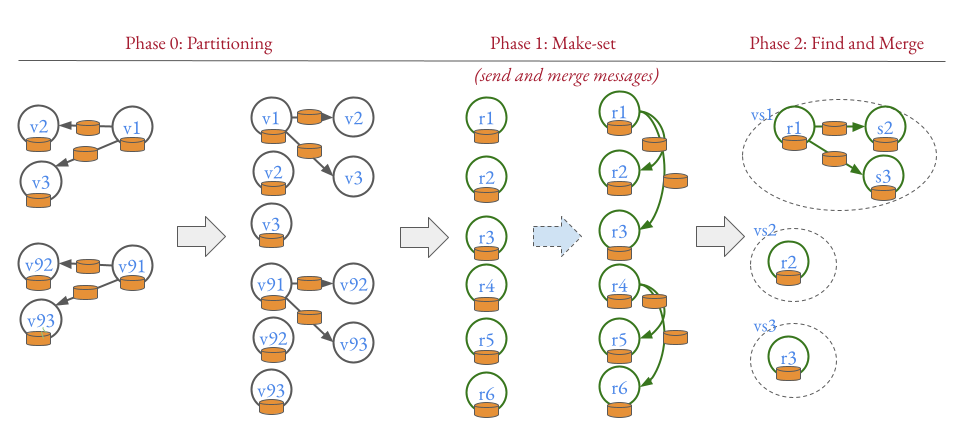
- Phase 0: partition the graph by a random vertex cut such that vertices and their outgoing (or incoming edges for undirected graphs) are in the same partition.
- Phase 1.1: each vertex computes its own local schema based on vertex label and edge label
- Phase 1.2: send and merge the neighbor information to construct complex schemas
- Phase 2: write the graph to OrientDB, merge on collision.
If incremental computation is used, skip step 6 (phase 2) for all unchanged vertices.
Figure 1: Label of vertices and edges are represented by orange db symbols. Grey vertices are data graph vertices, green vertices are graph summary vertices representing data graph vertices. Phase 0: Distribute parts of the data graph to the computing nodes. Phase 1: iteratively compute vertex summaries vs. Up to chaining parameter k, send local schema information (e.g., label) to neighbors inverse to the direction parameterization (e.g., if one uses outgoing edges, each vertex sends its schema information to incoming edges). Phase 2: merge equivalent vertex summaries, i.e., remove redundant information provided by r4, r5, and r6.
- install java oracle jdk 11 or later (tested with 11.05)
- install scala
sudo apt-get install scala- check version
scala -version
- check version
- install sbt
echo "deb https://dl.bintray.com/sbt/debian /" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/sbt.listsudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 2EE0EA64E40A89B84B2DF73499E82A75642AC823sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install sbt
- download and install spark
- download spark
wget http://archive.apache.org/dist/spark/spark-2.4.2/spark-2.4.2-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz - create spark directory
mkdir /usr/local/spark - extract spark
tar xvf spark-2.4.2-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz -C /usr/local/spark/ - you may need to change user permission so non-root users can read spark
- configure local environment for spark and scala. Add the following variables to your bashrc, adapt if necessary (Max RAM size).
export SCALA_HOME=/usr/bin/scalaexport SPARK_HOME=/usr/local/spark/spark-2.4.2-bin-hadoop2.7export SBT_OPTS="-Xmx200G"
- update bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
- download spark
-
build executable (optional):
sbt packageThis steps shows that everything (except spark) is correctly installed. -
setup OrientDB database (https://orientdb.com/)
- for convenience, we provide to pre-configured docker images in
resources/docker, one used for development and one used for experiments using different memory configurations. - see this manual to install docker-compose: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
- make sure read and write access is set properly to the data directory of OrientDB (
sudo chmod -R 777 orientdb)
- for convenience, we provide to pre-configured docker images in
-
run program from source:
sbt "runMain Main resources/configs/tests/manual-test-1.conf" -
the program runs using a small sample file, creates a database, and logs some performance data. For more details, see the configuration files provided.
-
for configurations using larger datasets, one can observe the progress via the Web UI (localhost:4040). When you run this on a server, you may want to consider using ssh port forwarding
ssh -NL <local port>:<server>:4040 <server>
- start the history server with the following command (change location if spark is installed somewhere else)
/./usr/local/spark/spark-2.4.2-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin/start-history-server.sh - view the history of all executed spark programs here, default location is
localhost:18080 - parse execution results by running the python script
collectPerformance.py. The script collects all execution times of for a given configuration and aggregates them in a csv file. - by default, the history files are stored in
/tmp/spark-events/. You may change this to avoid data loss.
- export FLUID_HOME=~/GIT/fluid-spark
- compile java agent (or use provided jar)
- cd src/main/java/instumentation/
- ``javac InstrumentationAgent.java
- jar cmf MANIFEST.MF InstrumentationAgent.jar InstrumentationAgent.class
- -javaagent:"$FLUID_HOME/src/main/java/instumentation/InstrumentationAgent.jar"`
export SBT_OPTS="-Xms4G -Xmx4G -Djava.io.tmpdir=/mypath/ -Dspark.metrics.conf=$SPARK_HOME/conf/metrics.properties -javaagent:$FLUID_HOME/src/main/java/instumentation/InstrumentationAgent.jar"
Run test.sh
If you are using our code, please consider citing our paper:
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/cikm/BlumeRS20,
author = {Till Blume and
David Richerby and
Ansgar Scherp},
title = {Incremental and Parallel Computation of Structural Graph Summaries
for Evolving Graphs},
booktitle = {{CIKM}},
pages = {75--84},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3340531.3411878},
publisher = {{ACM}},
year = {2020}
}